Embed presentation
Downloaded 55 times

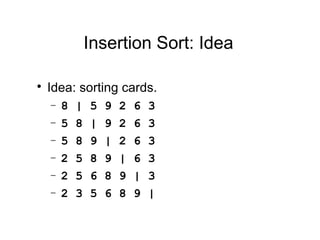

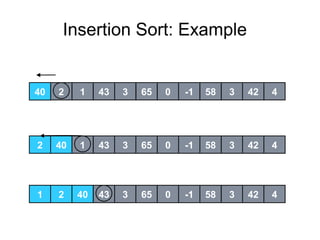
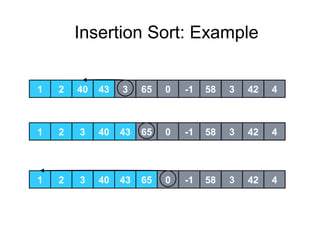
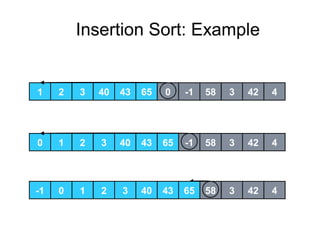
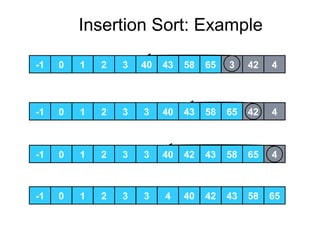



Insertion sort is a sorting algorithm that works by building a sorted array (or list) one item at a time. It maintains two groups, a sorted group and an unsorted group. It removes one element from the unsorted group, finds the location it belongs within the sorted group, and inserts it there. This continues until the unsorted group is empty, leaving a fully sorted list. The worst-case running time is O(n^2) as each insertion may require traversing the entire sorted portion. However, the average case is O(n) for nearly sorted data. A lower bound analysis shows that any algorithm relying on adjacent swaps has a worst case lower bound of Ω(n^2).











