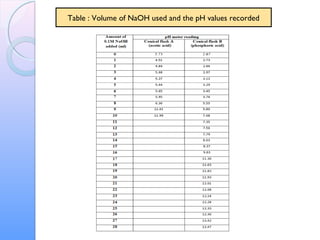
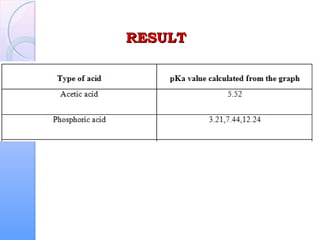
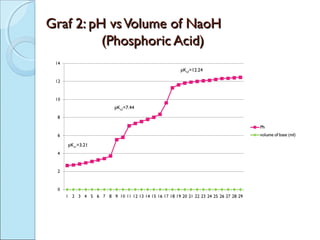
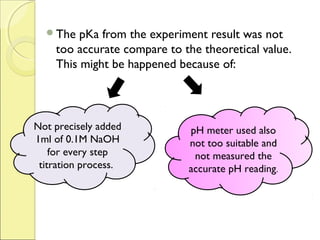
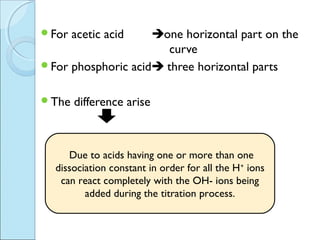
This document is a report on an acid-base titration experiment. The experiment involved titrating acetic acid and phosphoric acid with 0.1M NaOH solution and measuring the pH changes. Graphs of pH vs volume of NaOH added were plotted and used to determine the pKa values of the acids. For acetic acid the pKa was found to be 5.52, and for phosphoric acid the pKa values were determined to be 3.21, 7.44, and 12.24. The experiment helped to identify the pKa values of the acids and learn proper pH meter technique.