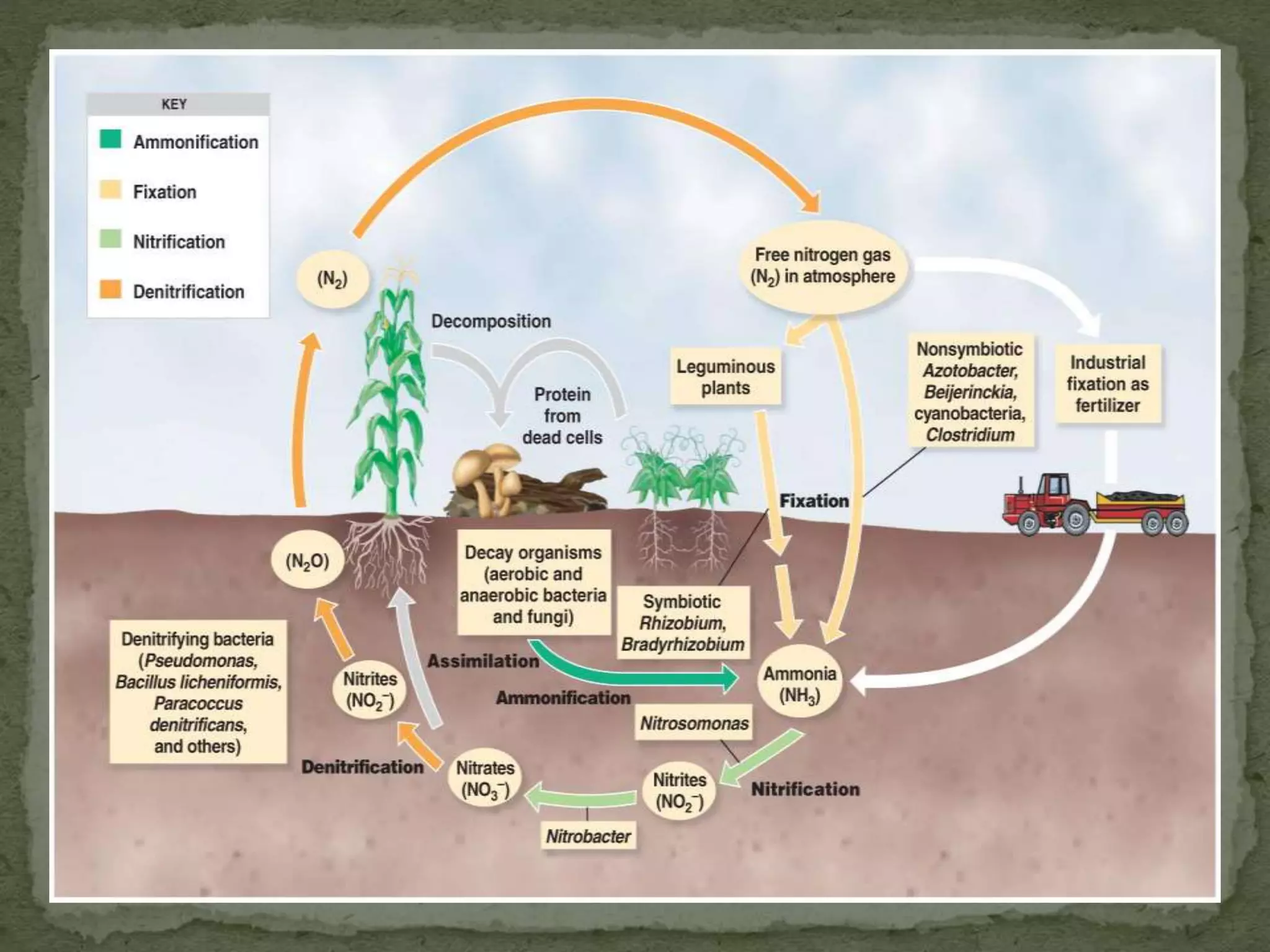
The document outlines the nitrogen cycle, emphasizing the importance of nitrogen in biological processes and its various transformations including nitrogen fixation, nitrification, immobilization, ammonification, and denitrification. Each process is described in terms of its biological agents, mechanisms, and implications for plant growth and ecosystem health. The nitrogen cycle is critical for converting inert atmospheric nitrogen into usable forms for living organisms, while the denitrification process highlights the potential drawbacks of nitrogen loss from soils.