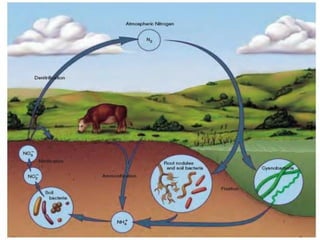
The ammonium stored in the soil has three possible fates:
1. It can be taken up by plant roots and used for growth. Many plants can directly use ammonium as a nitrogen source.
2. It can be converted to nitrate (NO3-) by soil bacteria in a process called nitrification. Nitrifying bacteria oxidize ammonium to nitrite (NO2-) and then to nitrate.
3. It can be immobilized by soil microbes. When soil microbes decompose organic matter, they incorporate ammonium into their biomass. This temporarily removes the ammonium from the soil solution.
So in summary, the ammonium stored in soil can be taken up by plants,