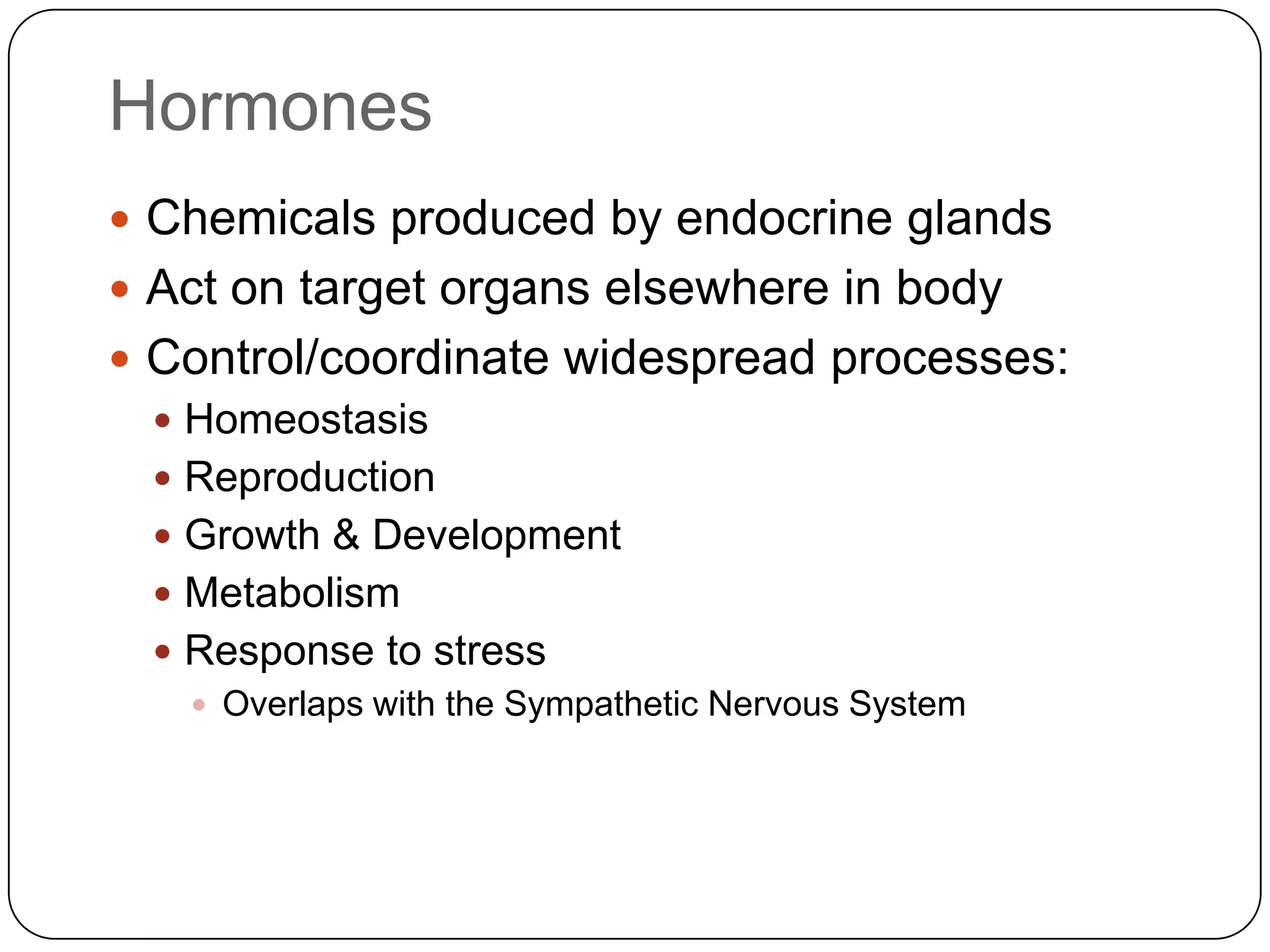
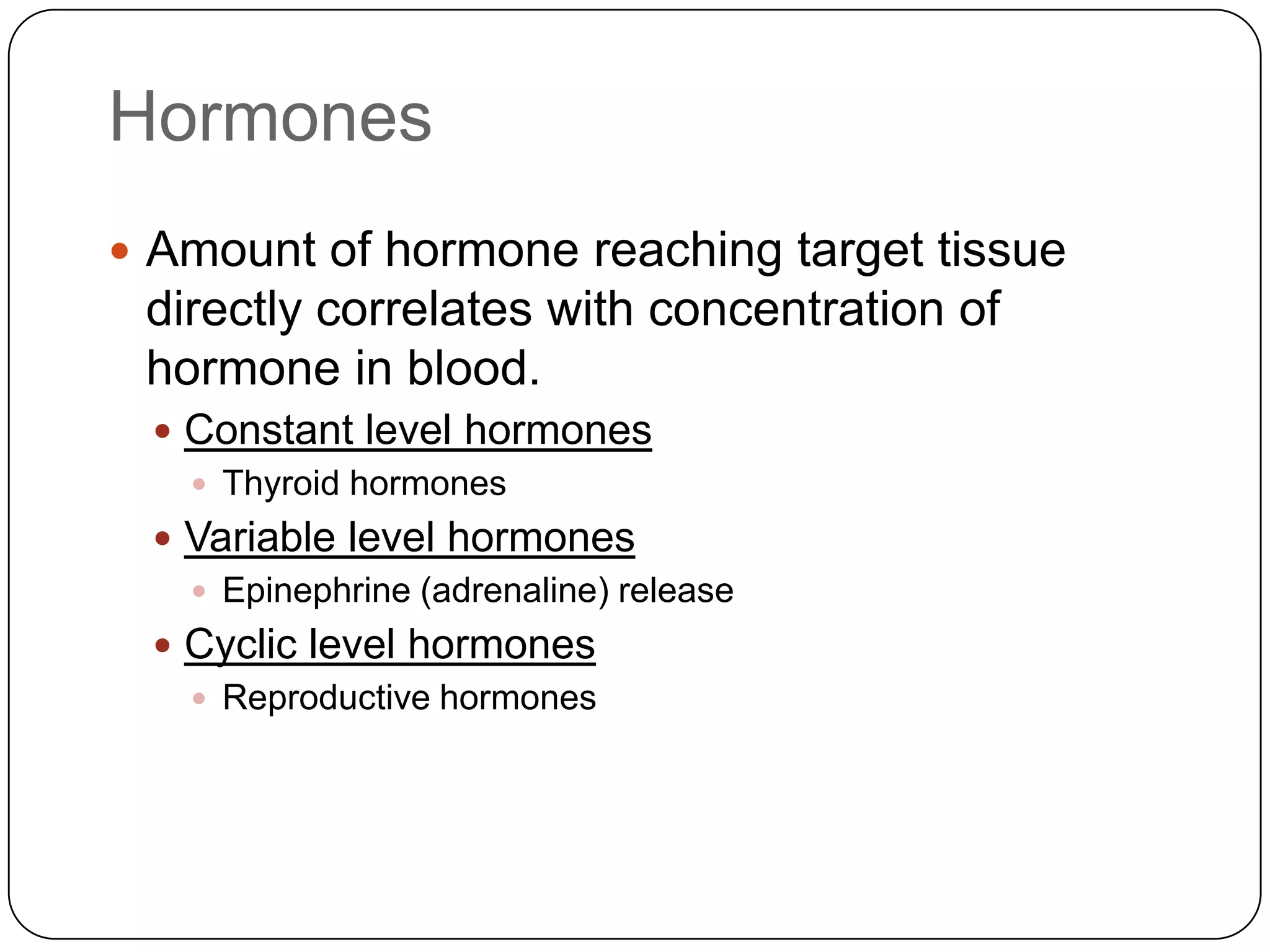
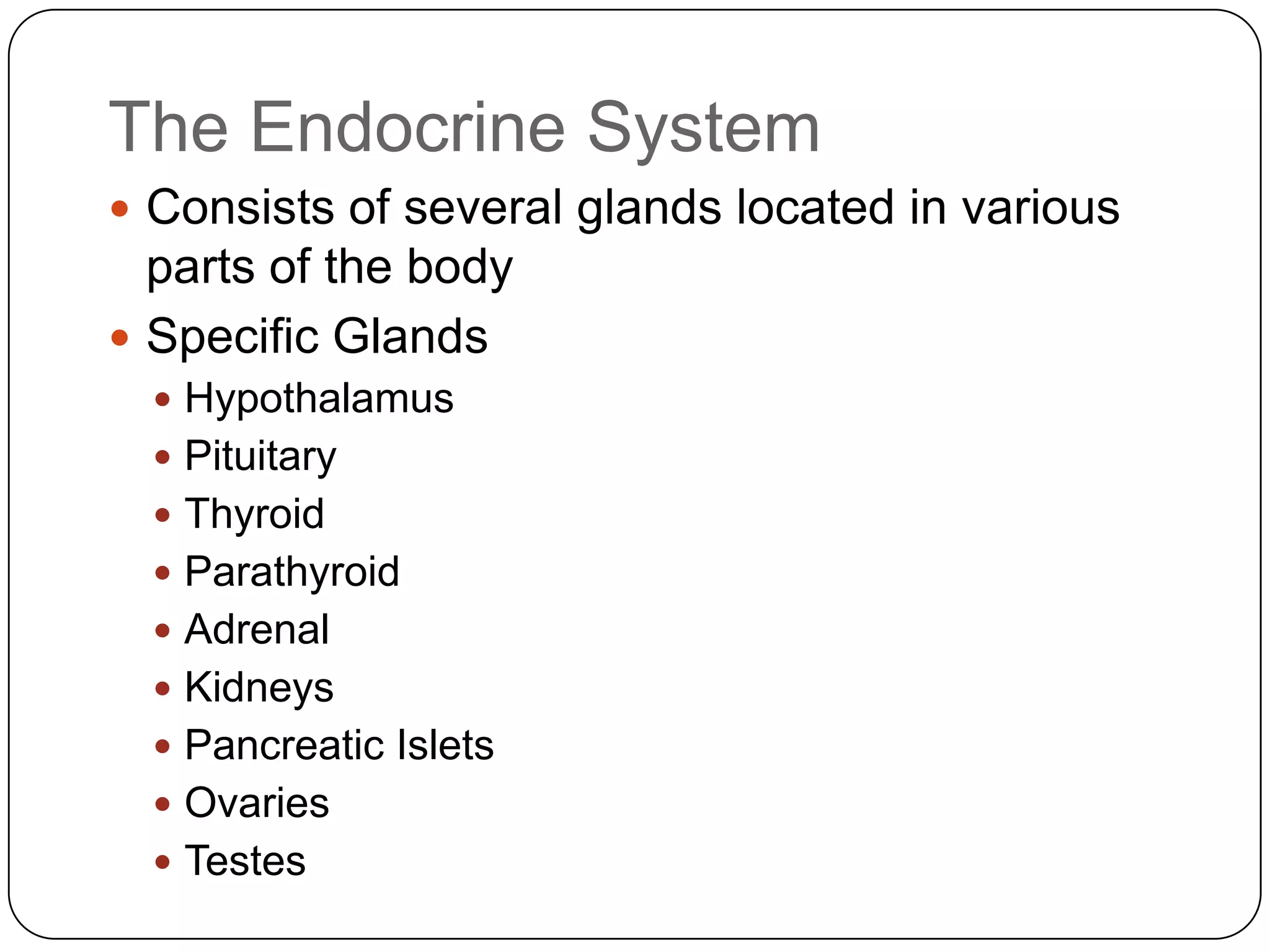
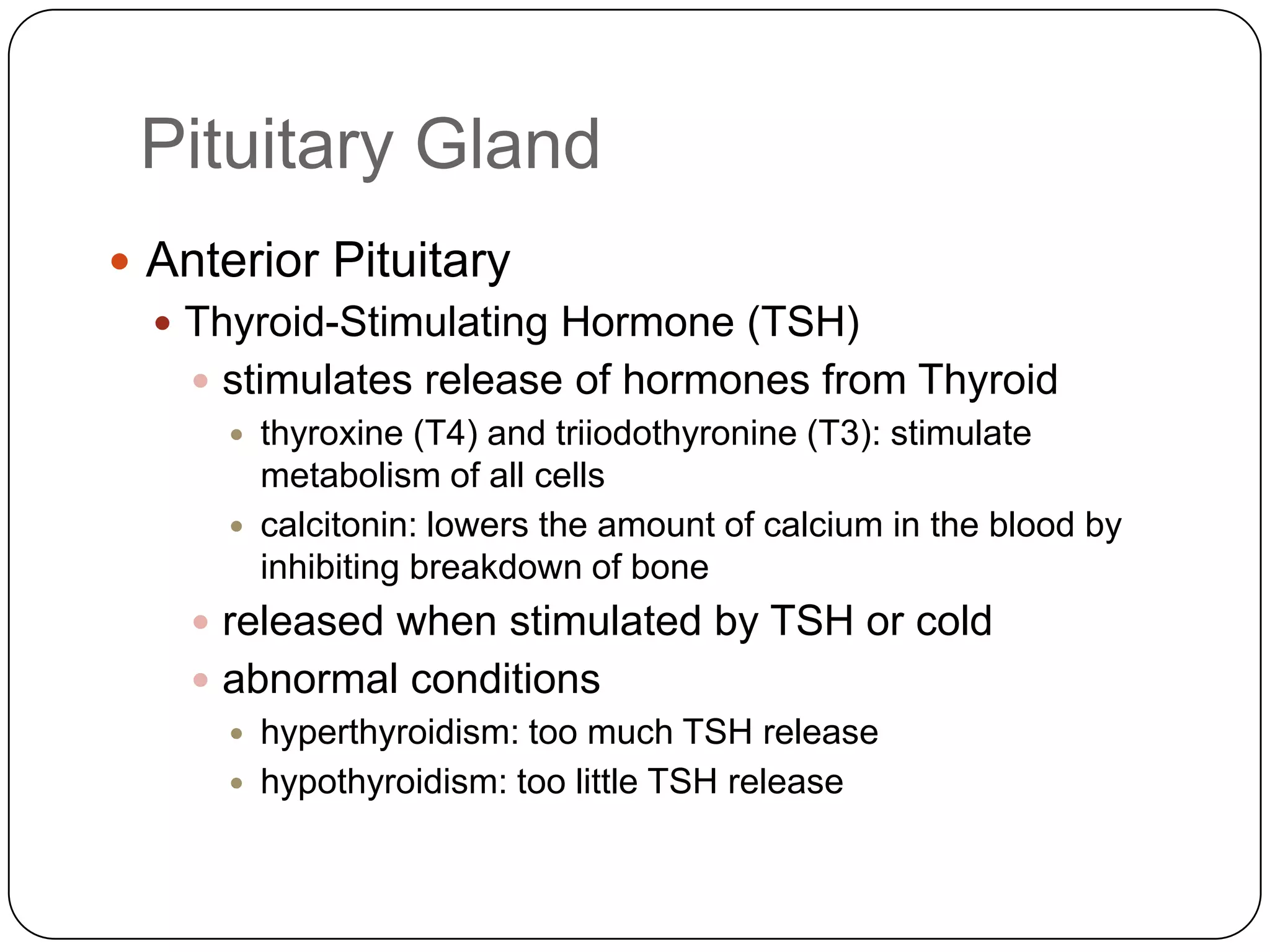
