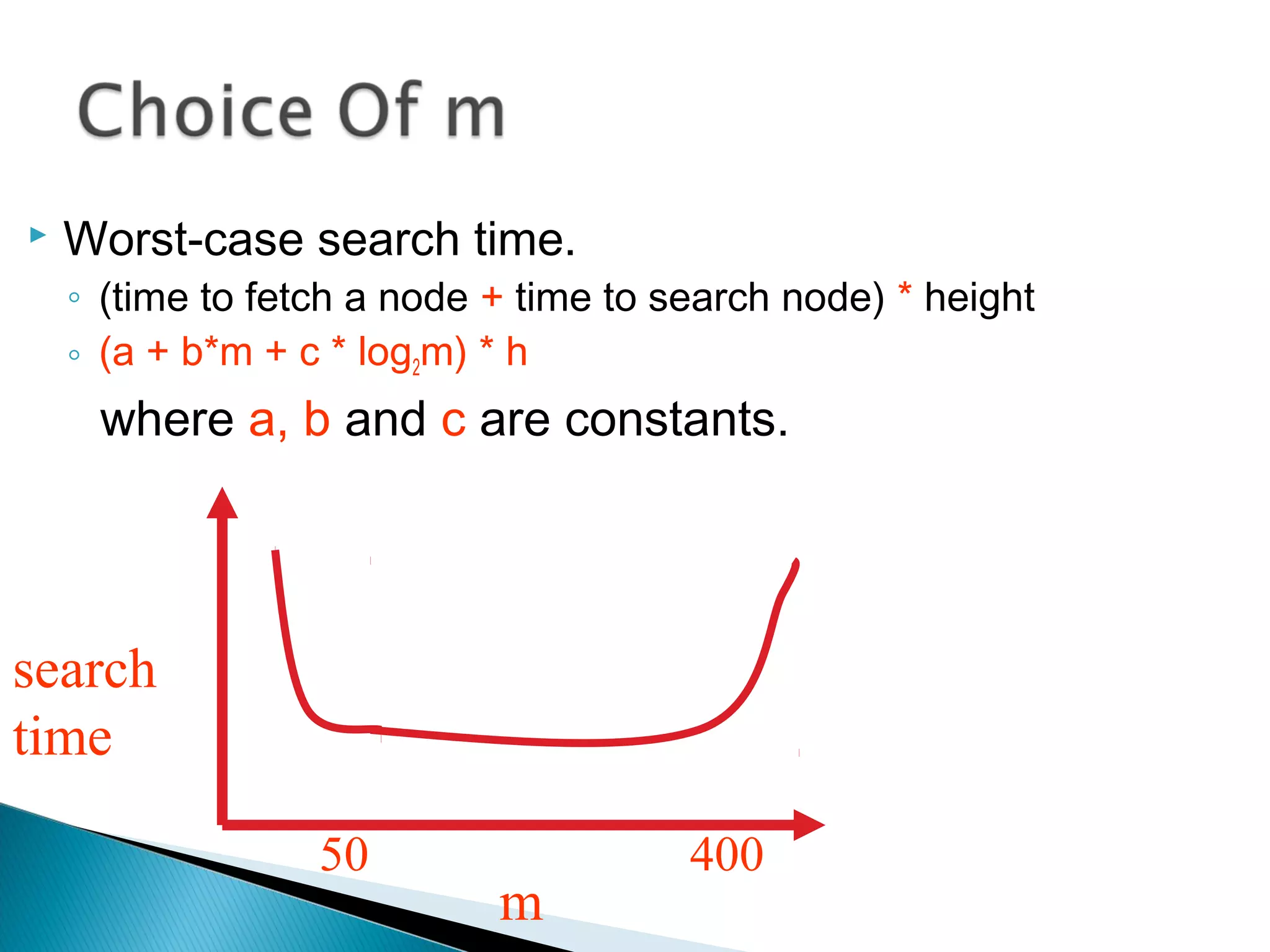
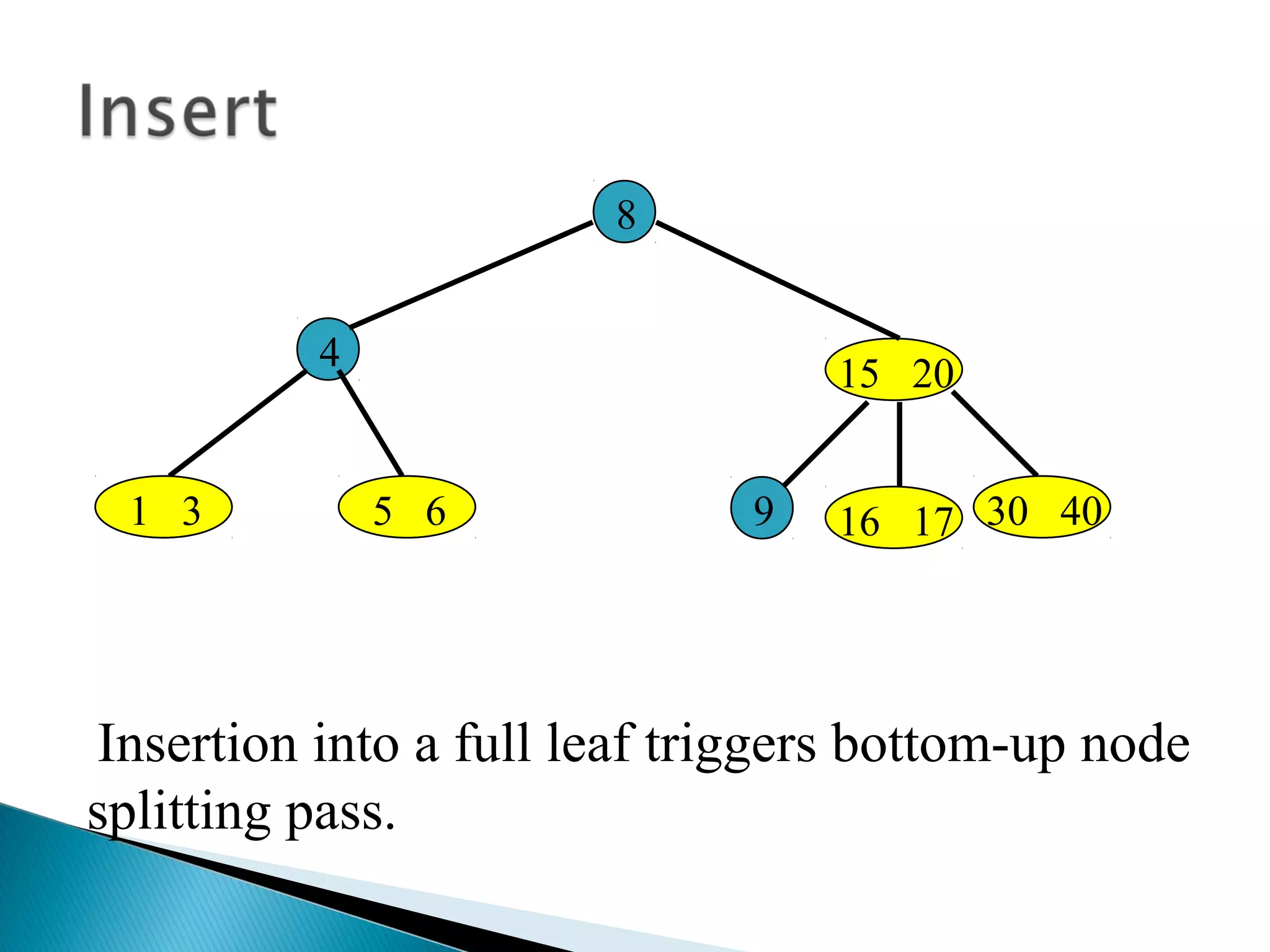
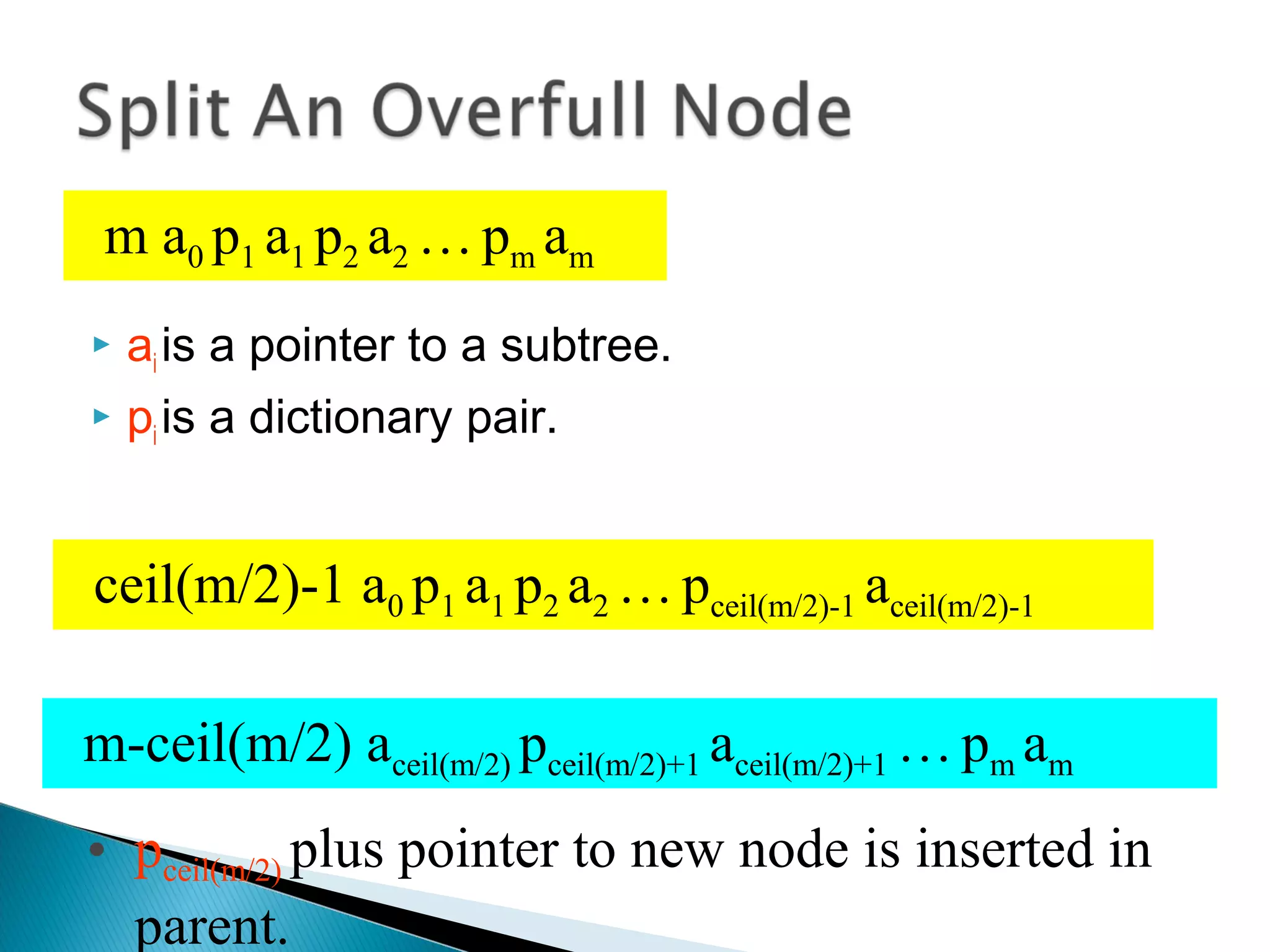
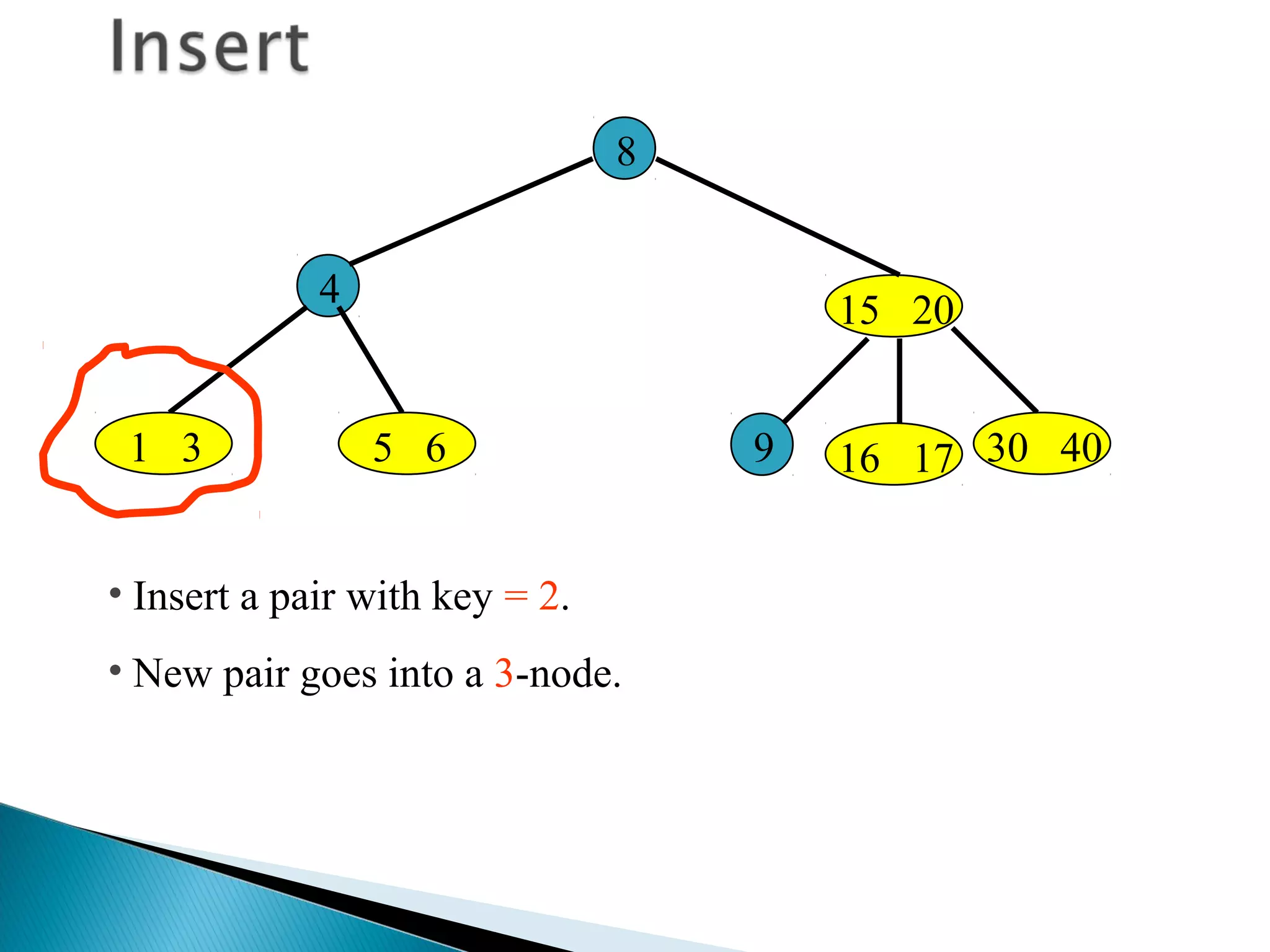
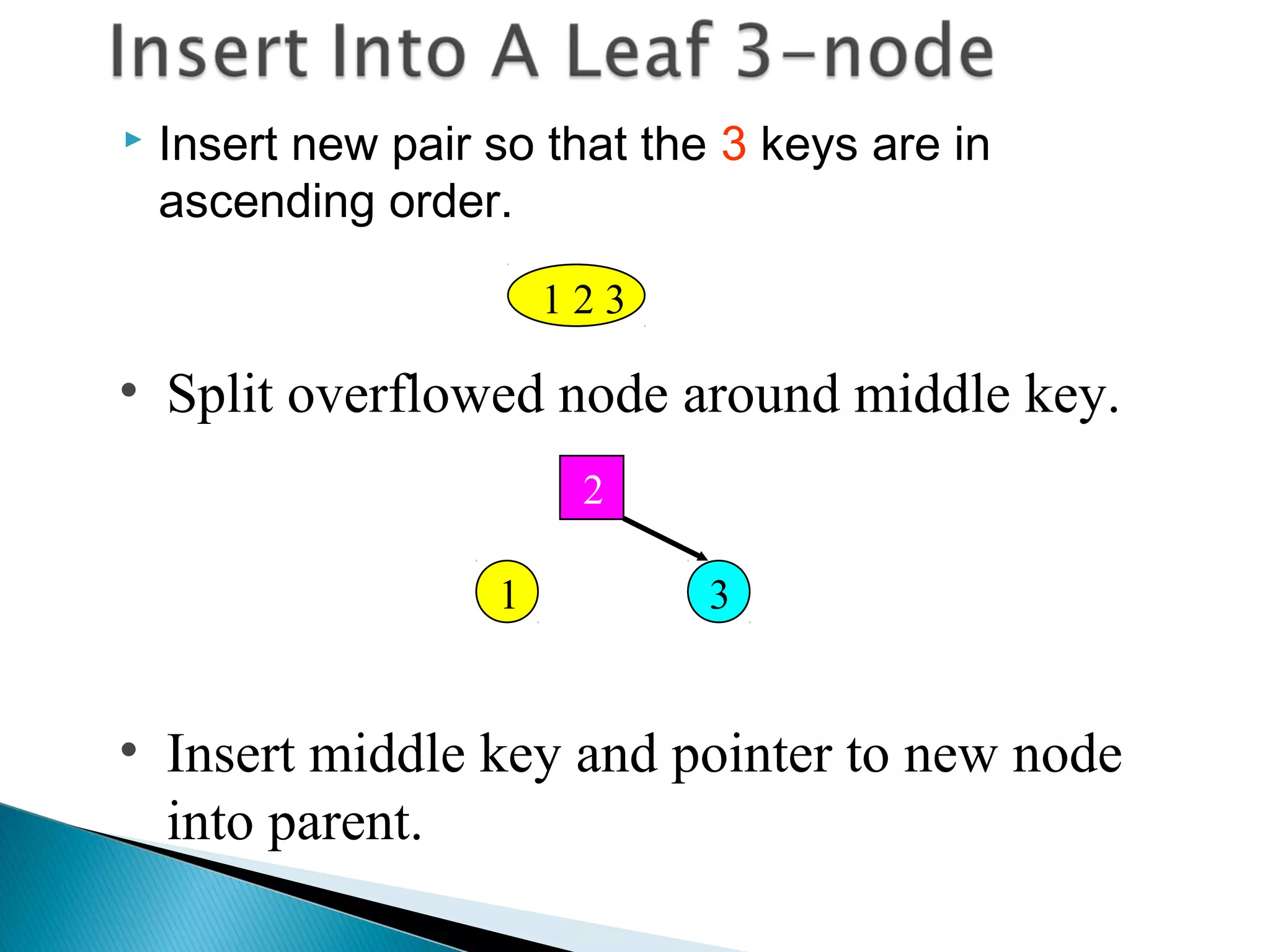
