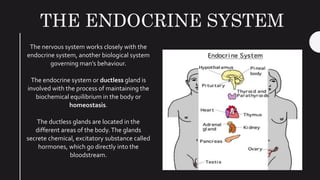
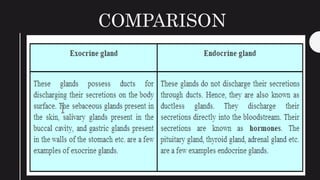
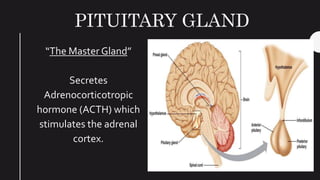
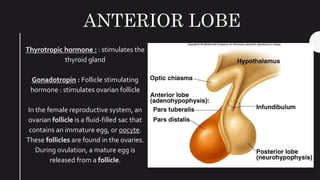
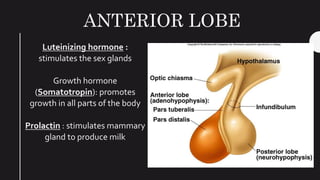
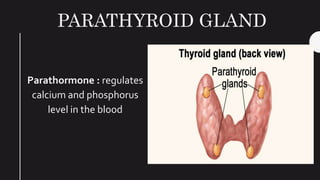
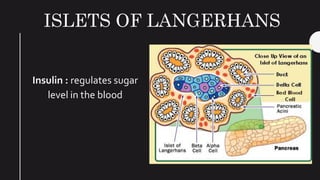
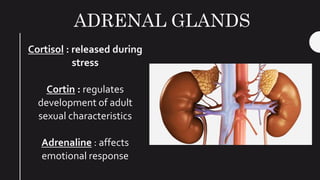
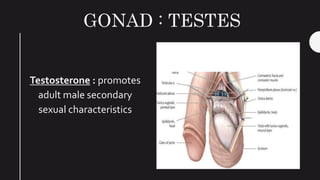
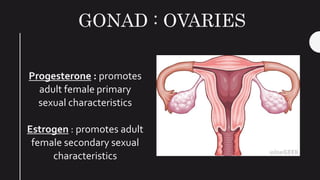
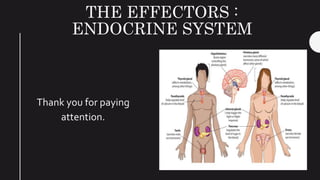
The endocrine system maintains homeostasis in the body through glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream. The major glands include the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal glands, pancreas and gonads. The pituitary gland is called the "master gland" as it controls many other glands by producing hormones like ACTH, TSH, FSH, LH and growth hormone. These hormones target various organs and tissues to regulate processes like metabolism, growth and development, sexual function, mood, and other bodily functions.