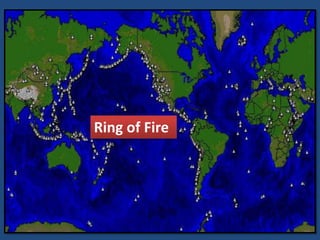
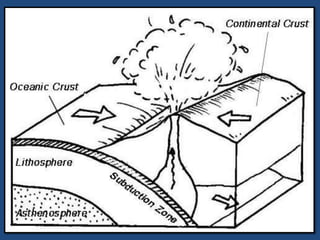
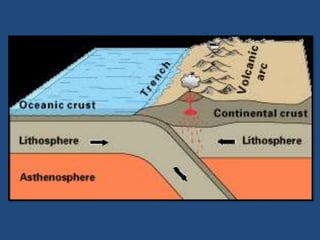
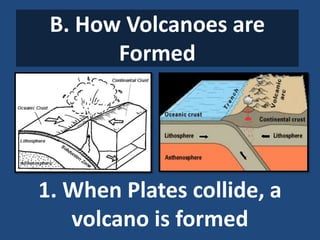
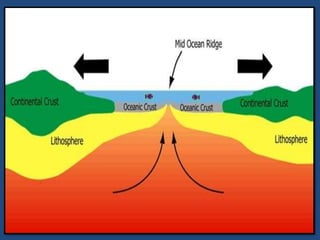
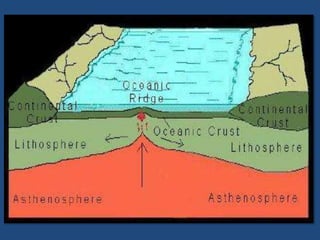
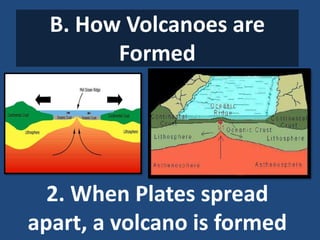
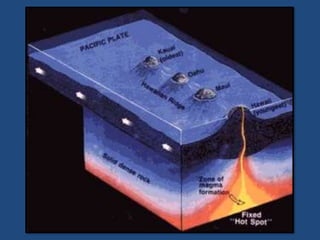
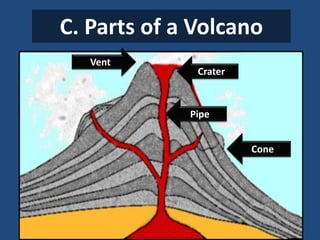
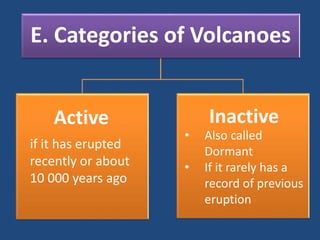
This document defines volcanoes as openings in the Earth's crust that allow molten rock and gases to escape. It notes that over half of the world's active volcanoes above sea level are located along the Ring of Fire. Volcanoes form when tectonic plates collide, spread apart, or interact under a plate. The parts of a volcano include the crater, pipe, cone, and vent. There are three main types of volcanoes: composite/strato volcanoes, shield volcanoes, and cinder cone volcanoes. Volcanic eruptions can have both beneficial effects like adding nutrients to soil or creating new islands, and harmful effects like releasing aerosols or abandoning land.