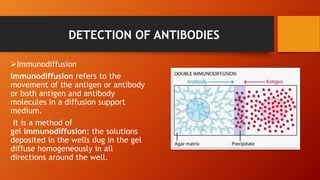
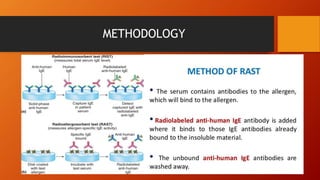
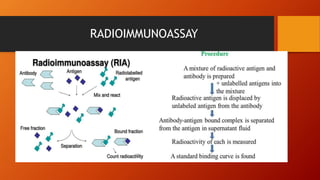
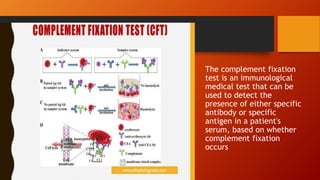
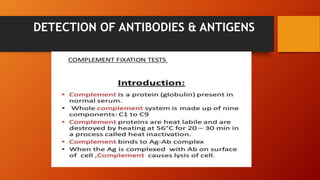
The document discusses various serological tests used for diagnosing fungal infections, emphasizing methods such as immunodiffusion, radioallergosorbent tests (RAST), and enzyme-linked immunoassays (ELISA). It highlights the advantages of rapid diagnosis through the detection of antigens and antibodies in body fluids, which can precede clinical symptoms by several days. Additionally, it notes the challenges of continuous monitoring and the costs associated with testing kits.













![REFERENCES
1.C. Vaman Rao (2005). Immunology: a textbook. Alpha Science Int'l Ltd. pp. 112–
. ISBN 978-1-84265-255-8. Retrieved 3 December 2010.
2.Engvall, E (1972-11-22). "Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, Elisa". The Journal
of Immunology. 109 (1): 129–135. ISSN 0022-1767. PMID 4113792.
3."Immunodiffusion". ScienceDirect. Elsevier B.V. Archived from the original on 2017-
05-02. Retrieved 2017-05-19.
4. "Ouchterlony double immunodiffusion" (photograph). Retrieved 2017-05-
15.[permanent dead link]
5."Radial Immunodiffusion". Edvotek, Inc. 2017. Archived from the
original (photograph) on 2017-08-07. Retrieved 2017-08-07. Photograph of precipitin
circles in a Petri dish during radial immunodiffusion.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/serologicaltestforfungi-200729080932/85/Serological-test-for-fungi-20-320.jpg)