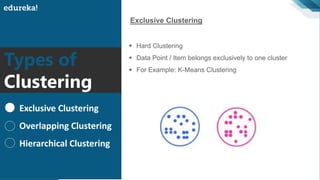
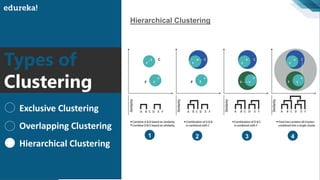
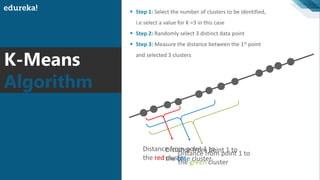
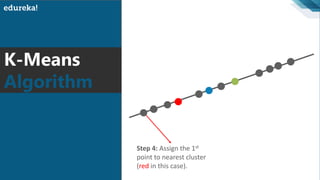
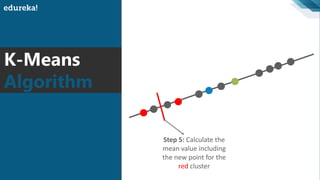
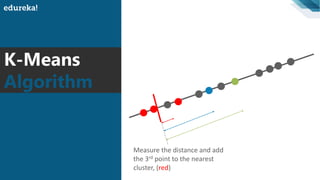
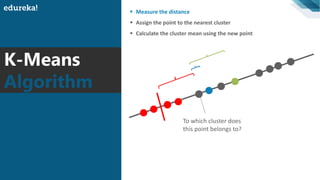
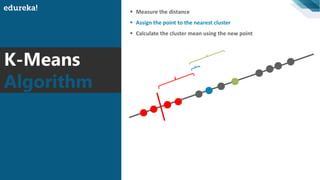
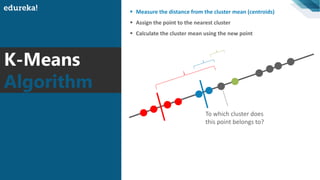
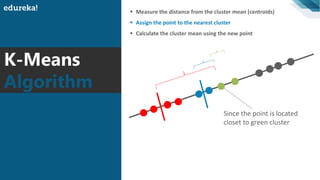
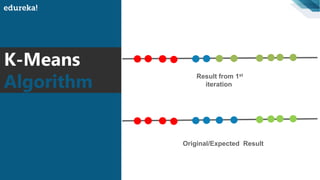
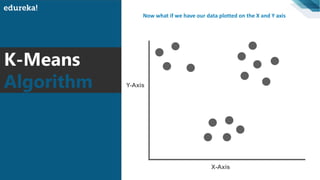
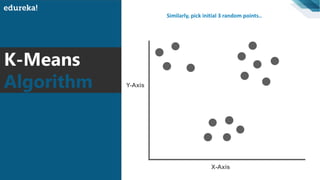
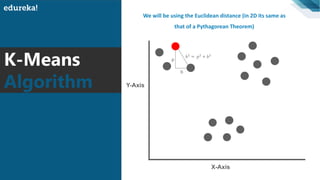
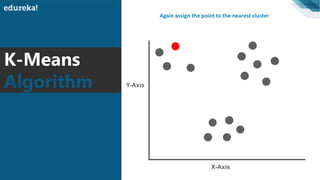
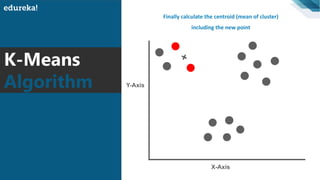
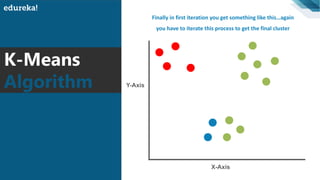
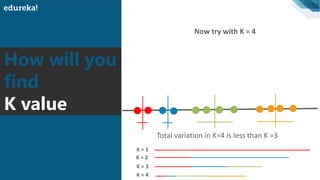
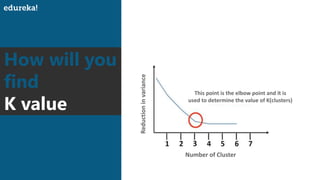
The document discusses the K-Means clustering algorithm. It begins by defining clustering as grouping similar data points together. It then describes K-Means clustering, which groups data into K number of clusters by minimizing distances between points and cluster centers. The K-Means algorithm works by randomly selecting K initial cluster centers, assigning each point to the closest center, and recalculating centers as points are assigned until clusters stabilize. The best number of K clusters is found through trial and error to minimize variation between points and clusters.