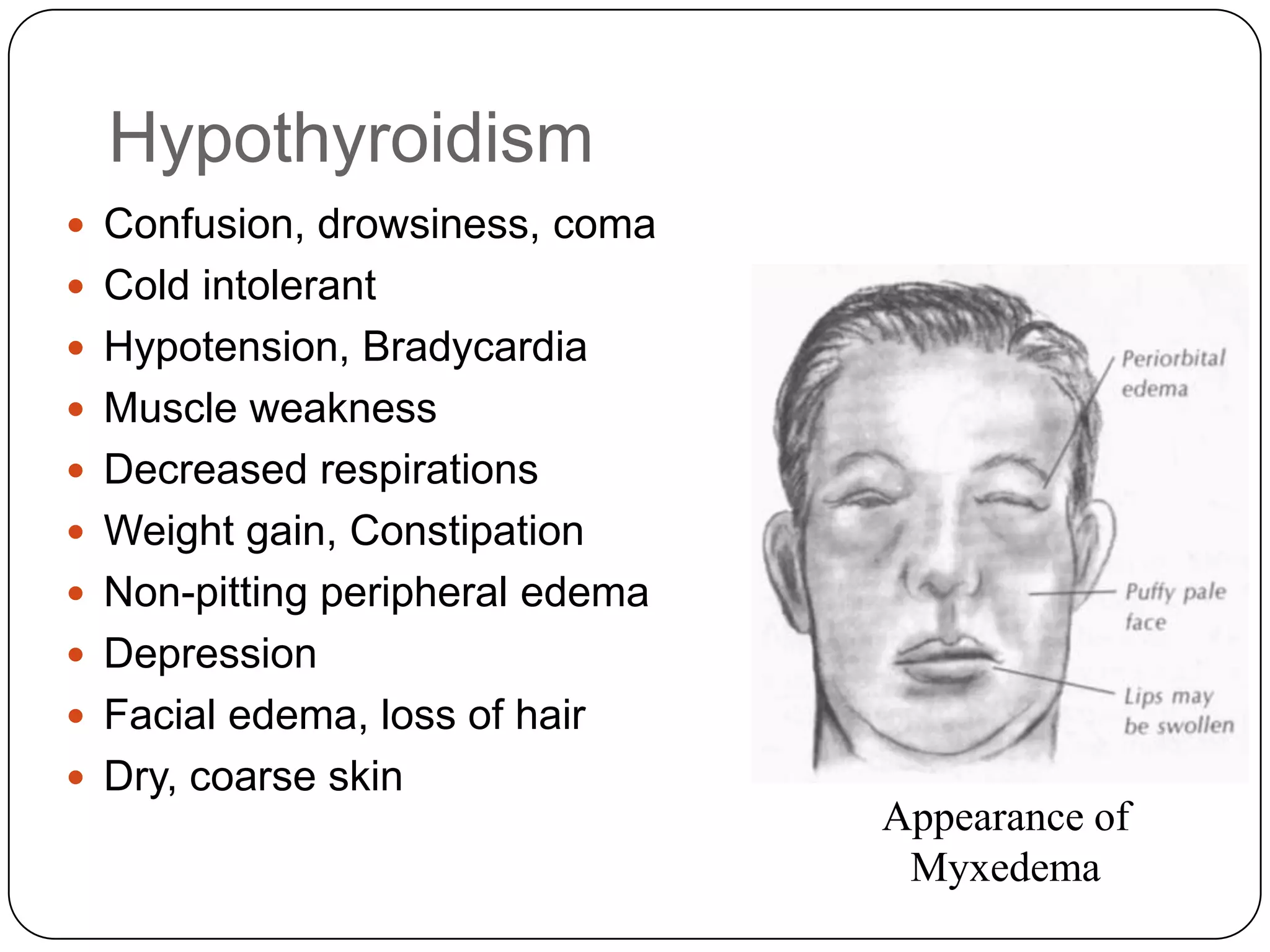
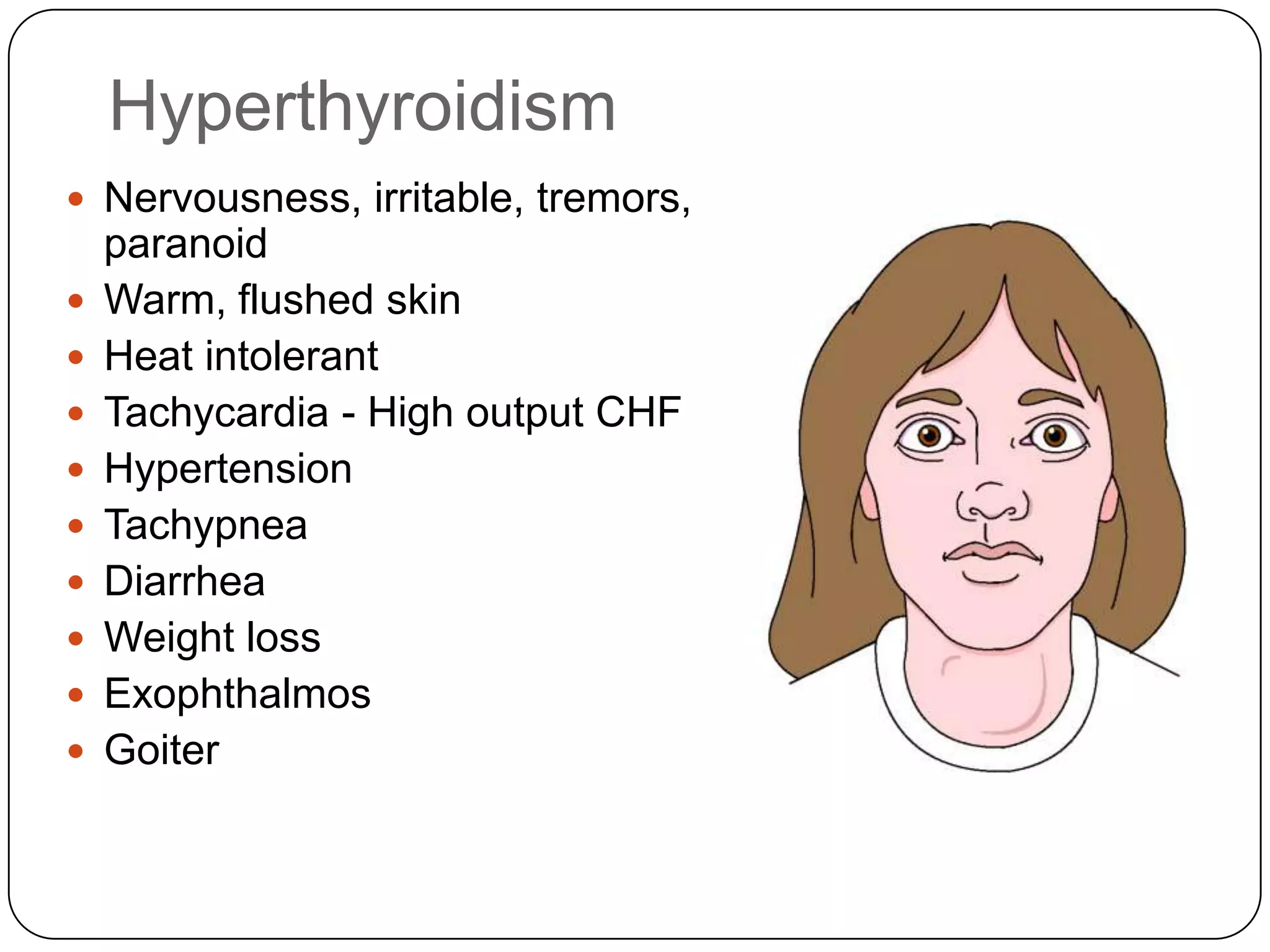
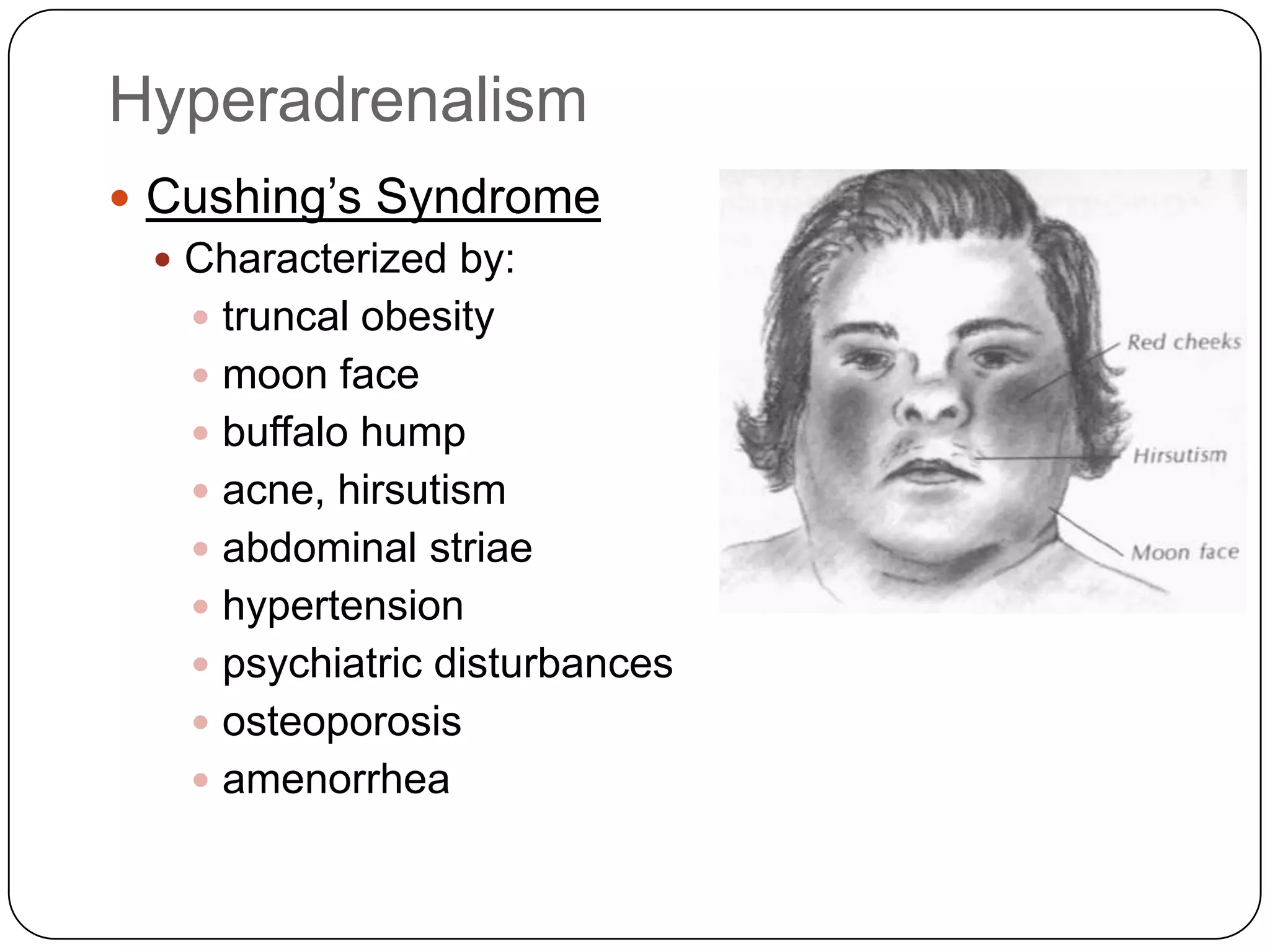