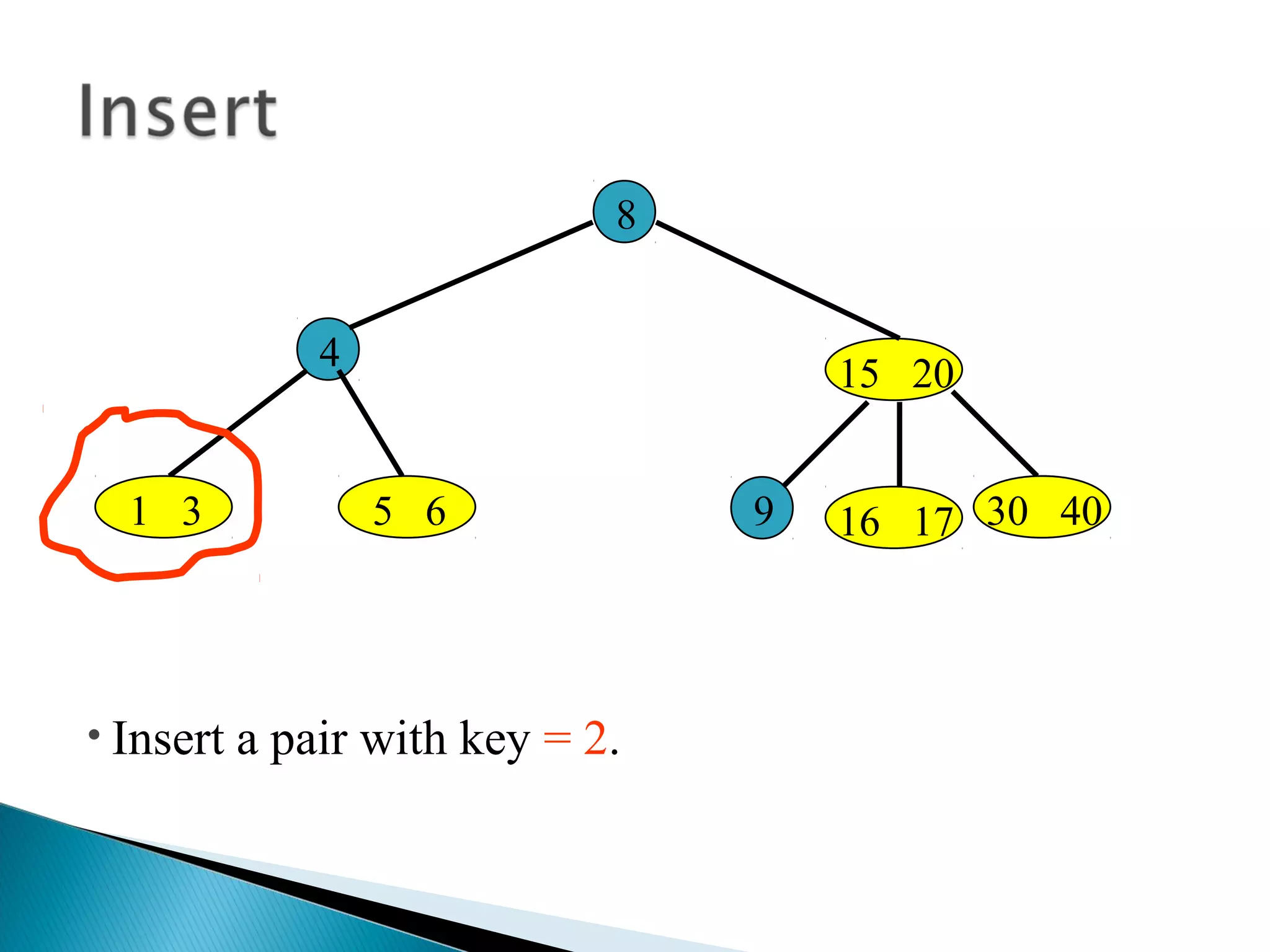
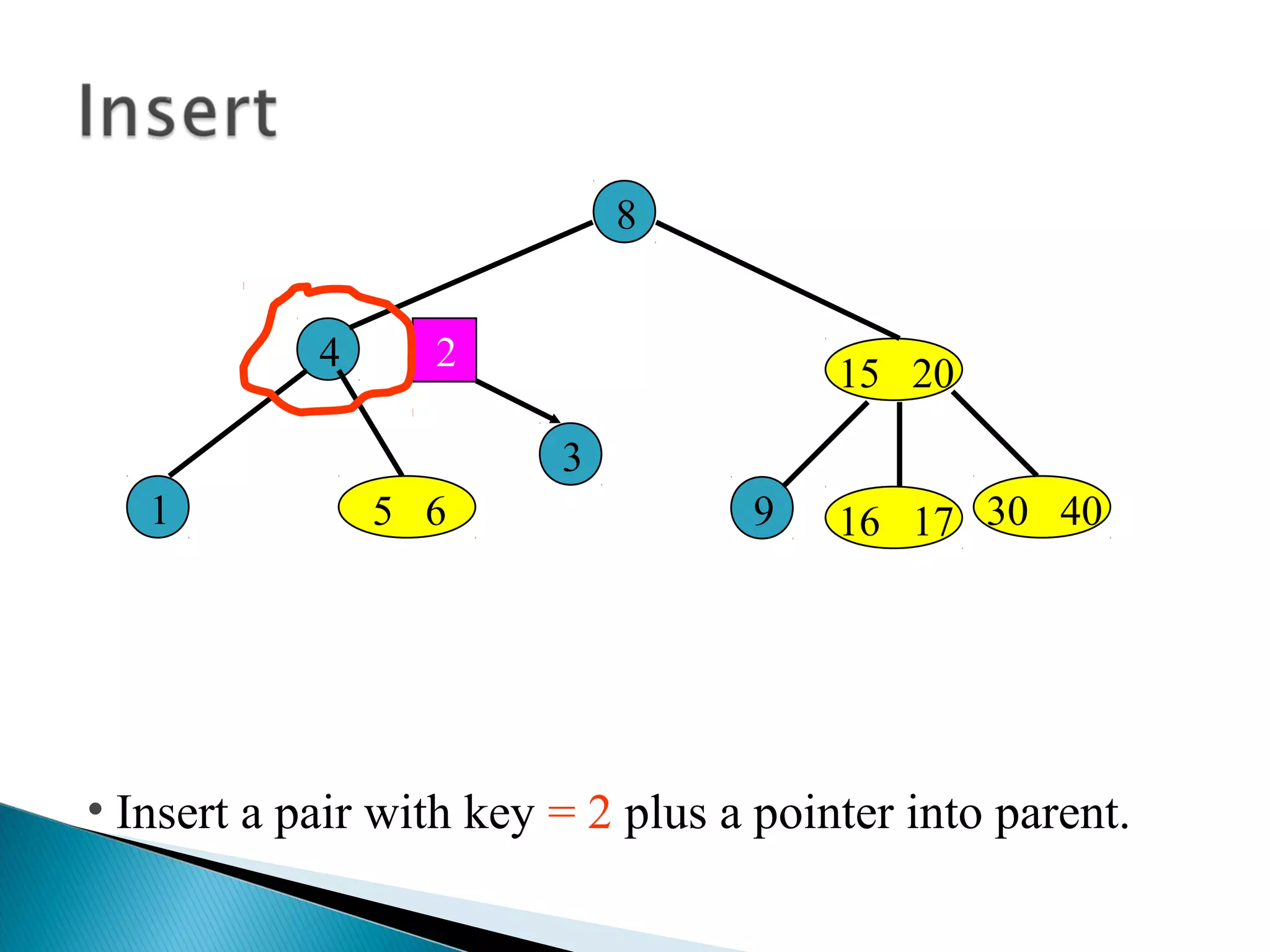
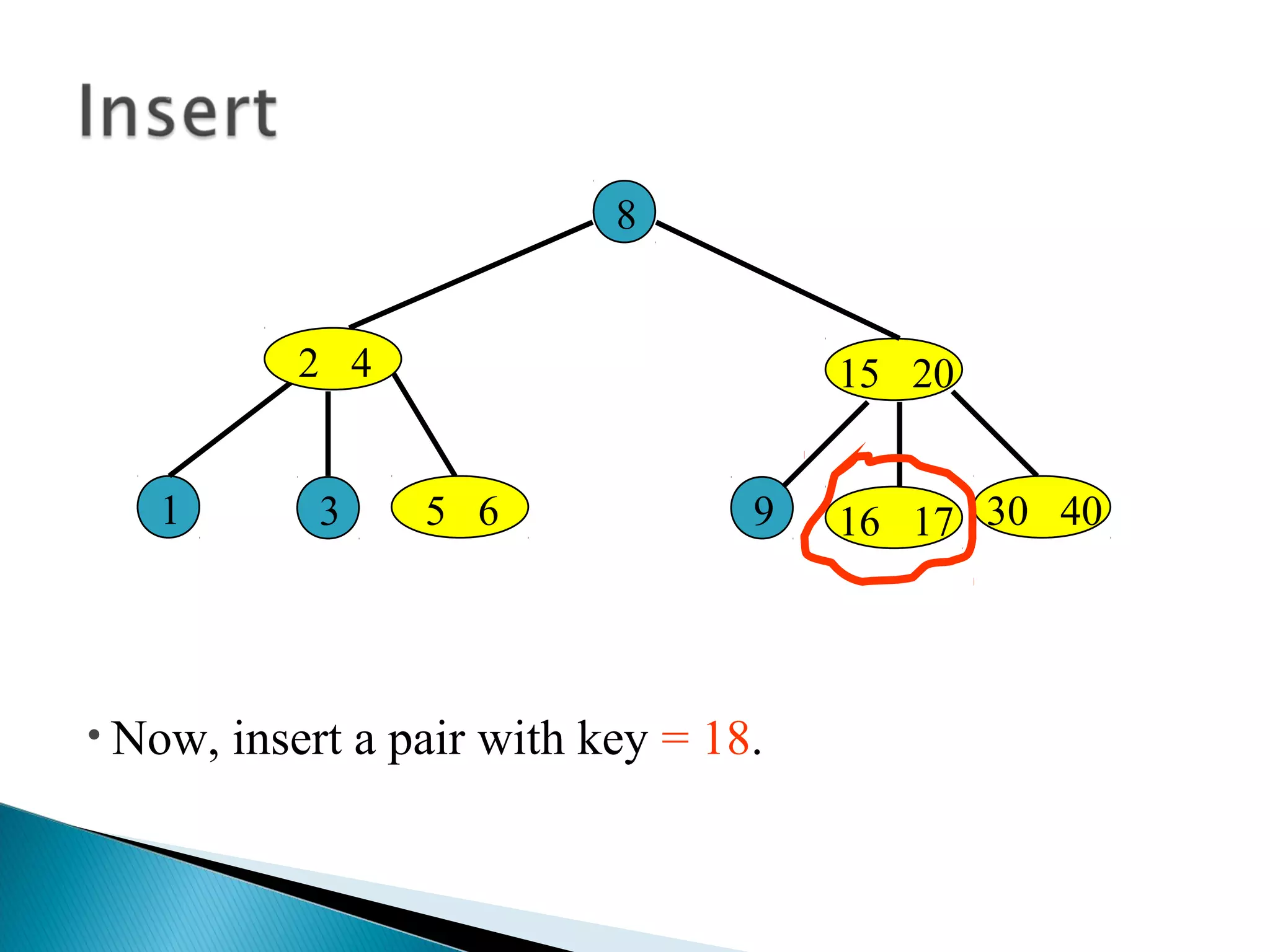
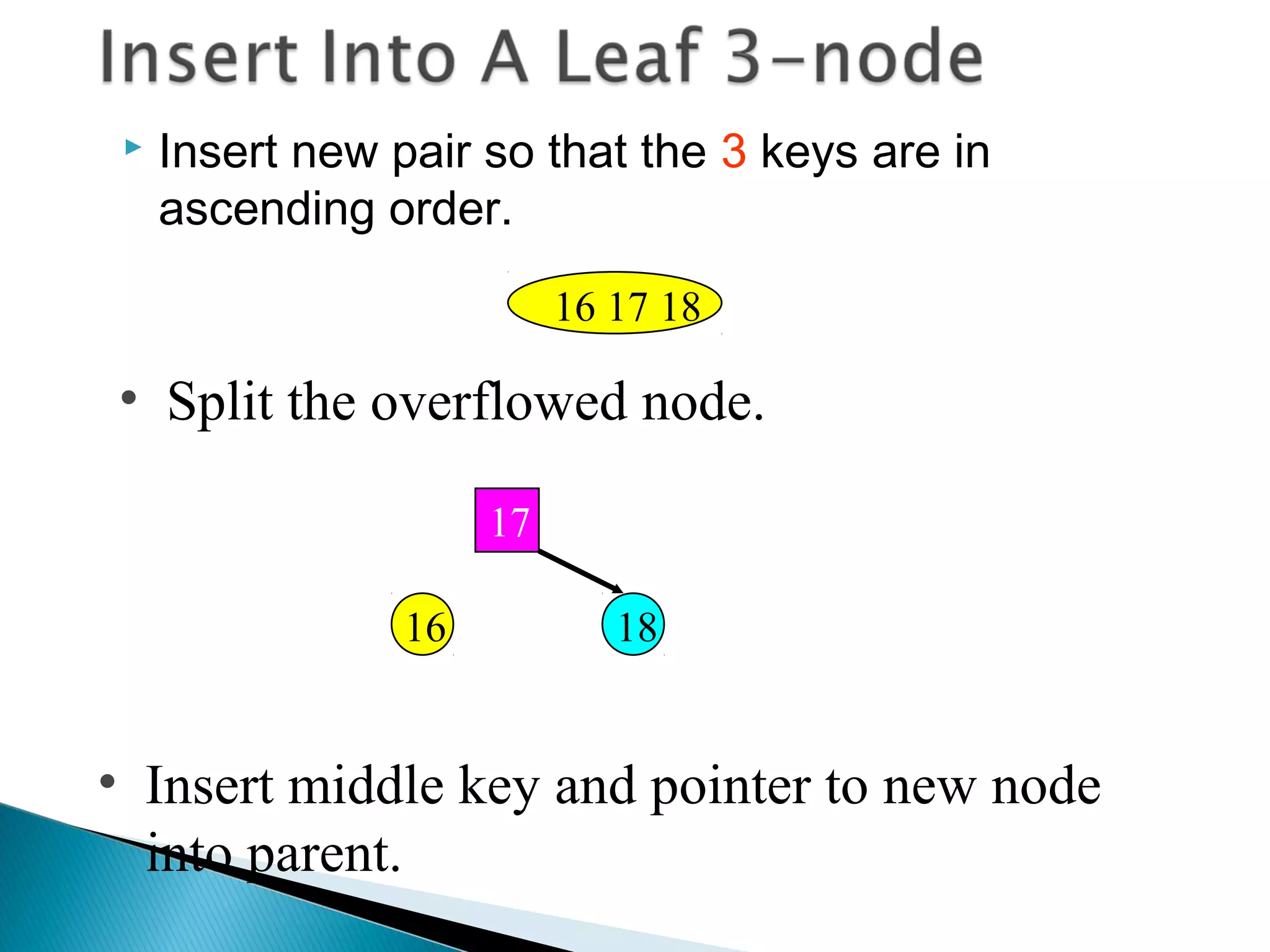
