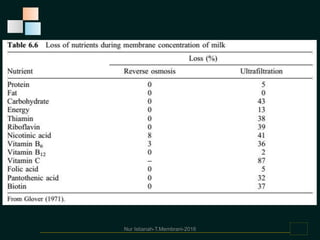
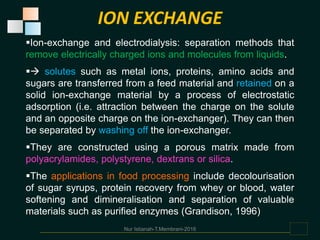
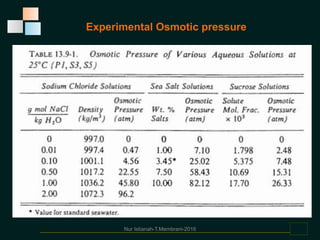
Membranes are thin films that allow some types of matter to pass through while restricting others. They work by exploiting differences in molecular size, shape, or solubility. There are various types of membrane processes that separate components of a solution based on factors like pressure, concentration, voltage, or temperature differences. These include reverse osmosis, microfiltration, ultrafiltration, nanofiltration, and others. Membrane processes have many applications in food processing, such as concentrating fruit juices, separating whey from cheese, and purifying water and wastewater. Key factors that determine membrane performance include thickness, molecular structure, chemical composition, and configuration.