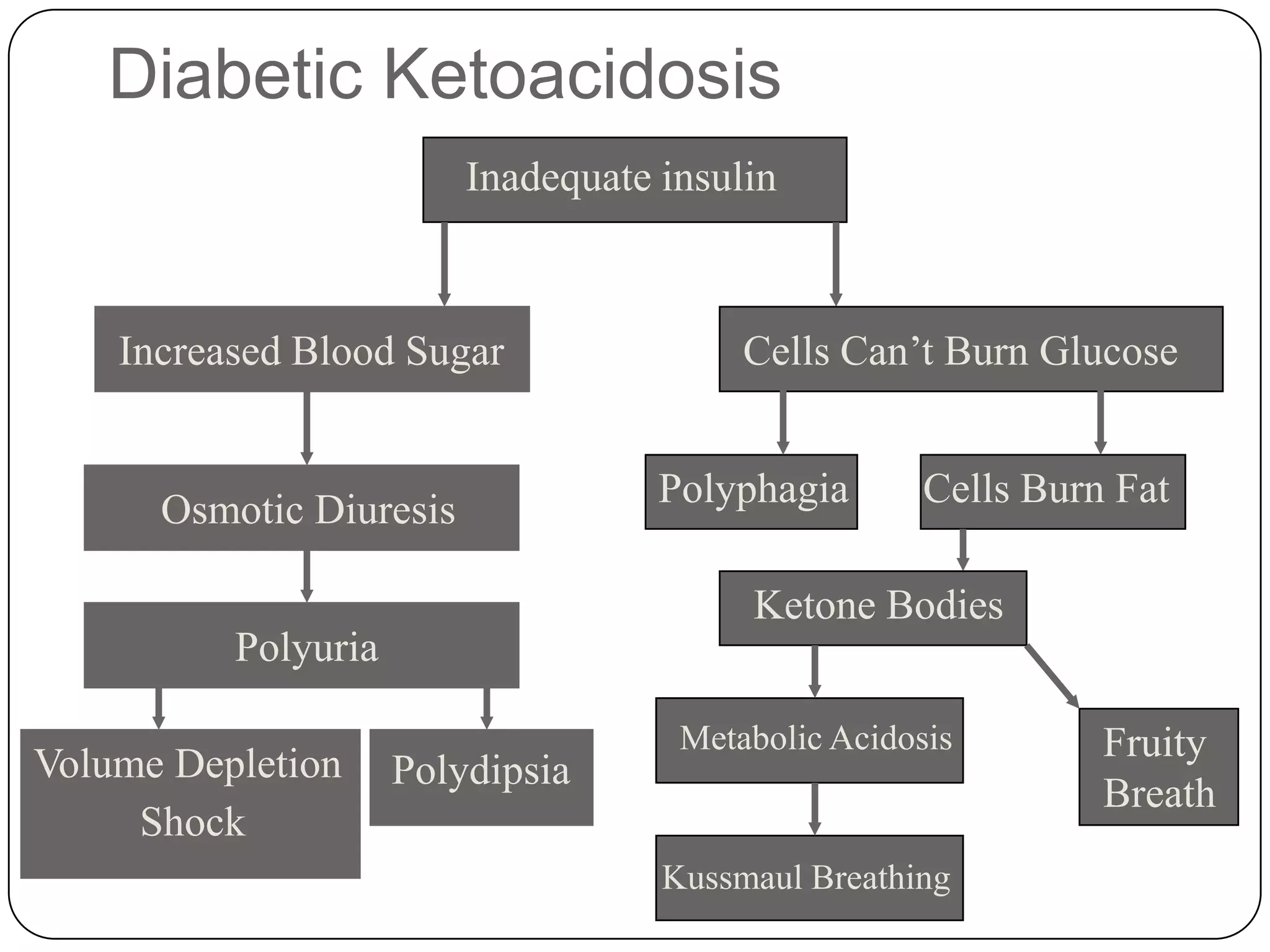
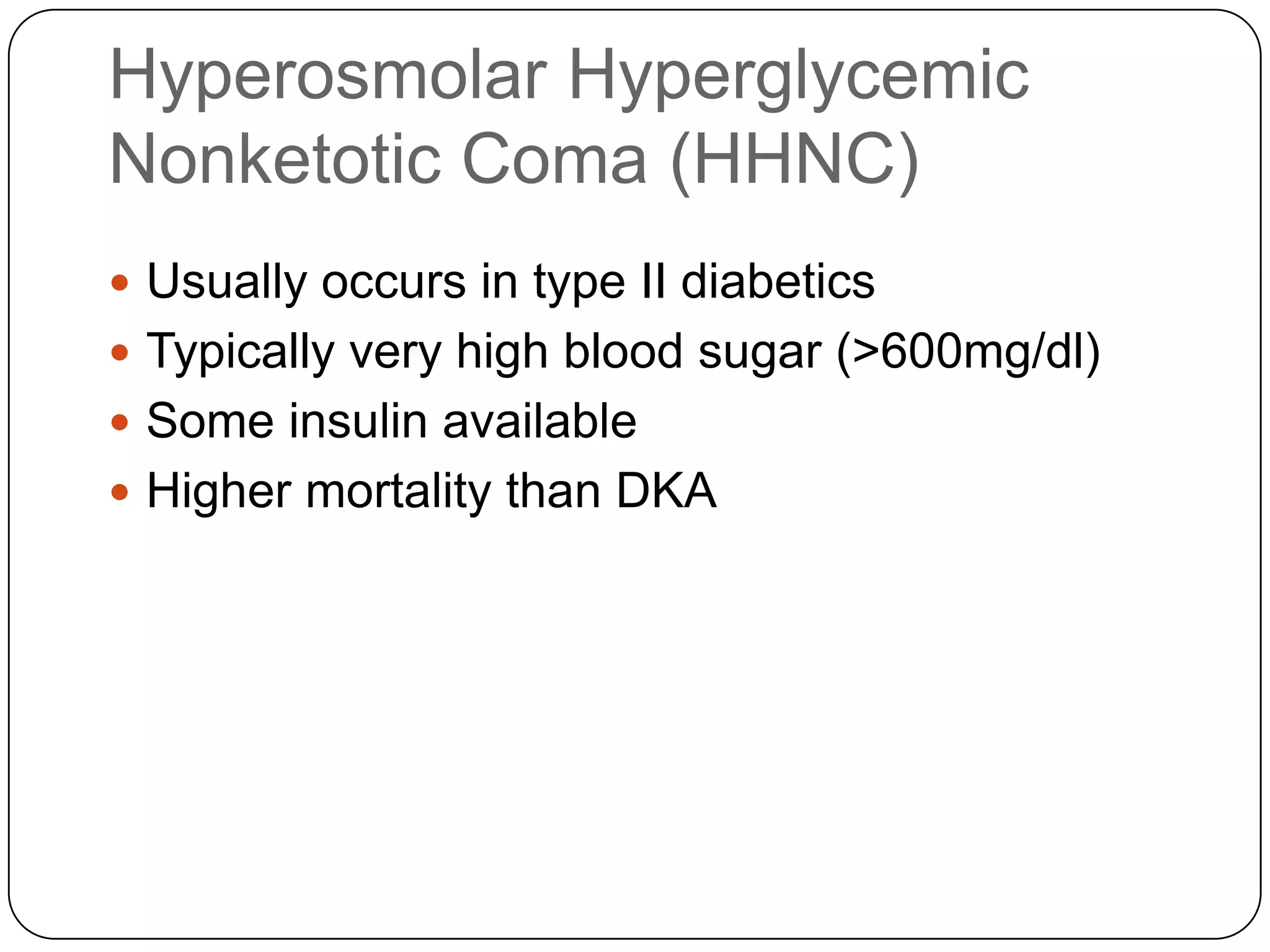
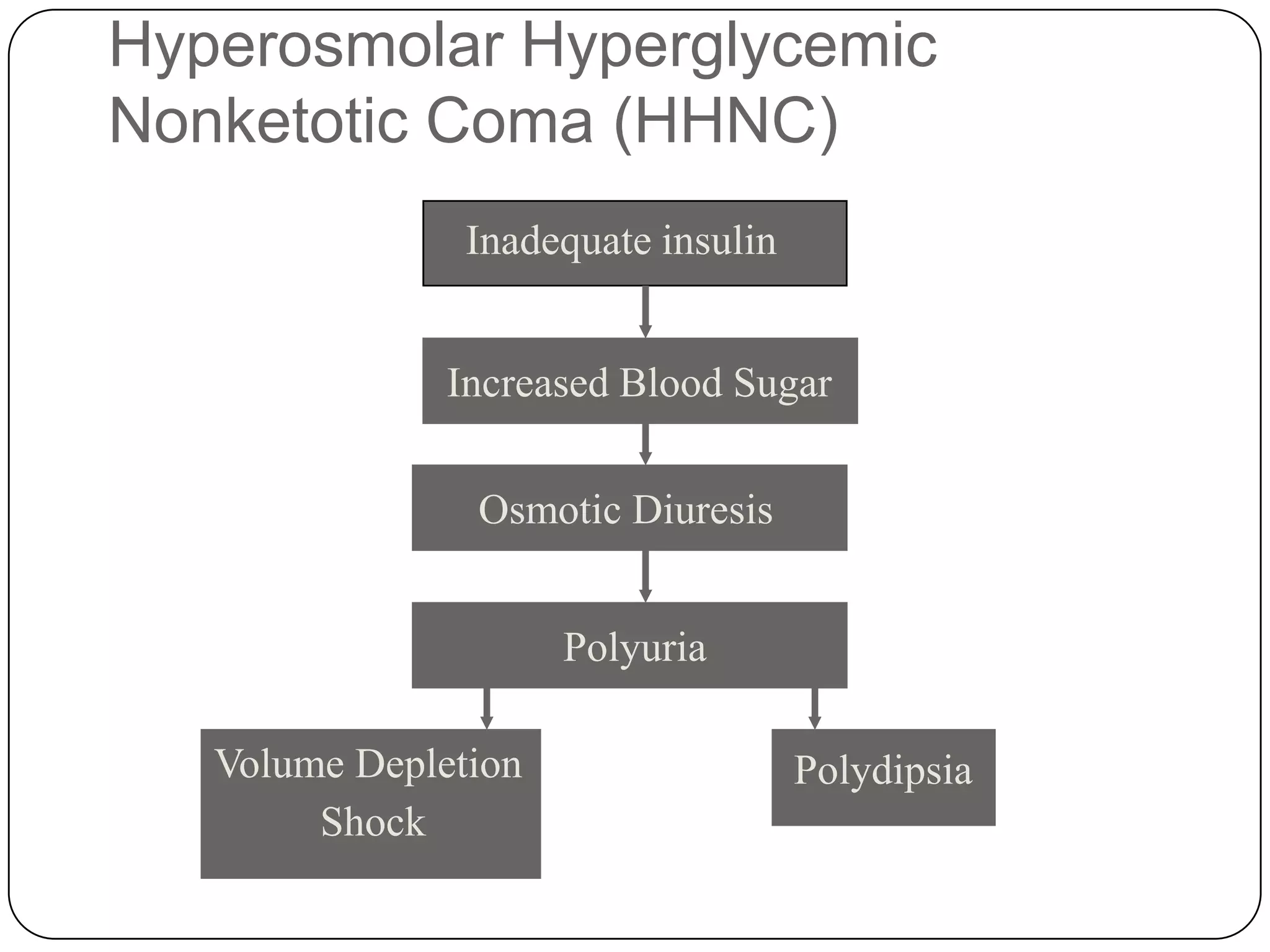
The endocrine system consists of glands that secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream to regulate distant target organs and tissues. The pituitary gland is called the "master gland" as it controls other endocrine glands by producing hormones that stimulate or inhibit their secretions. Disorders of the endocrine system can result from too little or too much hormone production and can have wide-ranging effects on the body if left untreated.

















































