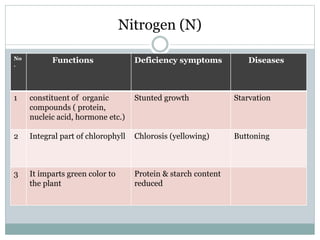
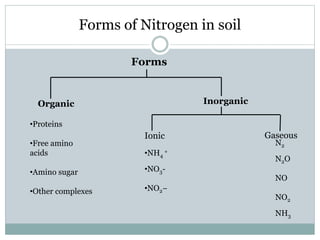
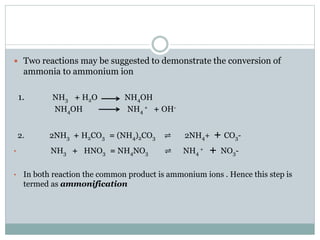
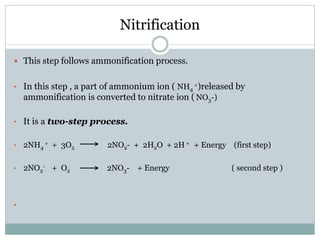
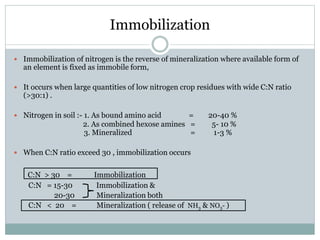
Nitrogen is an essential nutrient for plants that exists in soil in various organic and inorganic forms. The processes of mineralization and immobilization control nitrogen availability. Mineralization converts organic nitrogen into plant-available inorganic forms like ammonium and nitrate through aminization, ammonification, and nitrification carried out by soil microbes. Immobilization occurs when carbon-rich residues cause microbes to use inorganic nitrogen, decreasing availability for plants. Maintaining a proper carbon-to-nitrogen ratio in soil is important to promote nitrogen mineralization while avoiding immobilization.