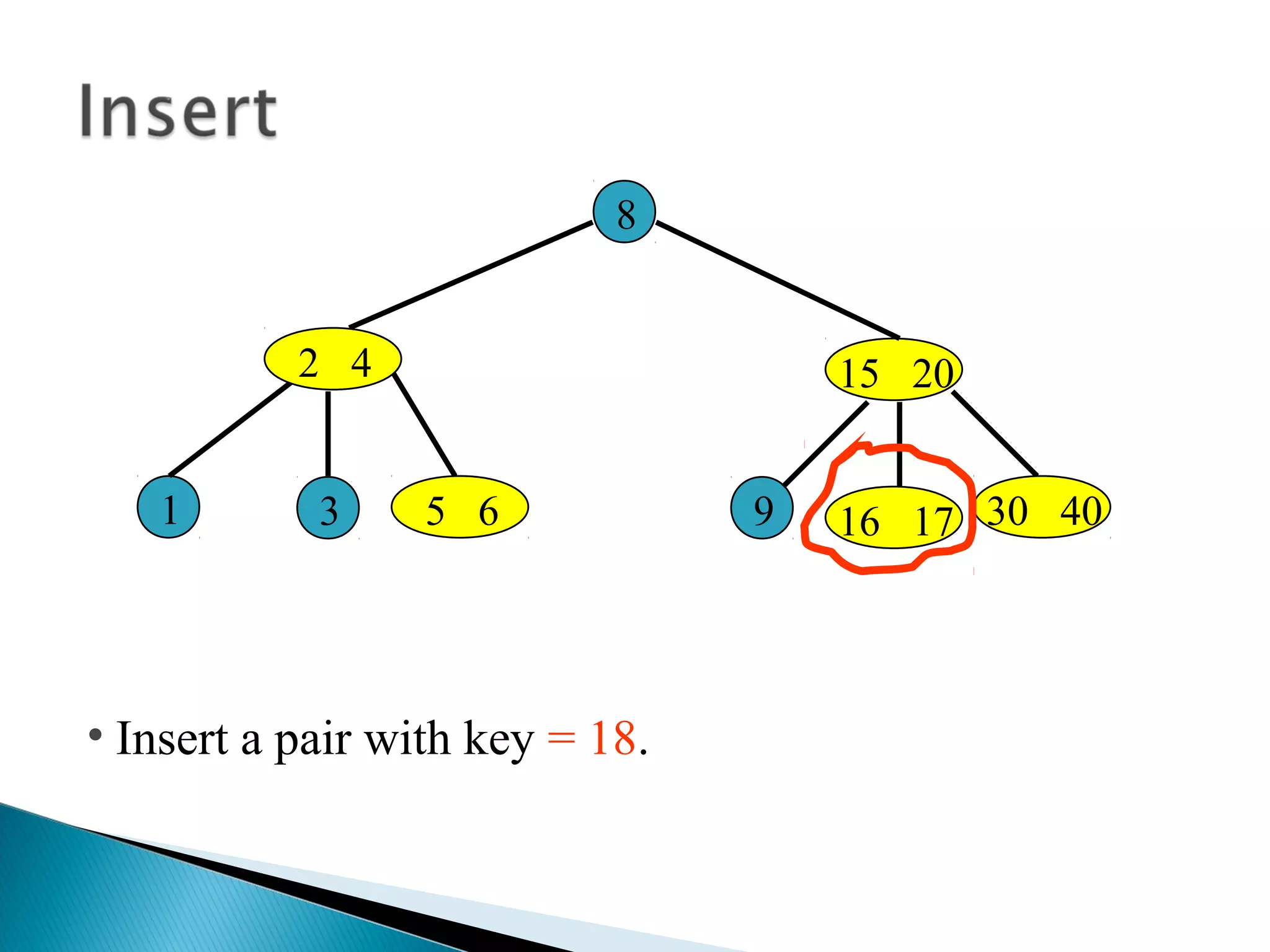
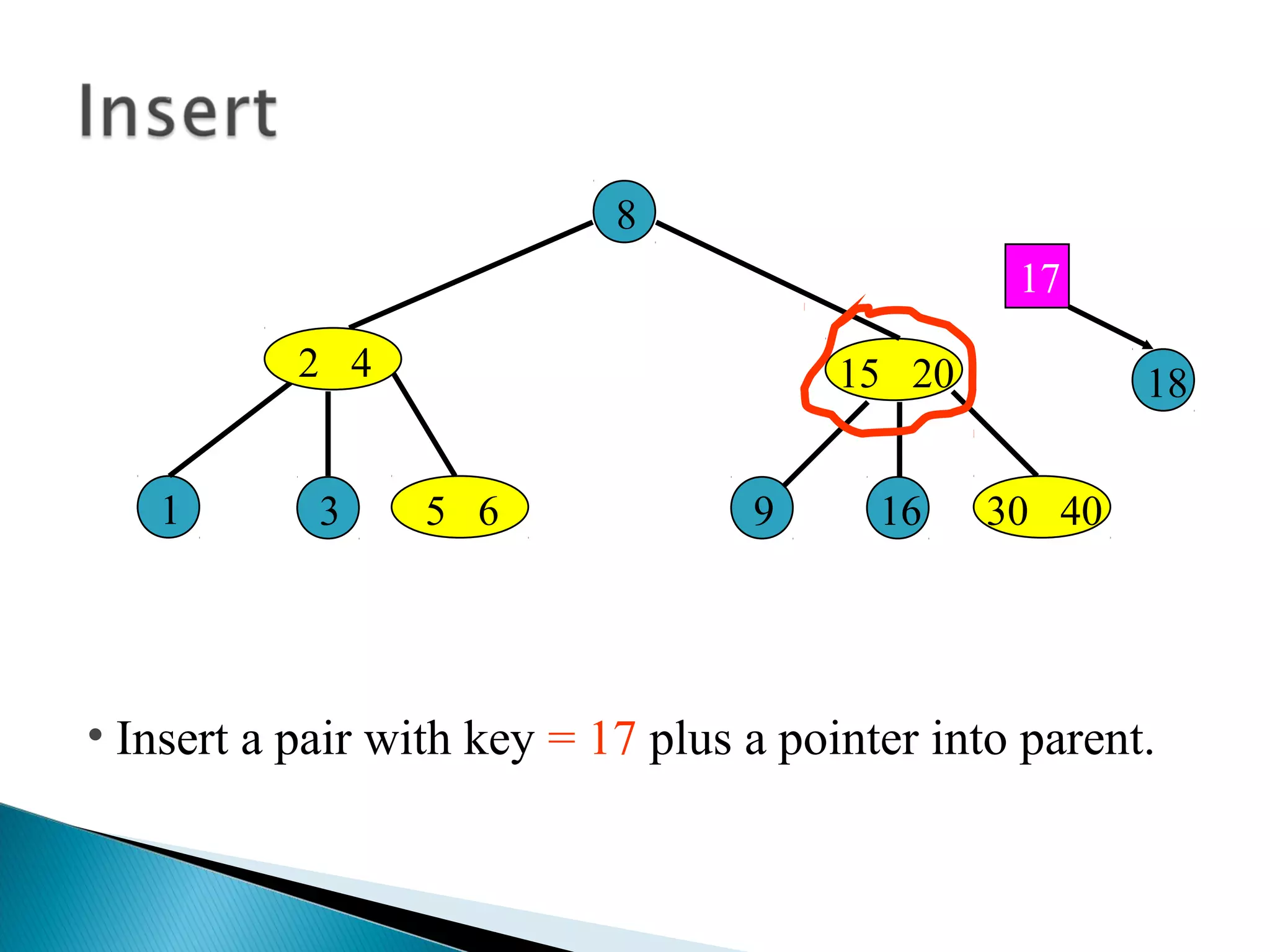
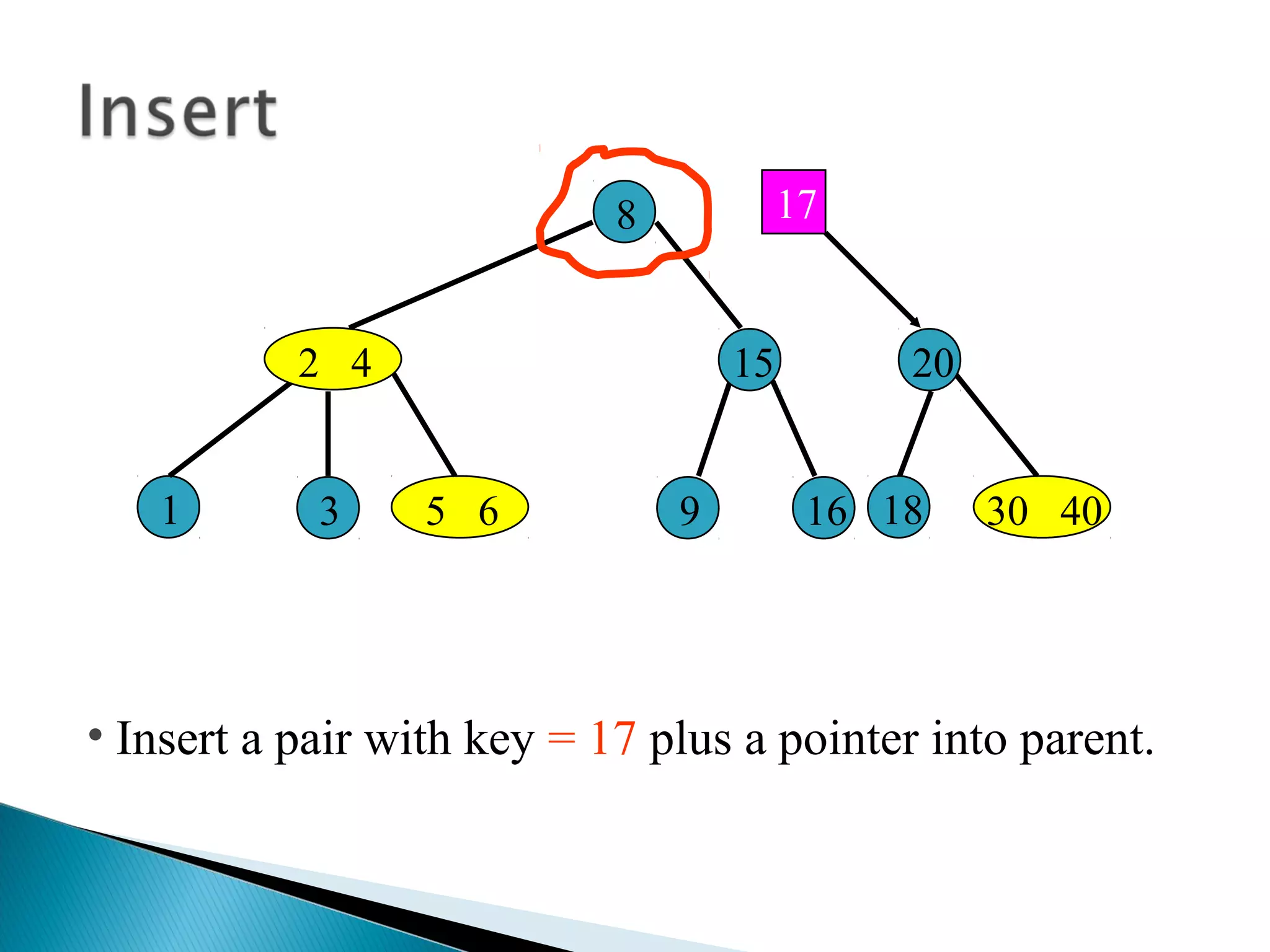
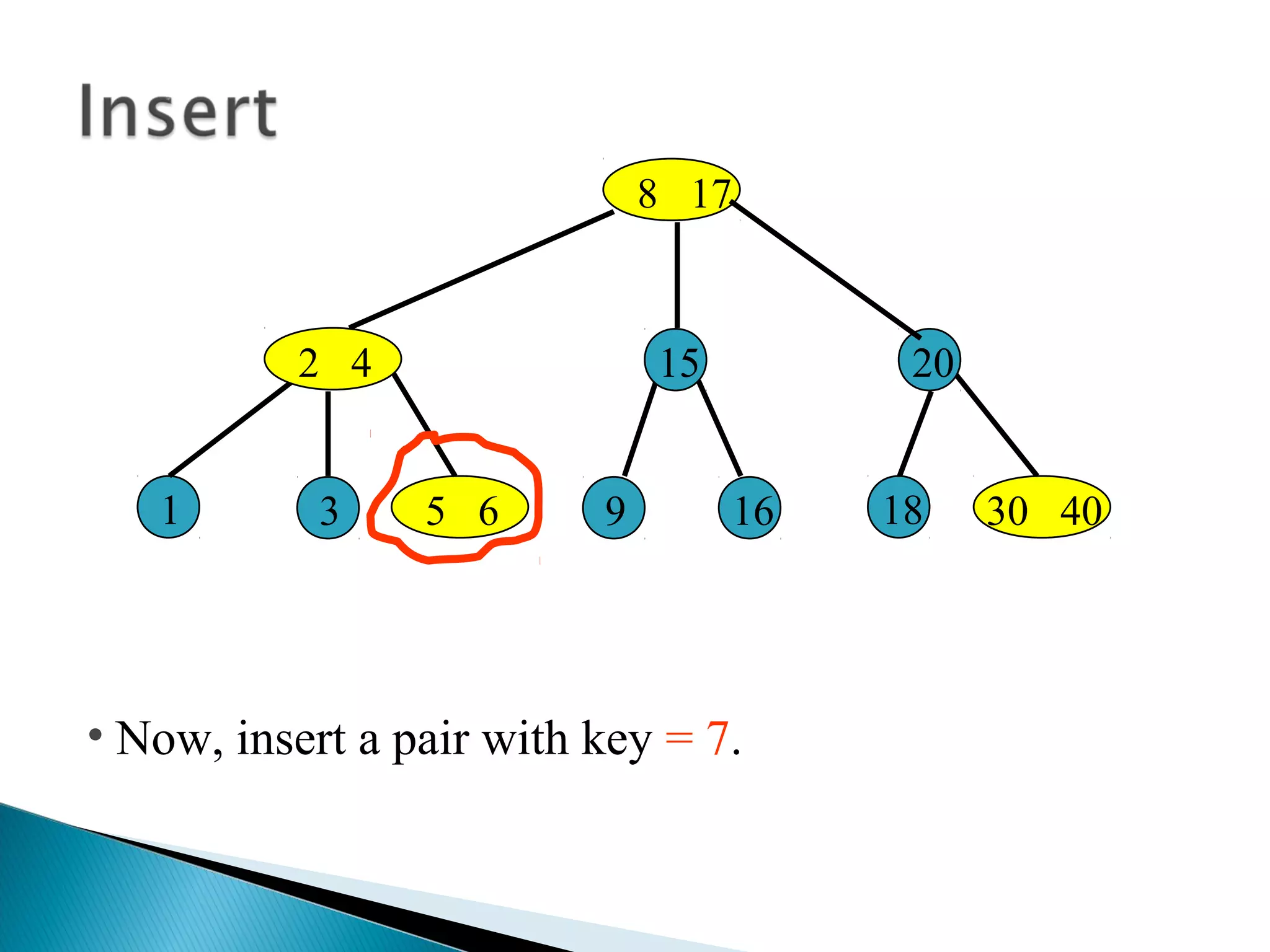
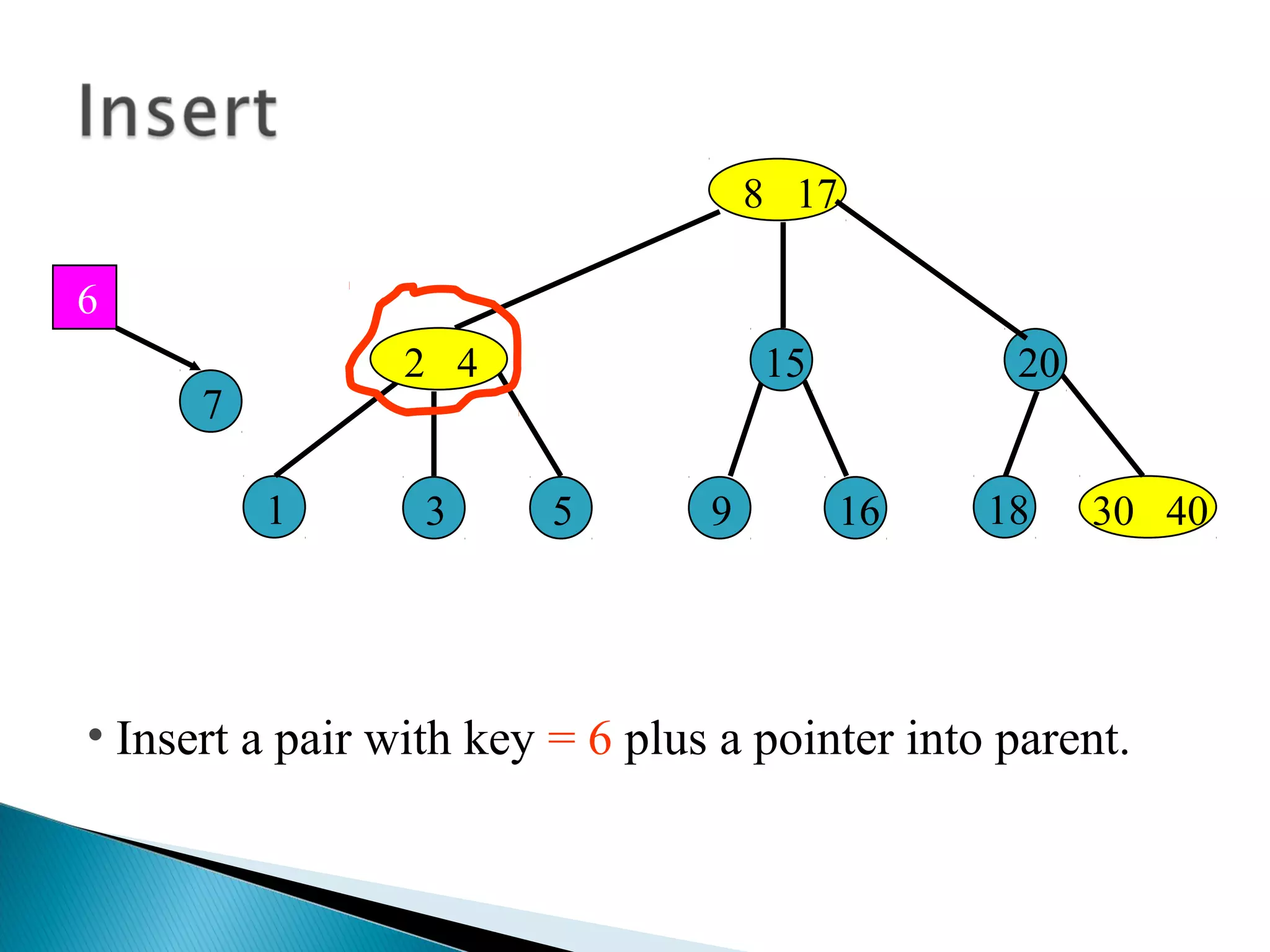