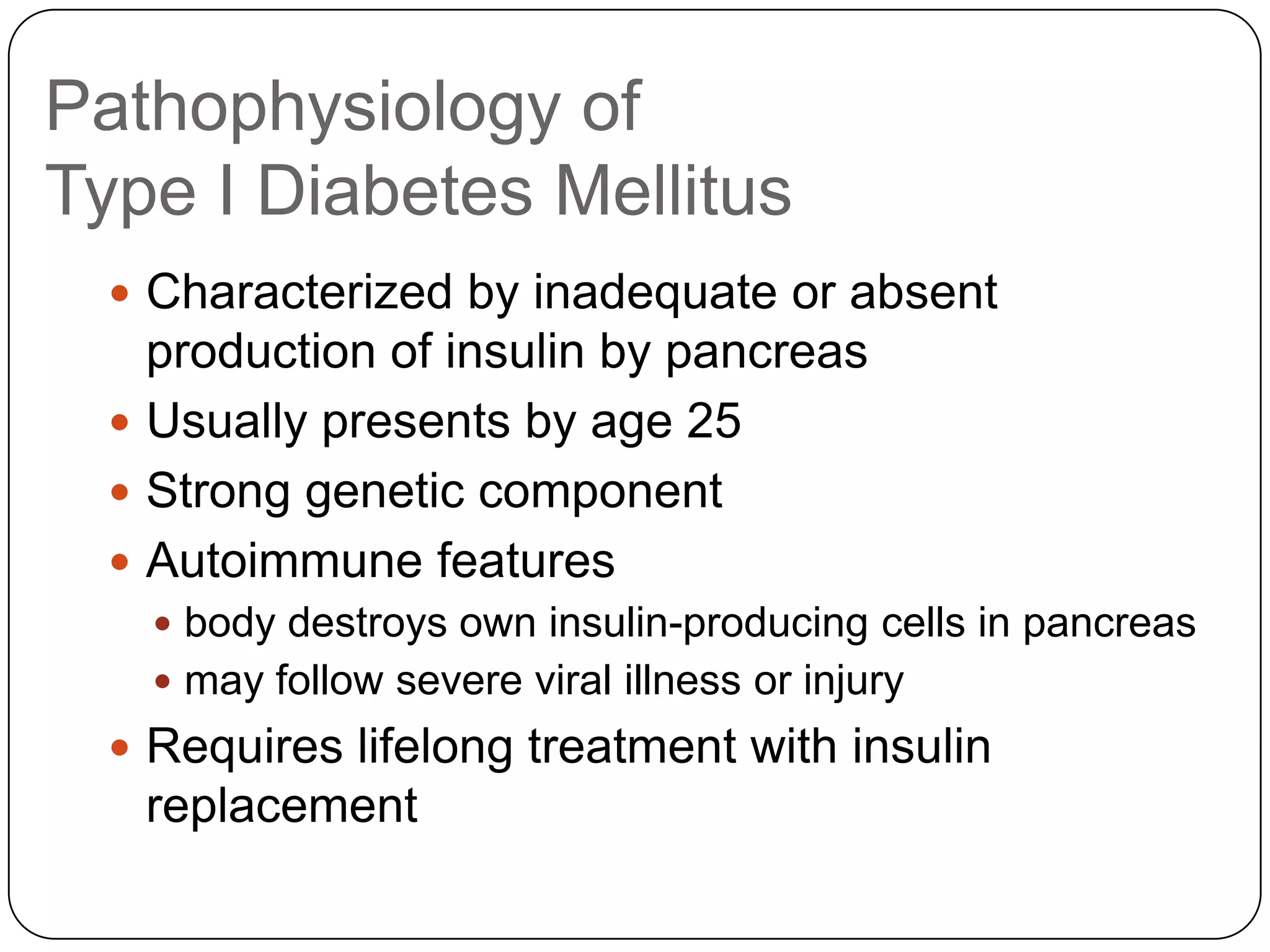
