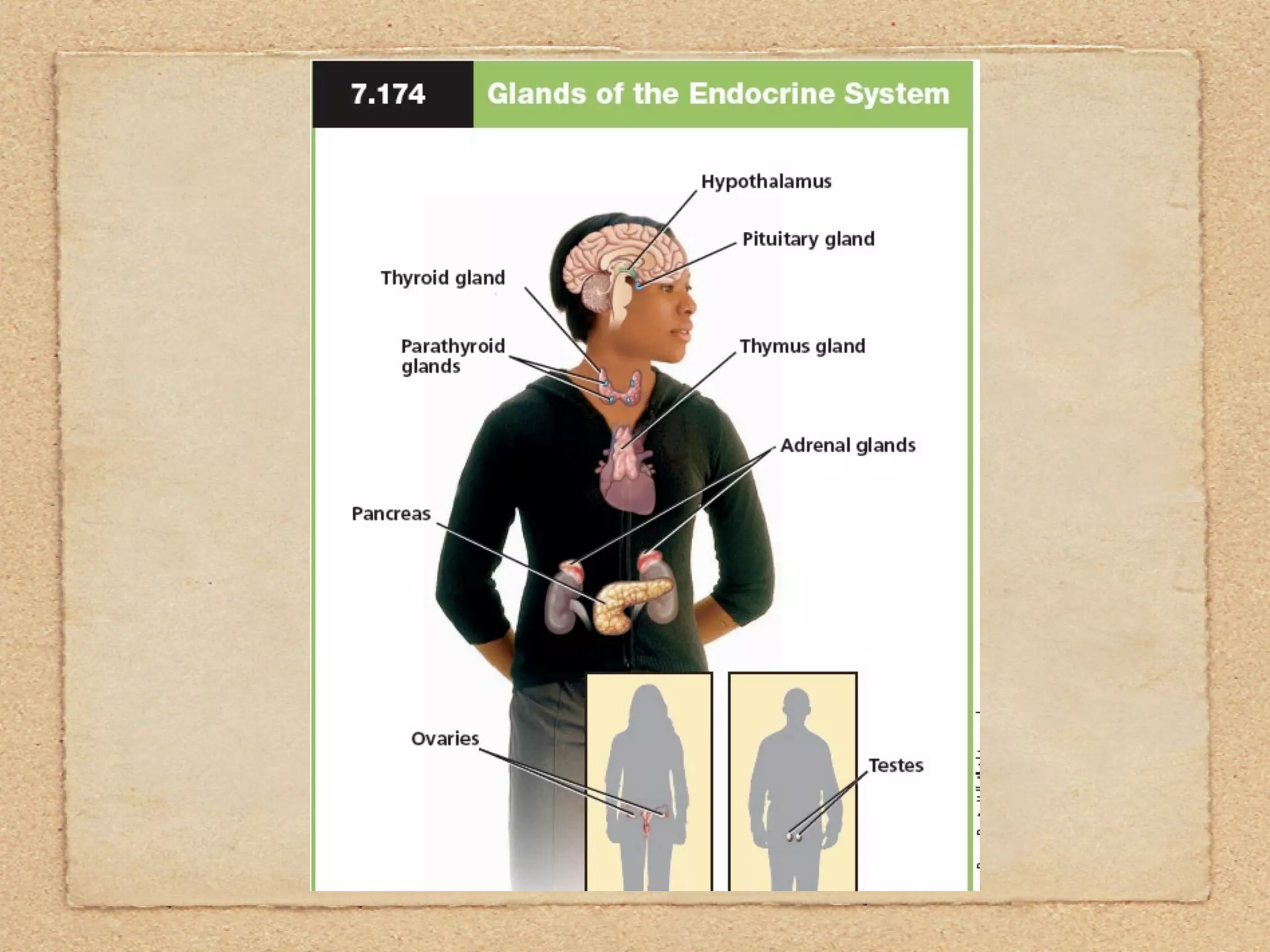
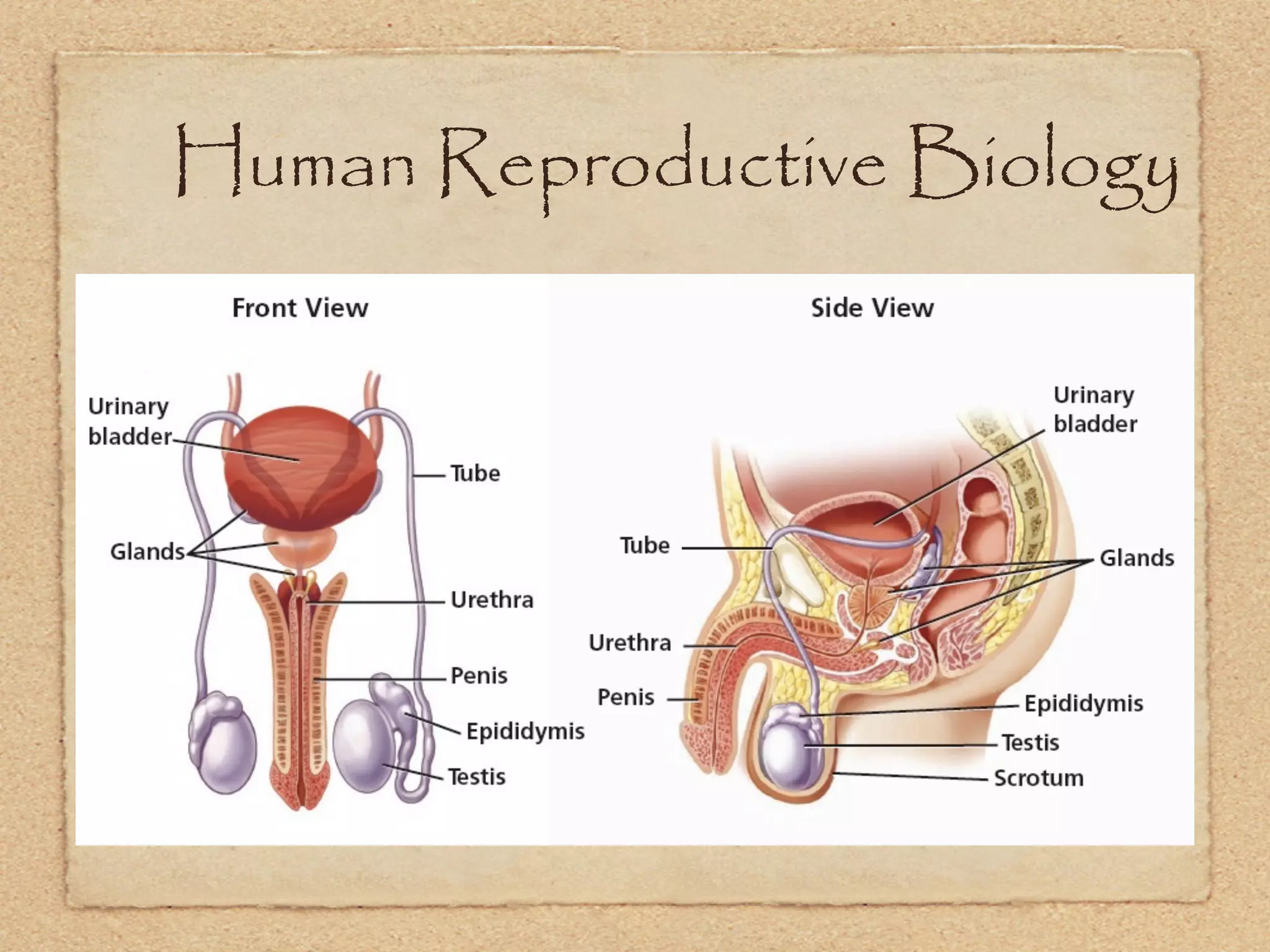
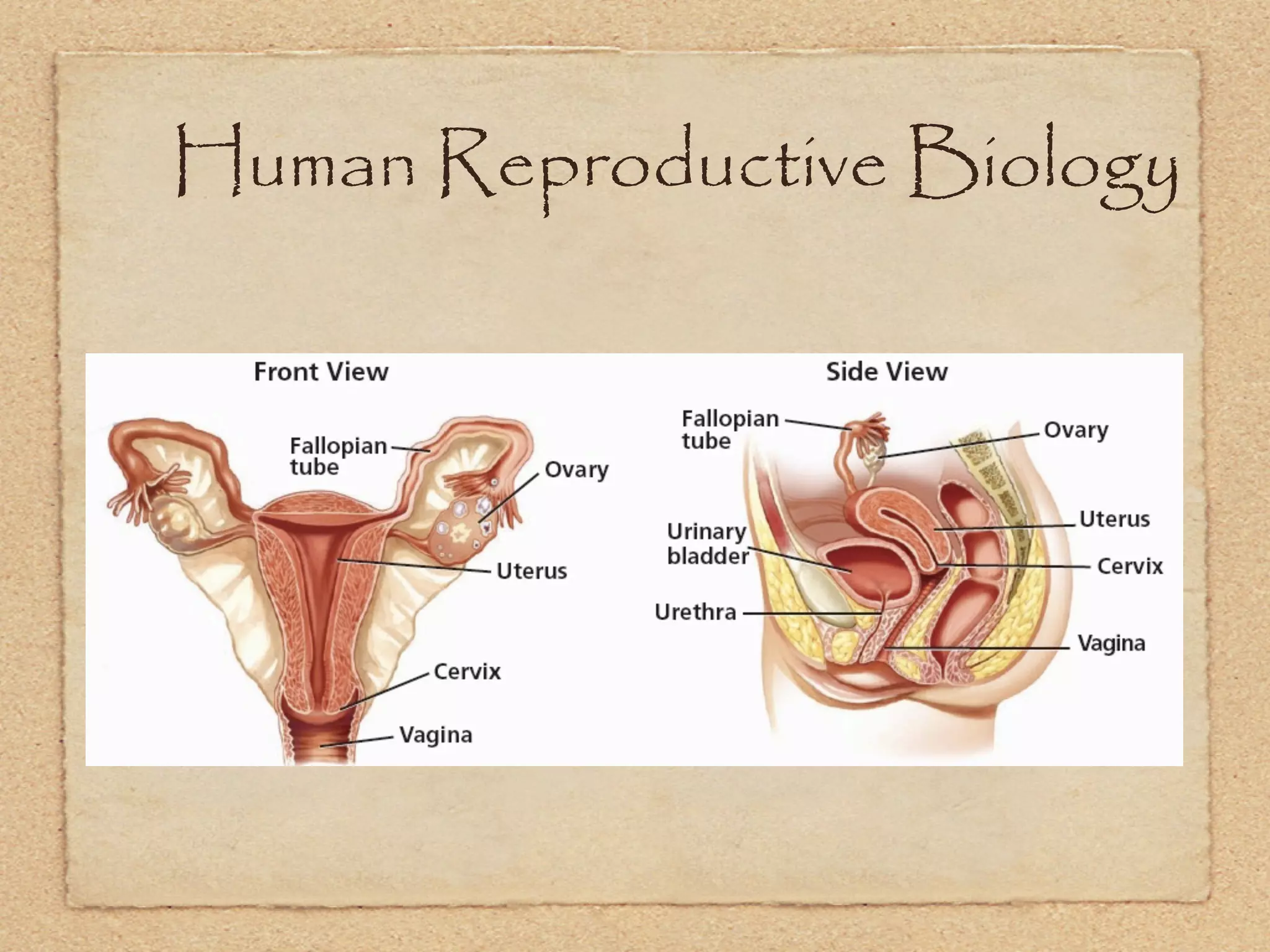
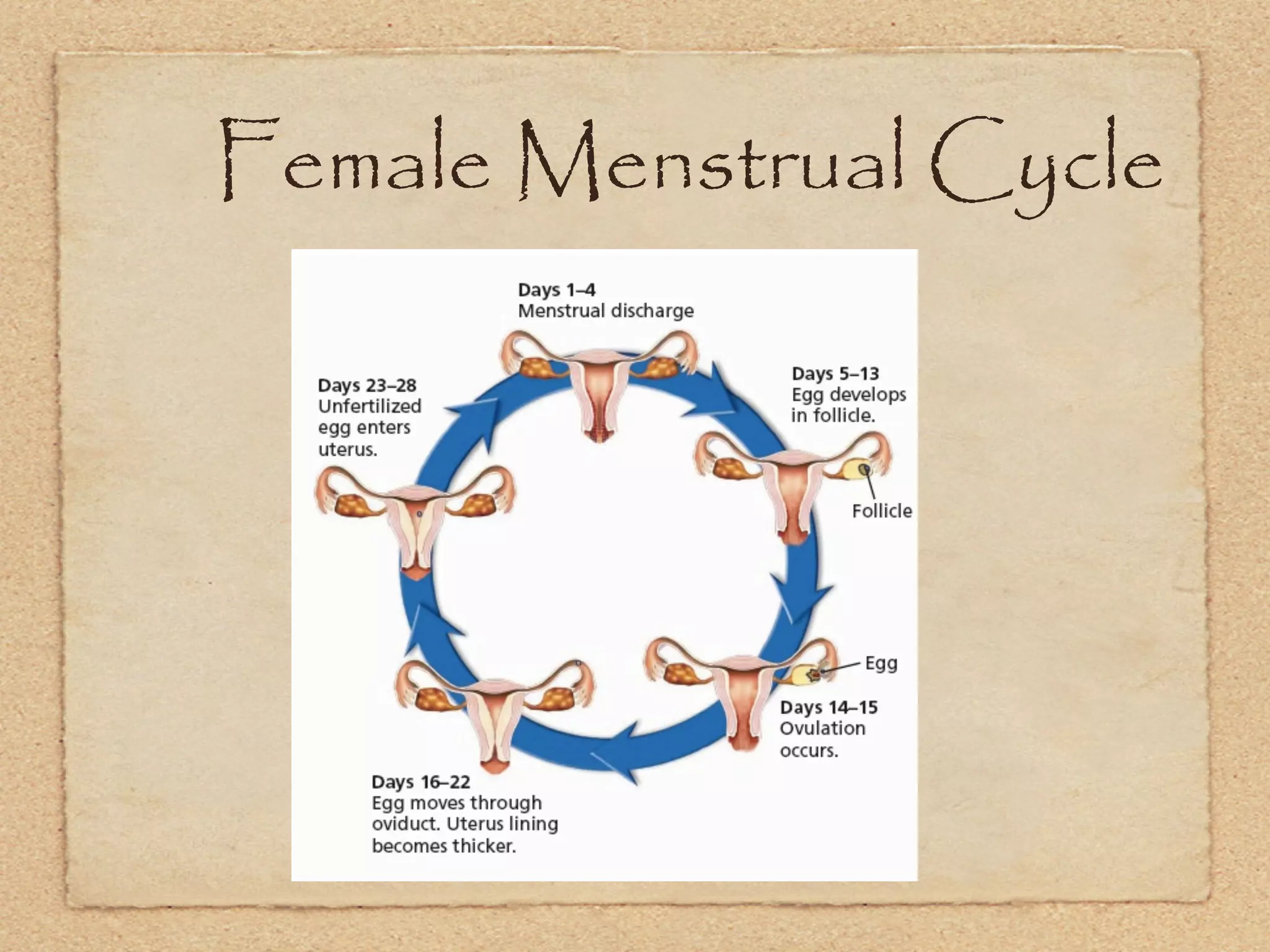
