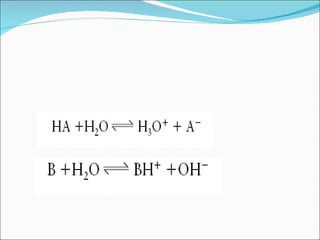
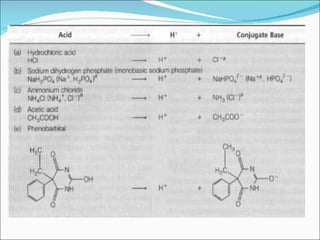
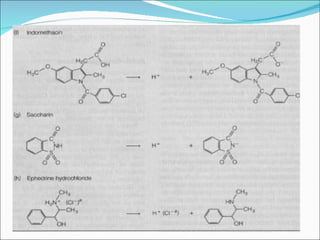
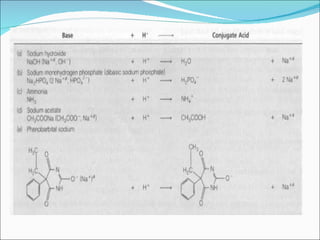
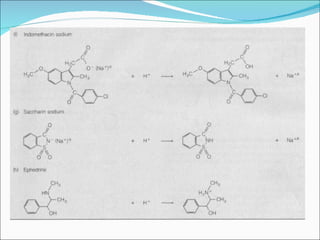
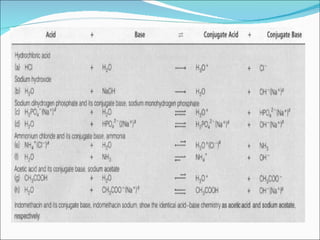
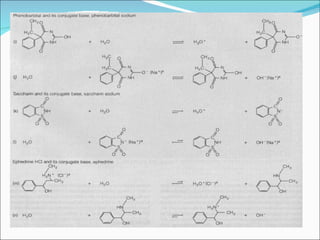
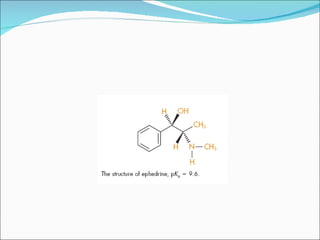
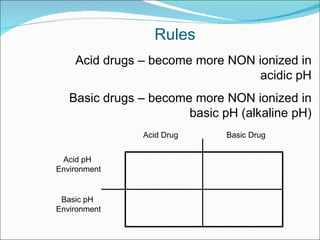
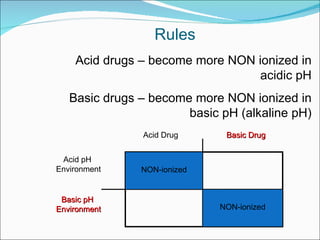
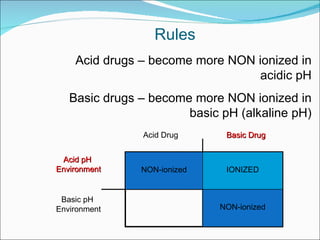
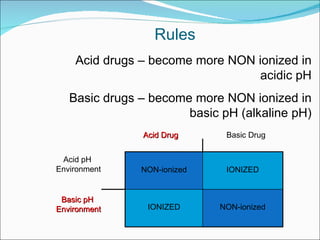
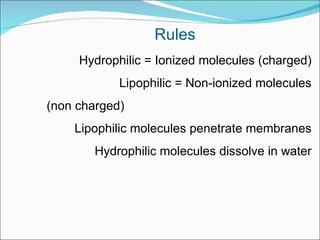
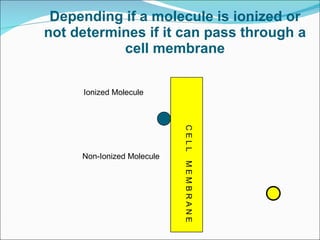
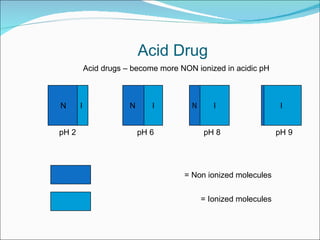
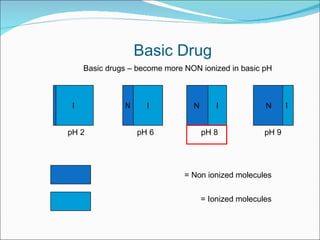
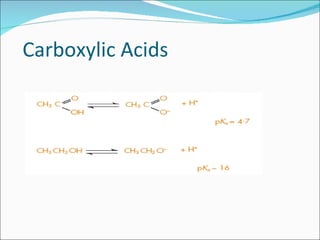
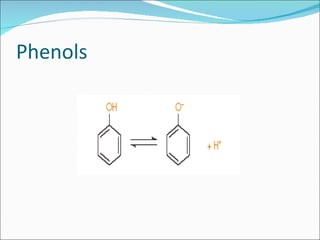
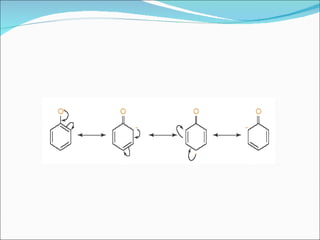
The document discusses physicochemical properties of drugs, specifically how the acid-base properties and pKa values of drugs influence their distribution and partitioning in the body. It provides definitions of acid-base concepts like pH, pKa, and the Arrhenius definition of acids and bases. It also explains how the percentage of ionization of acid and base drugs depends on the environmental pH relative to the drug's pKa. The ionization state determines if a drug is hydrophilic and water-soluble or lipophilic and able to pass through cell membranes. Rules are provided about how acid and base drugs behave in different pH environments and whether they will be ionized or non-ionized.