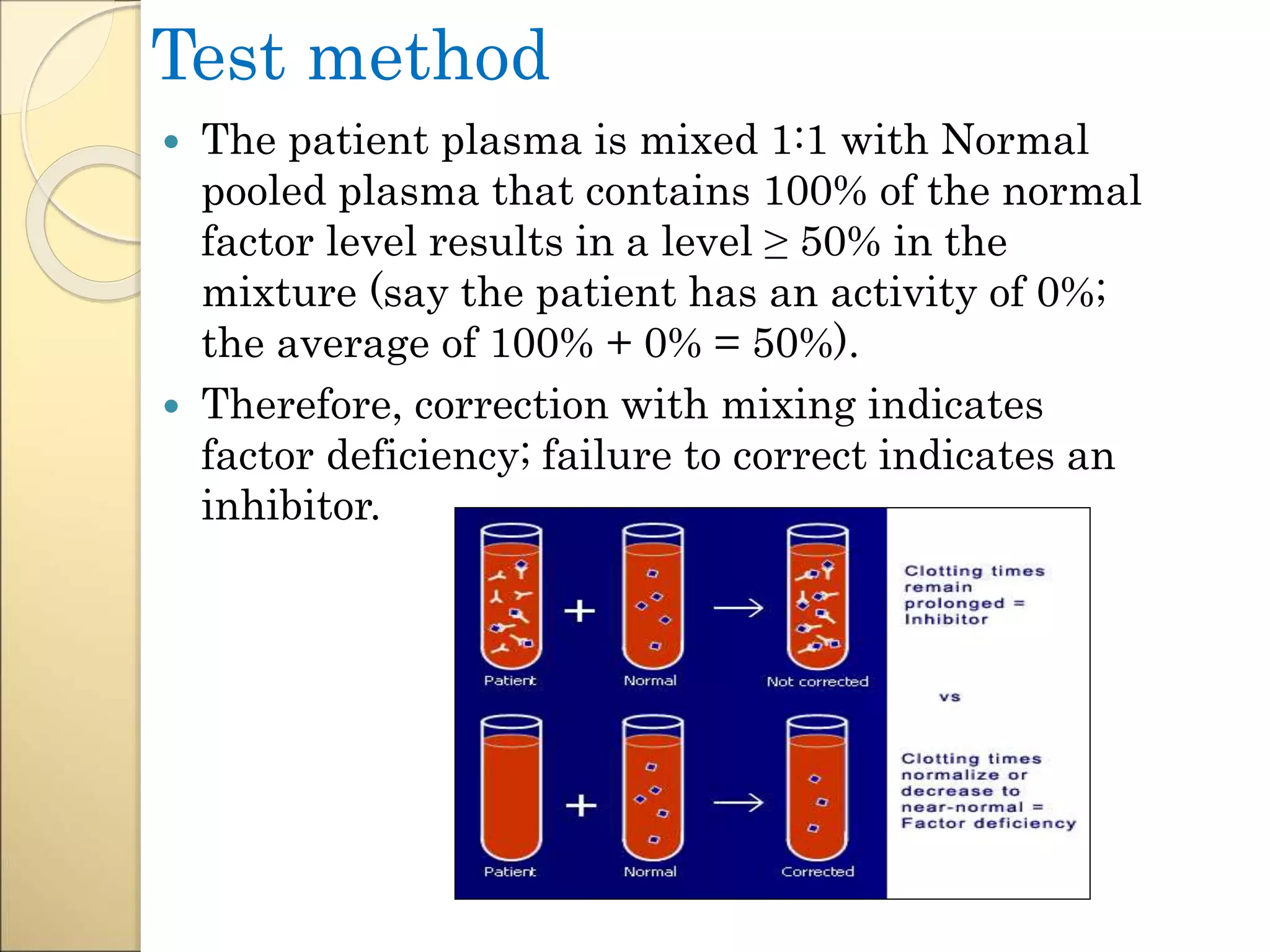
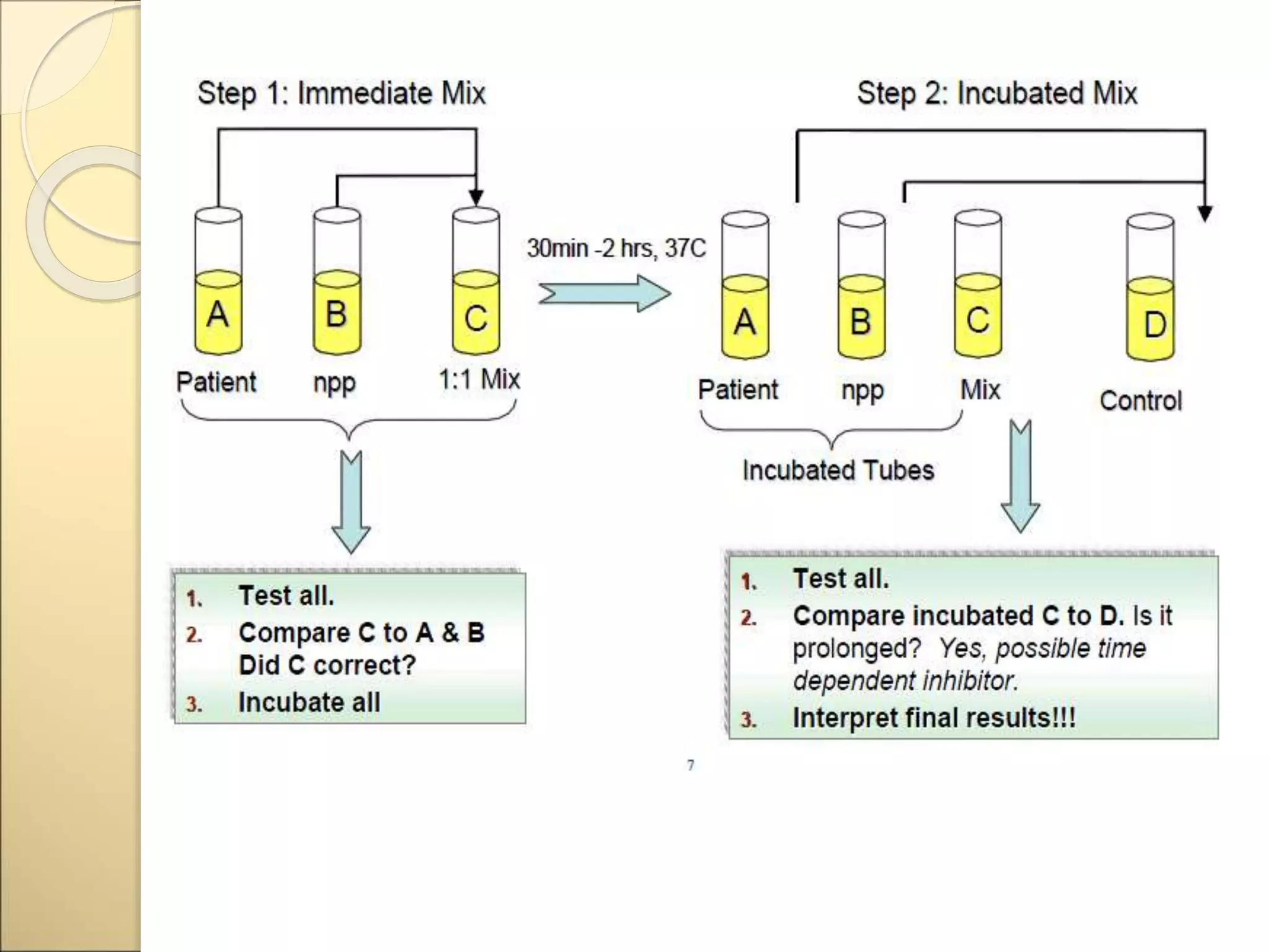
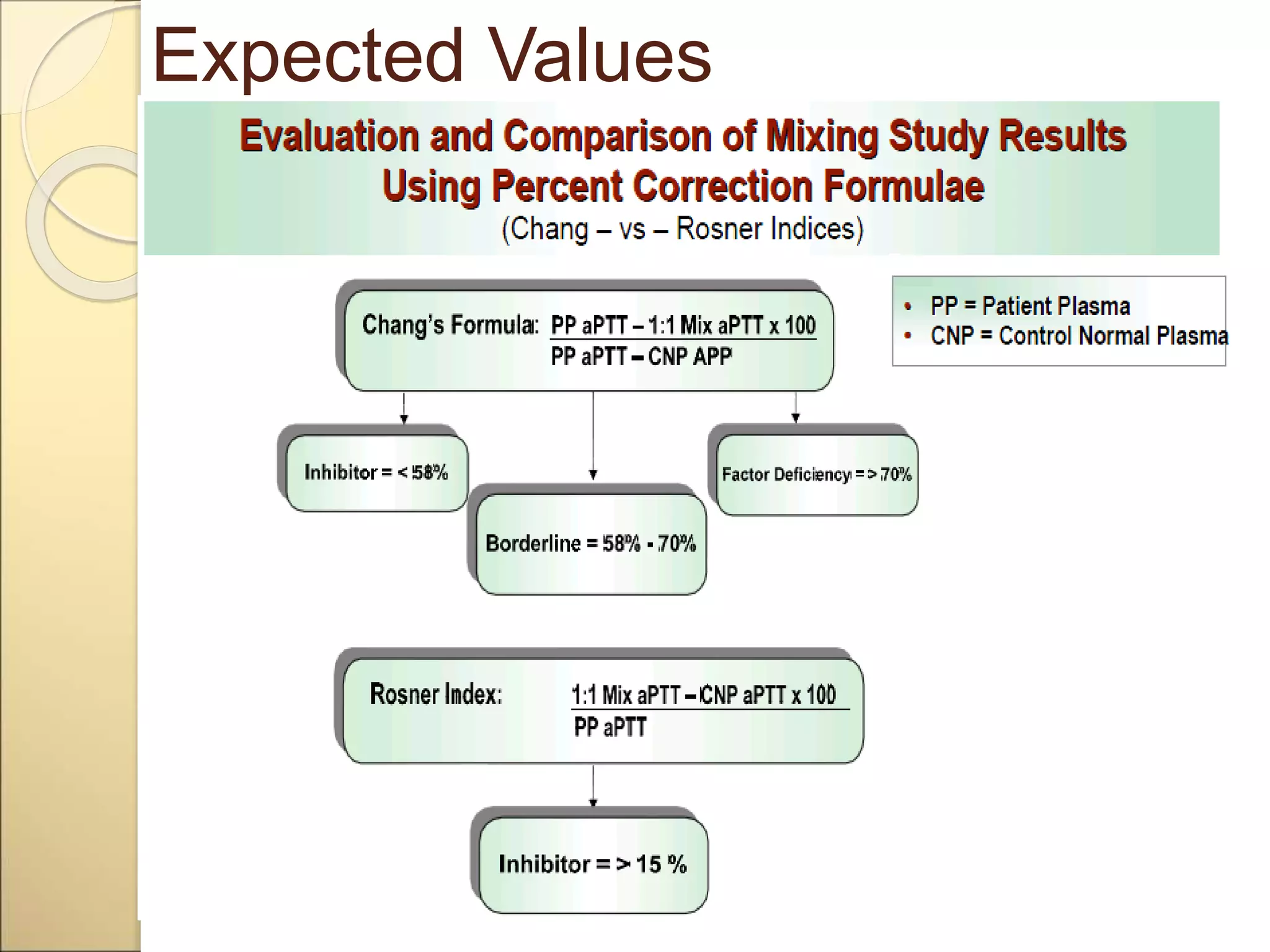
Mixing studies involve mixing a patient's plasma sample with normal pooled plasma in a 1:1 ratio. This distinguishes between factor deficiencies and inhibitors. If the abnormal coagulation test corrects to normal with mixing, it indicates a factor deficiency. If there is no correction, it suggests an inhibitor. Some inhibitors are time-dependent, so tests are repeated after incubation. Mixing studies help determine the cause of abnormal coagulation test results and guide further diagnosis and treatment.