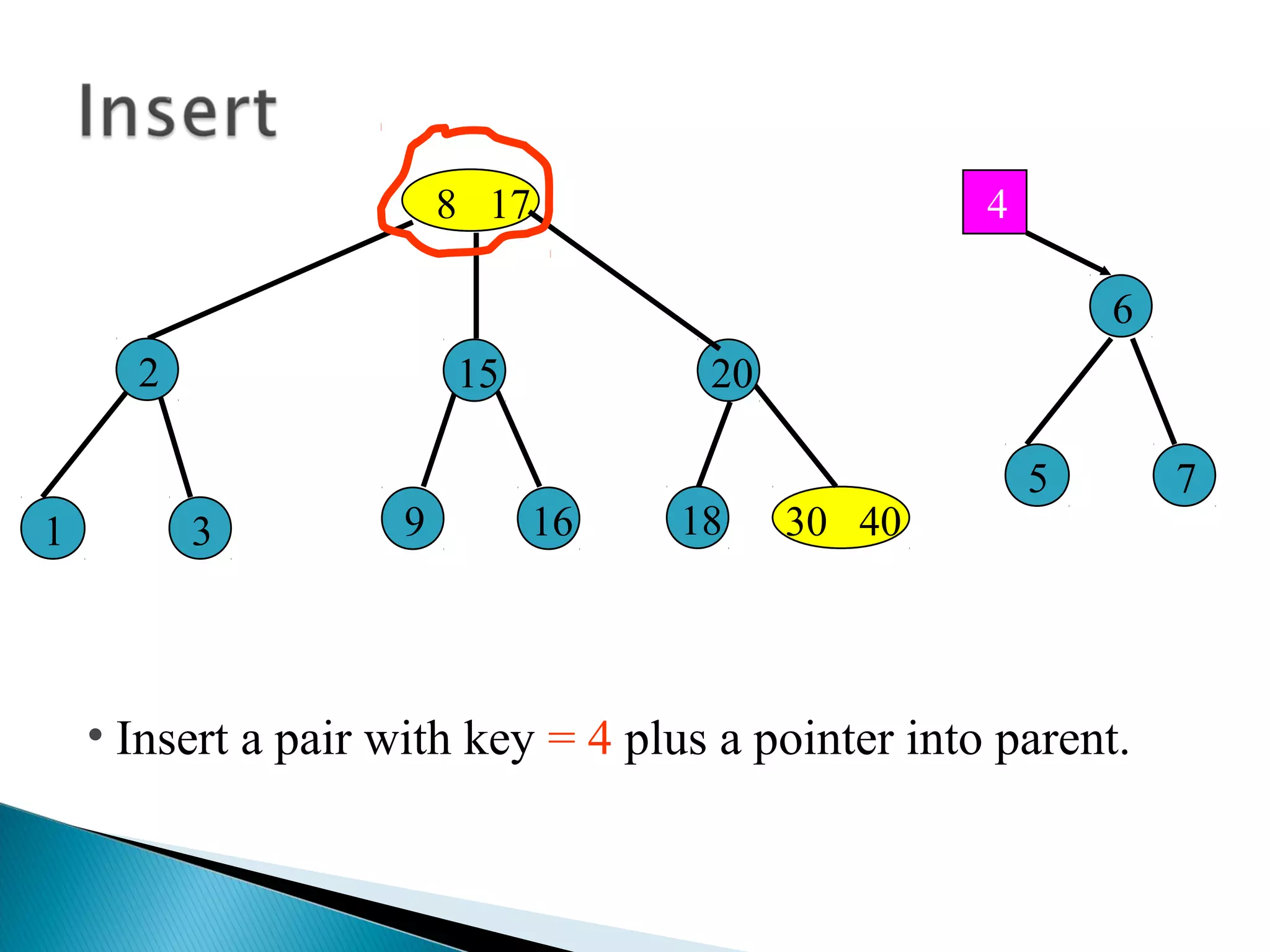
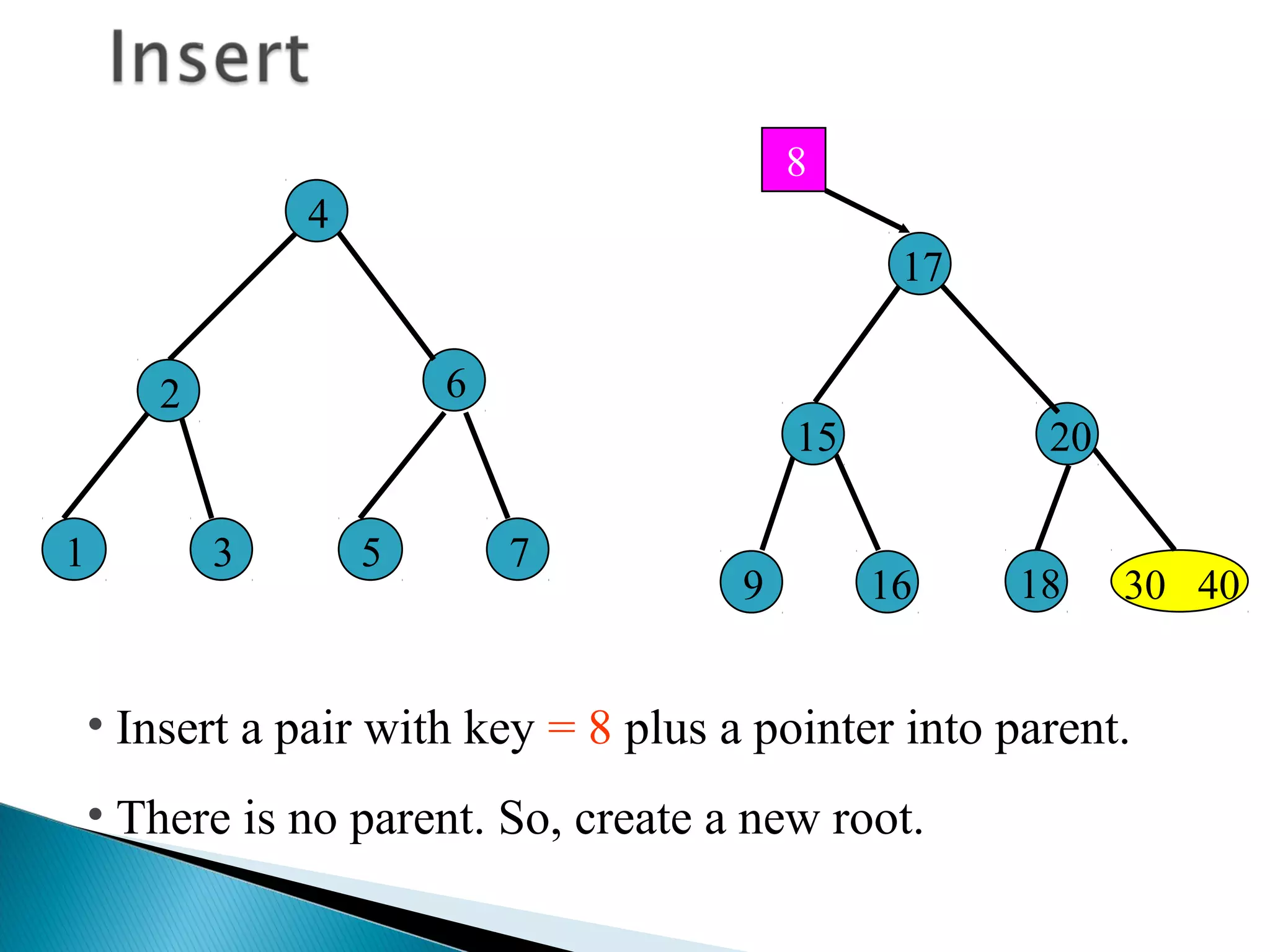
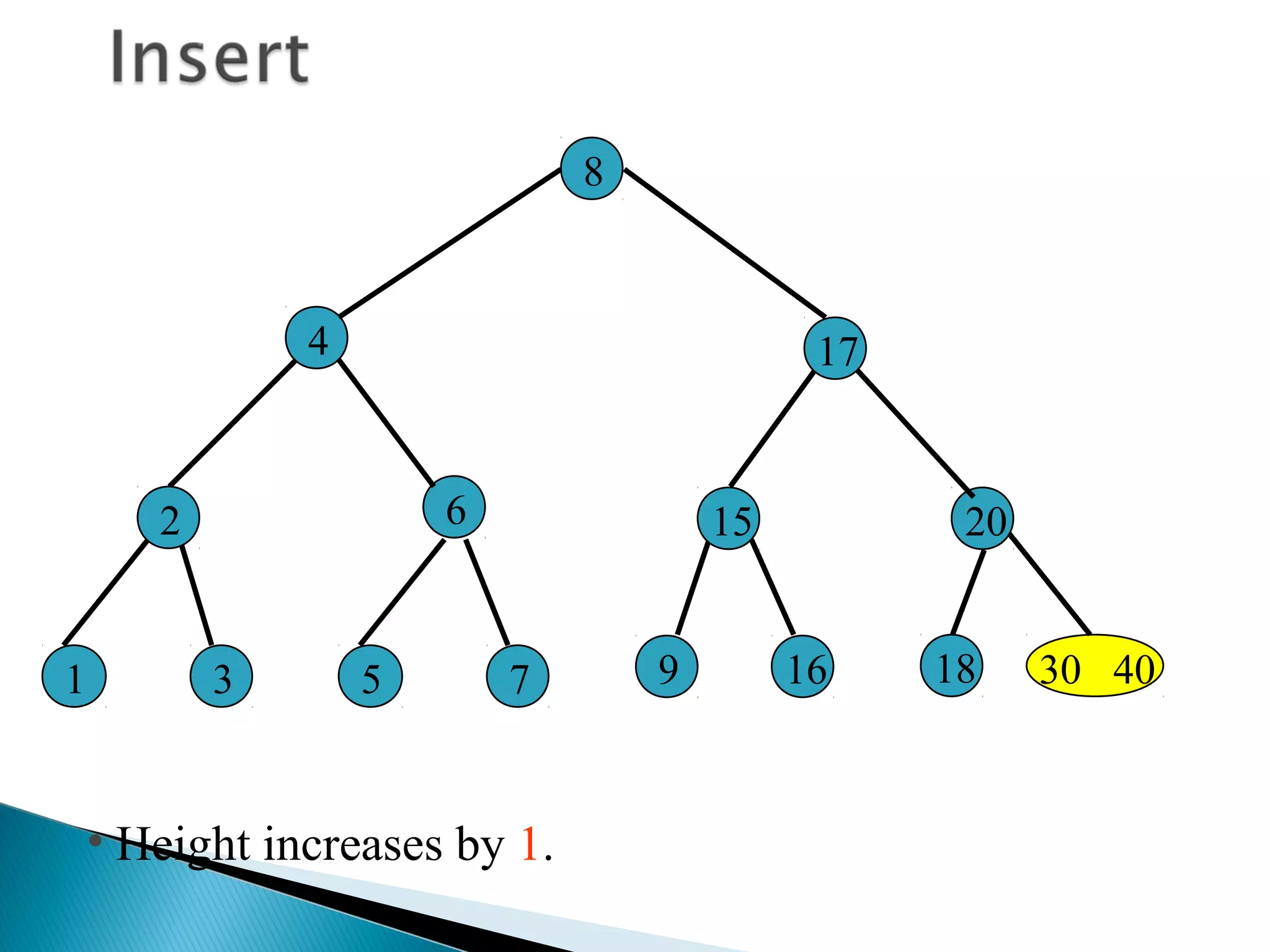
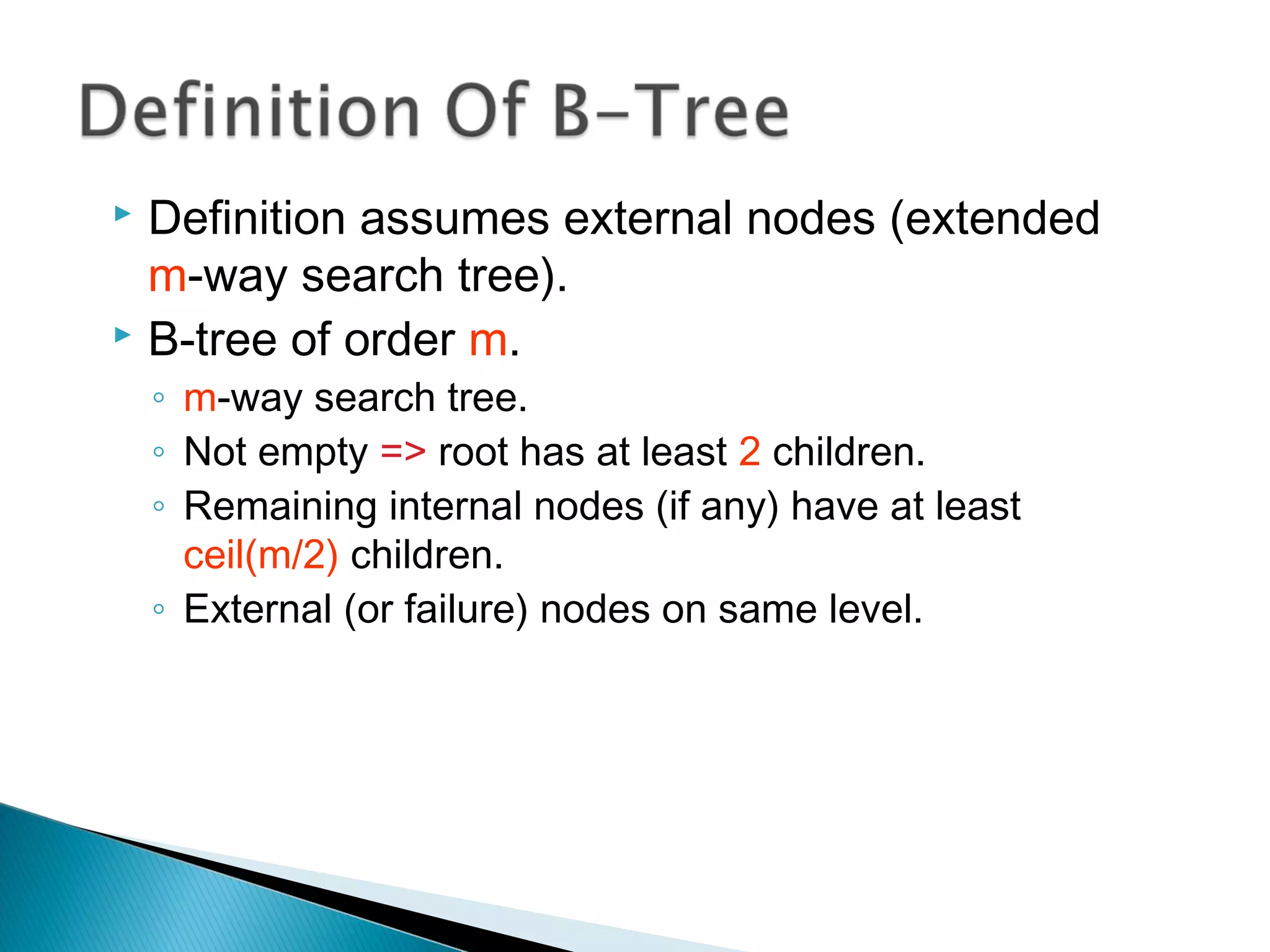
