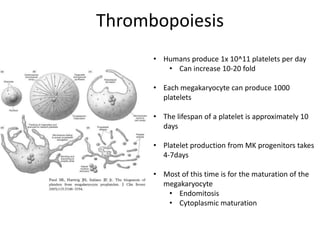
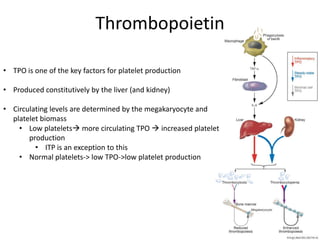
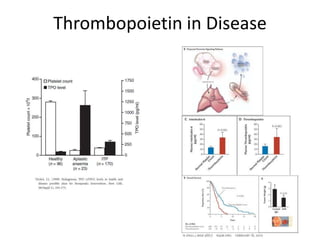
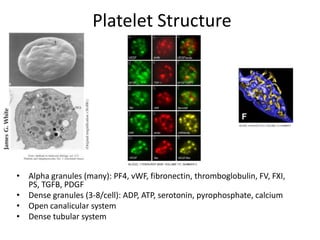
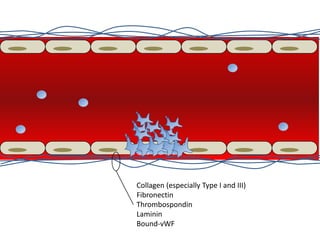
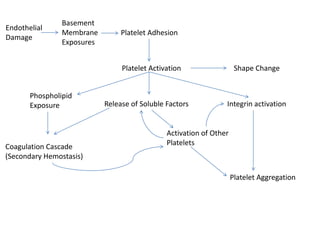
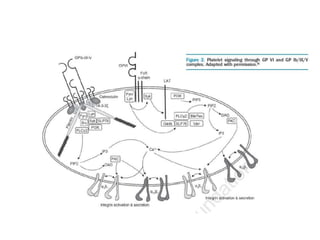
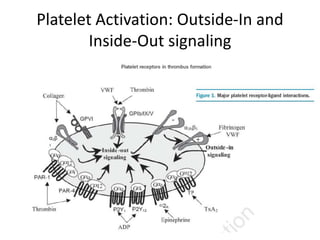
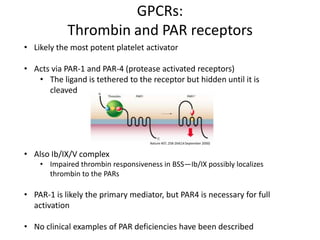
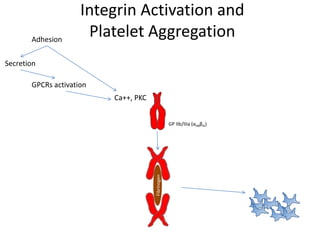
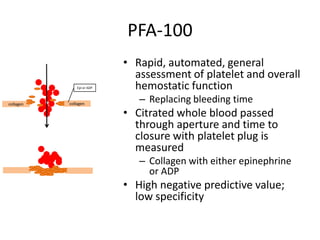
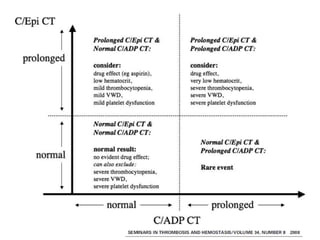
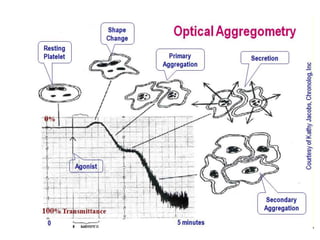
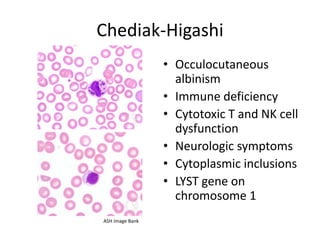
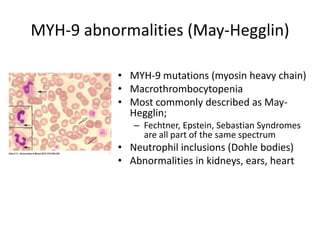
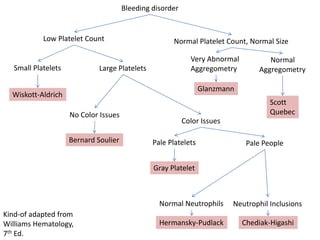
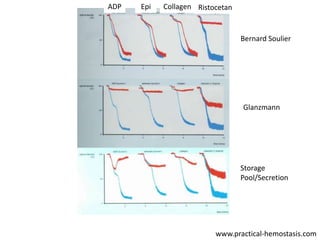
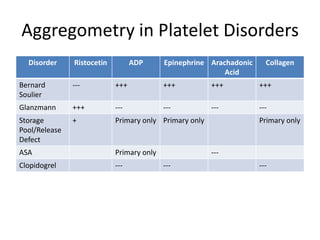
This document provides an overview of platelet function and dysfunction. It discusses platelet production, structure, activation pathways, assessment of function, and inherited and acquired disorders. Key points include: platelets are produced from megakaryocytes at a rate of 1 trillion per day; contain granules storing factors like ADP and serotonin; activate via receptors for collagen, thrombin, ADP; aggregation is mediated by integrin GP IIb/IIIa; testing includes aggregometry and PFA-100; inherited disorders impact receptors like Glanzmann thrombasthenia or Bernard-Soulier syndrome; and acquired causes include medications like aspirin or clopidogrel that inhibit platelet activation pathways.