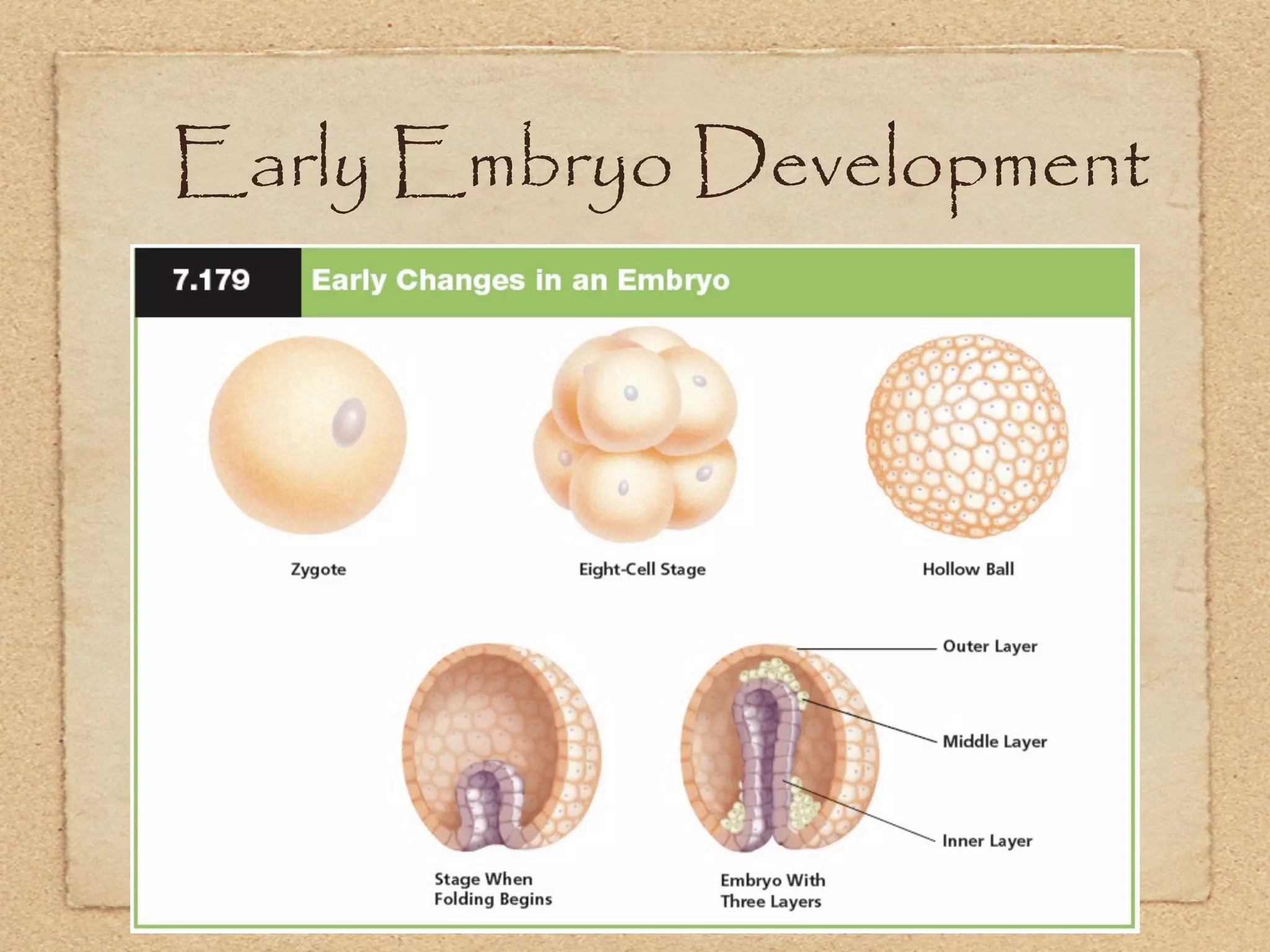
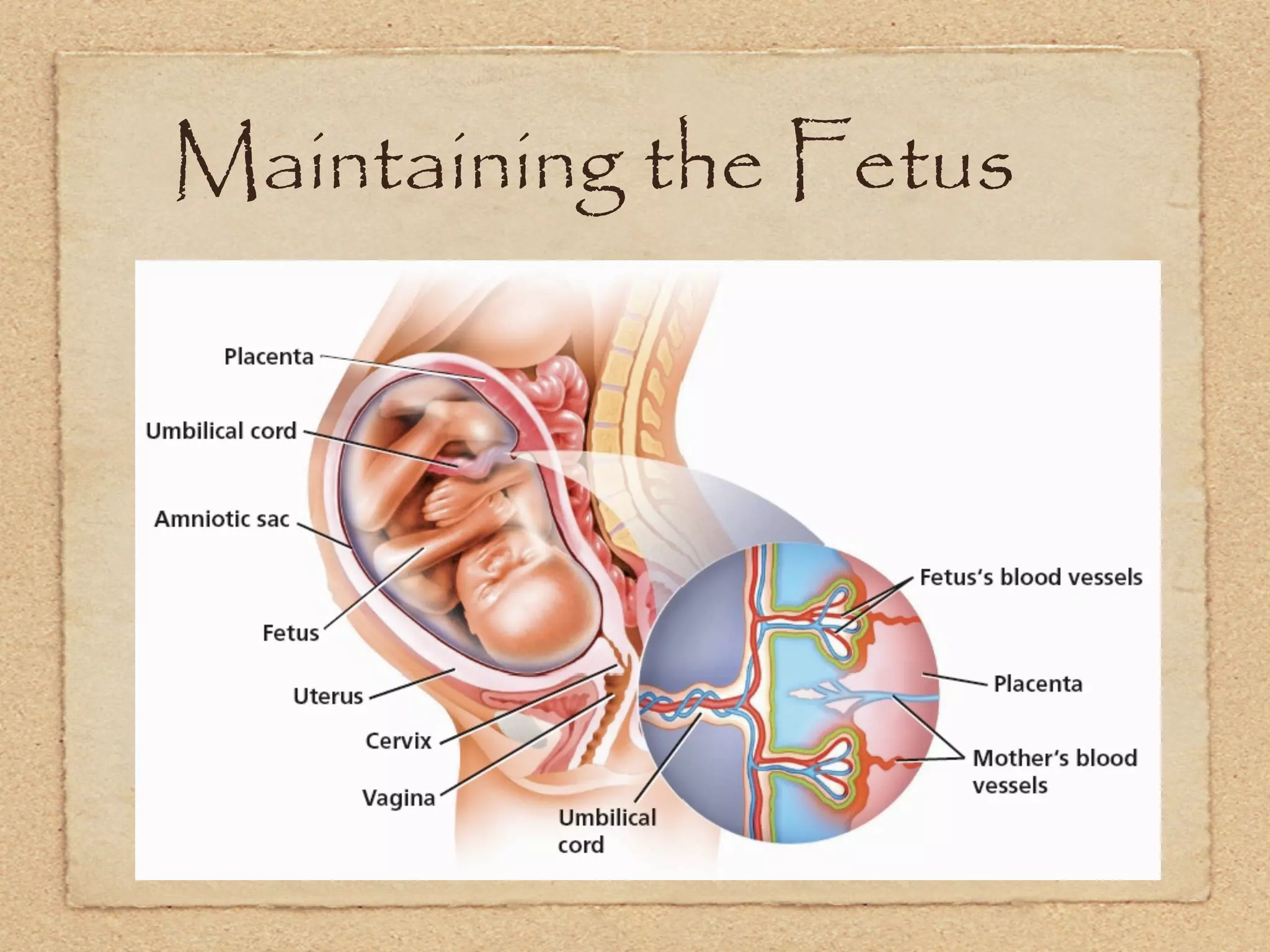
The endocrine system regulates metabolism, growth, development, emotions, and reproduction through hormones released into the bloodstream from endocrine glands. It acts more slowly than the nervous system but has longer-lasting effects. Some key endocrine glands include the hypothalamus, pituitary, thyroid, adrenals, ovaries, and testes. Important hormones include insulin, cortisol, testosterone, estrogen, progesterone, and thyroxine which regulate processes like blood sugar, stress response, and metabolism. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland work together to control hormone release from other glands through negative feedback loops.