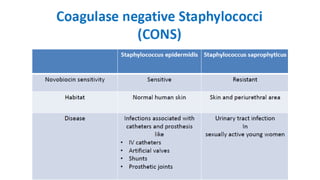
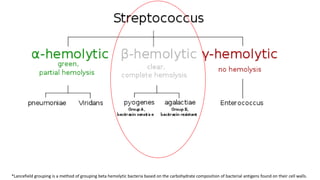
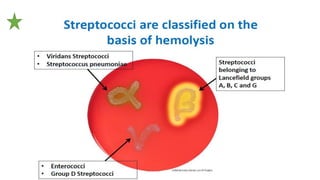
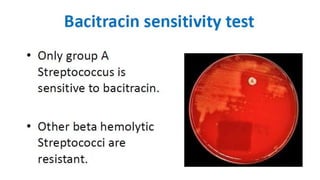
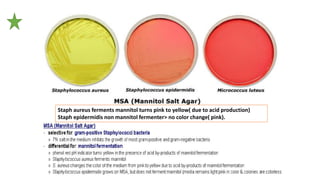
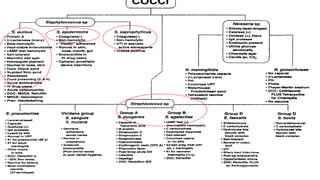
This document summarizes key microbiological characteristics of gram positive cocci including staphylococci and streptococci. It describes how staphylococci such as Staphylococcus aureus appear as golden yellow colonies with beta hemolysis on blood agar and are catalase positive. It also discusses the coagulase test to differentiate S. aureus from other staphylococci. For streptococci such as Streptococcus pyogenes, it notes their appearance as pinpoint colonies with wide beta hemolysis on blood agar. The document also briefly mentions Lancefield grouping and characteristics of common pathogenic strains of S. pyogenes and S. agalactiae.