The document discusses B-trees, which are self-balancing search trees used to store large datasets. B-trees overcome limitations of storing data in memory by keeping the tree partially balanced and stored on disk. The document outlines properties of B-trees including that internal nodes must have a minimum number of children based on the tree's order, and that inserting data may cause nodes to split and keys to propagate up the tree to maintain balance.



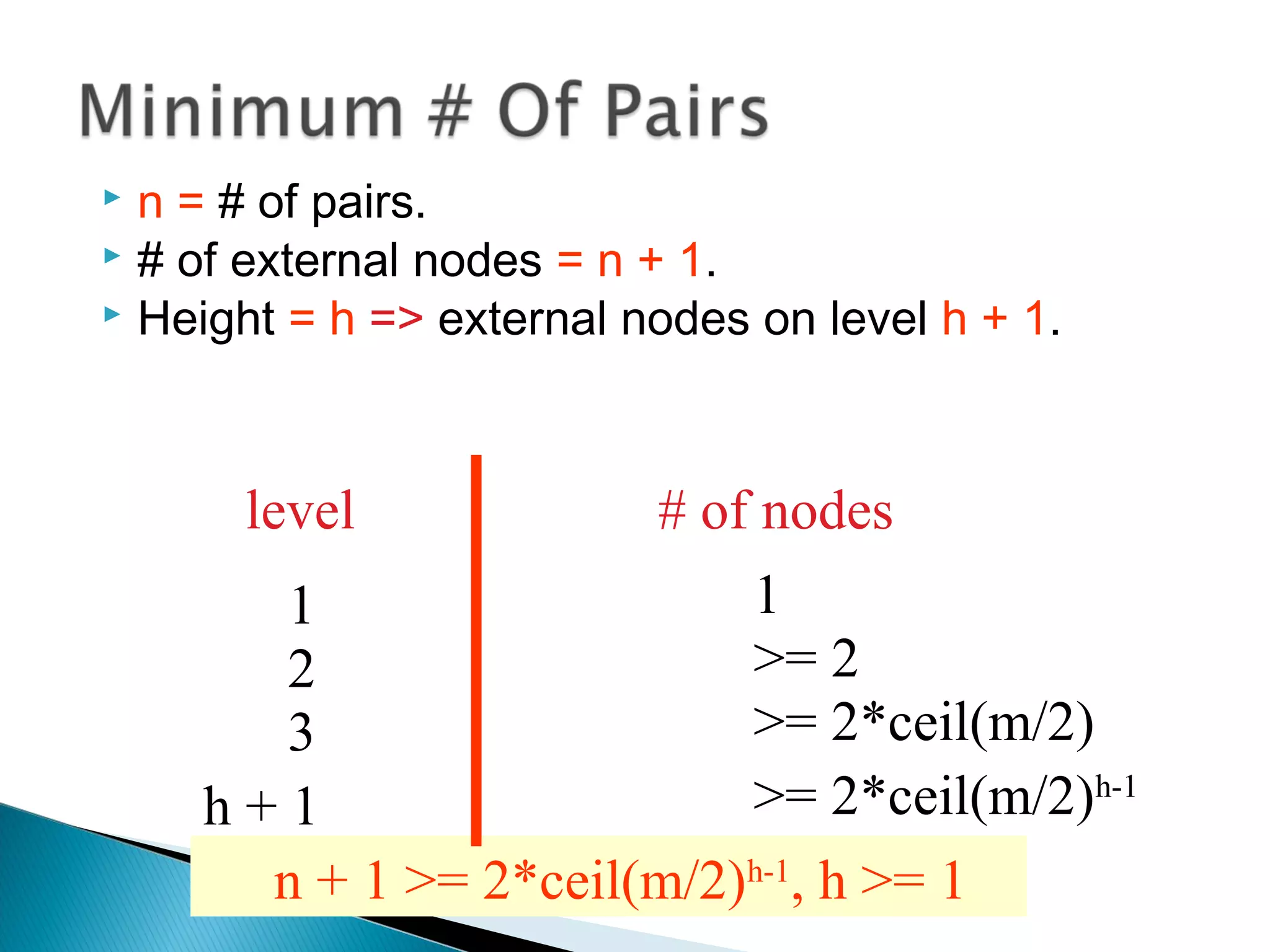
![ m = 200.
n + 1 >= 2*ceil(m/2)h-1
, h >= 1
height # of pairs
2 >= 199
3 >= 19,999
4 >= 2 * 106
–1
5 >= 2 * 108
–1
h <= log ceil(m/2) [(n+1)/2] + 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/b-tree-150704112739-lva1-app6892/75/B-tree-6-2048.jpg)