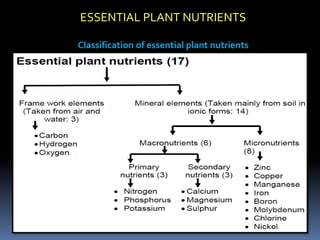
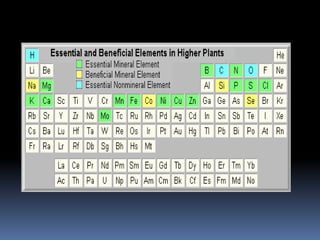
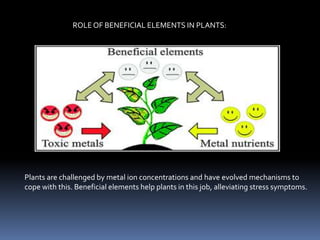
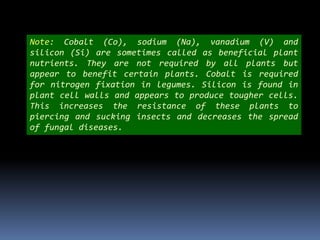
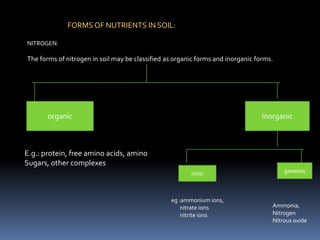
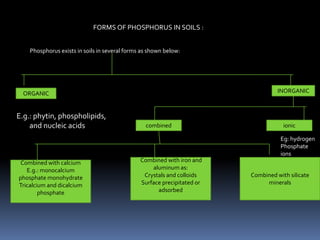
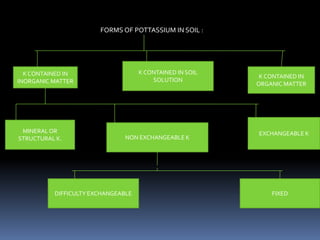
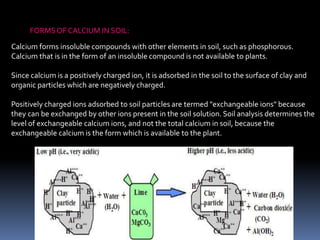
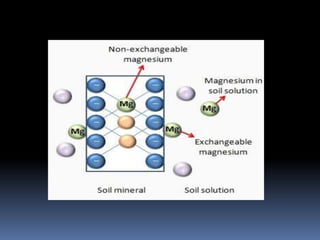
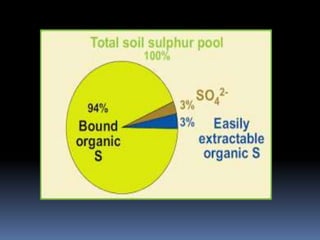
This document discusses essential and beneficial plant nutrients and their forms in soil. It explains that 17 elements are essential for plant growth according to established criteria. These essential nutrients can be classified as macronutrients or micronutrients. In addition, some elements like sodium, aluminum, nickel, and vanadium may be beneficial for certain plants under specific conditions. The document then describes the various organic and inorganic forms nutrients can take in soil, including nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, sulfur, and micronutrients. Maintaining nutrients in available forms is important for plant uptake and growth.