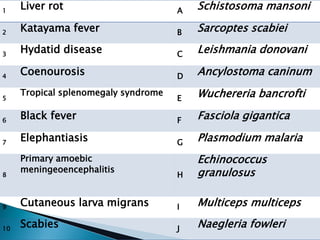
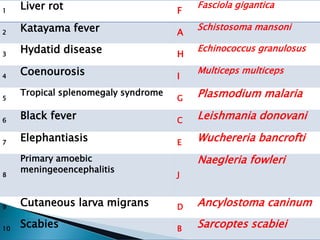
The document contains information about an exam including:
- Instructions for answering questions from left to right and writing the question number before answering.
- The exam contains 6 questions worth 5 marks each for a total of 30 marks.
- Example questions are provided about disease transmission mechanisms, parasitic diseases transmitted by flies, malaria complications, leishmaniasis classification and causative parasites, helminths transmitted by autoinfection, and parasitic causes of various diseases.