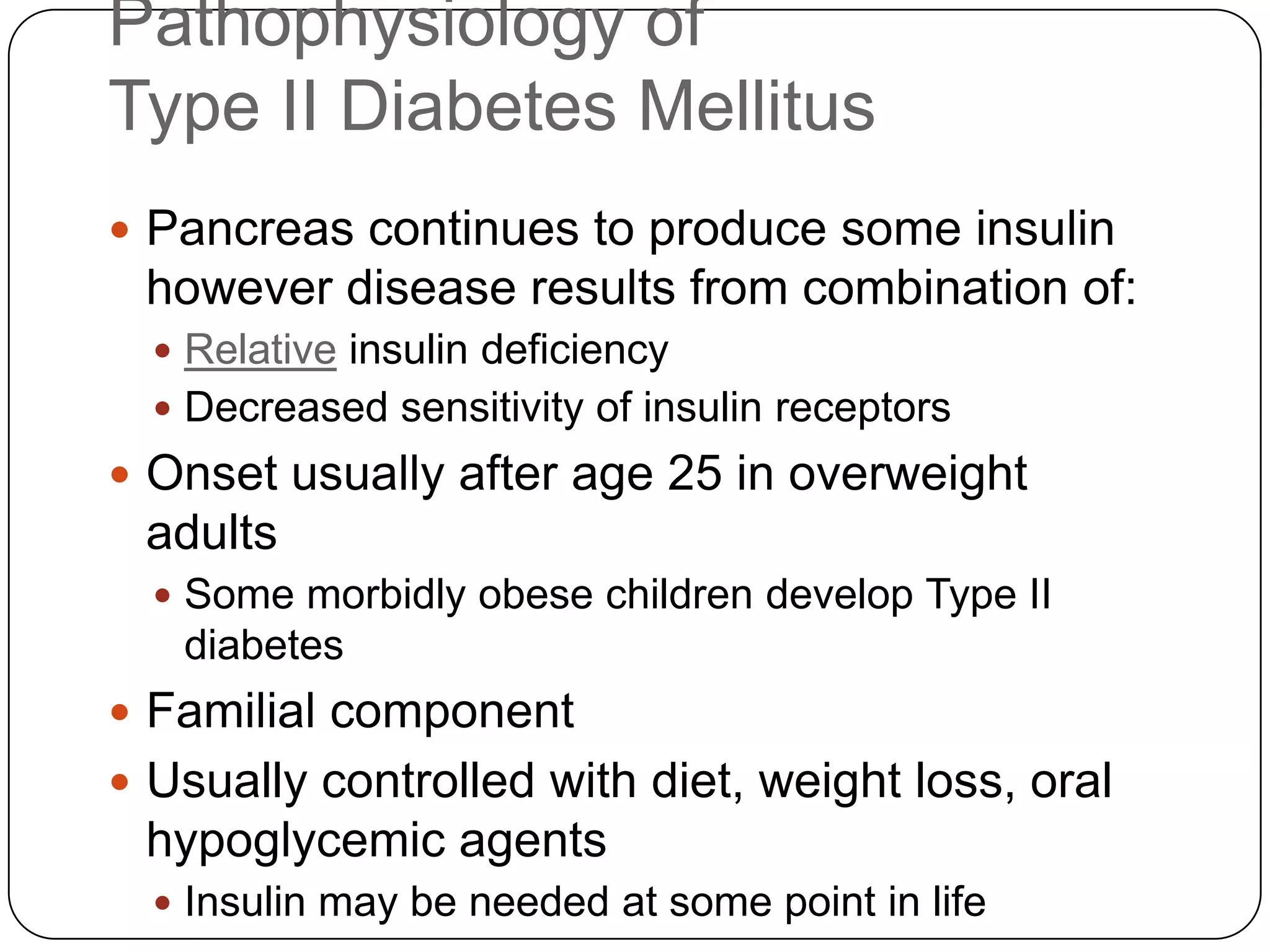



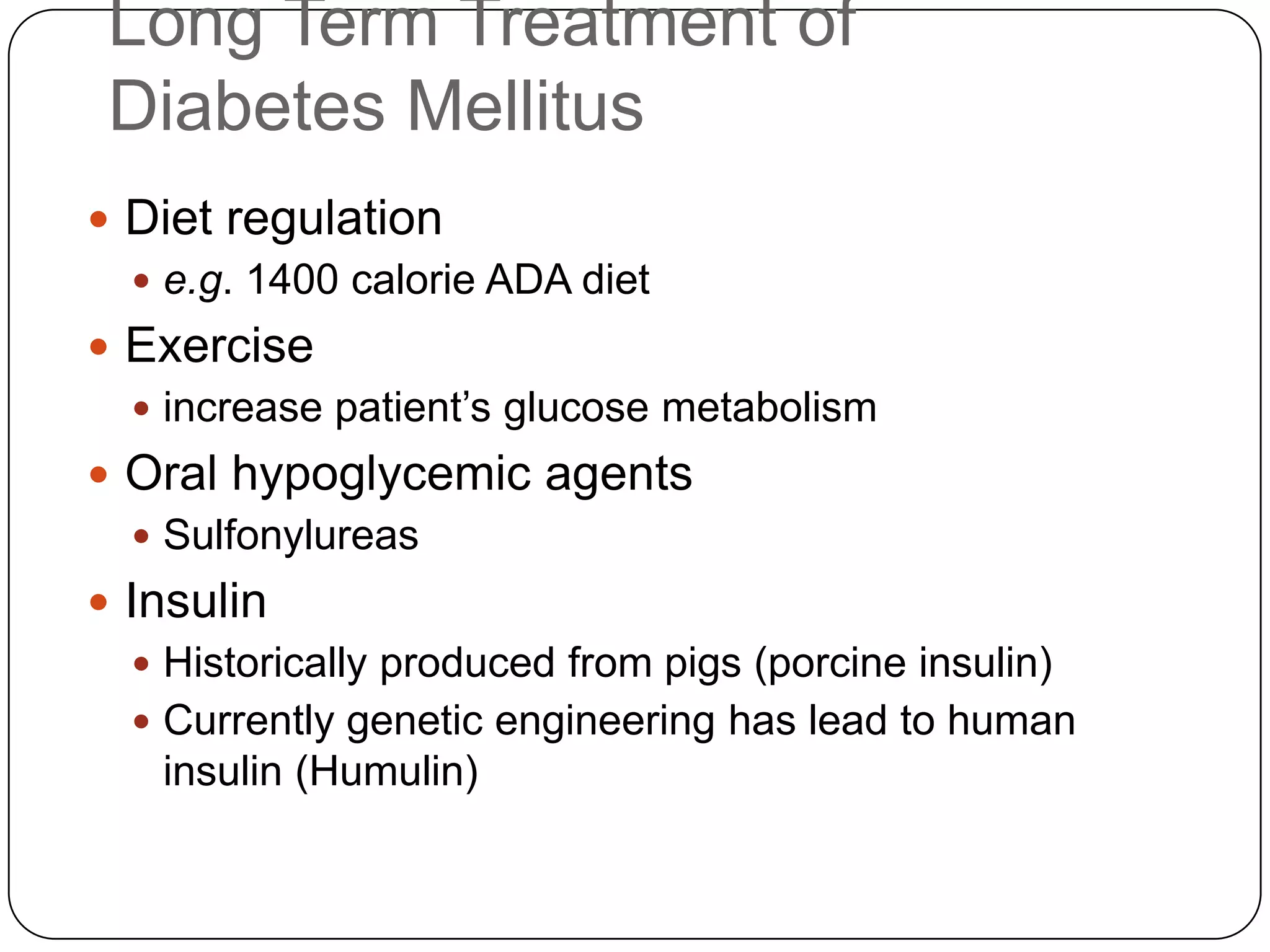
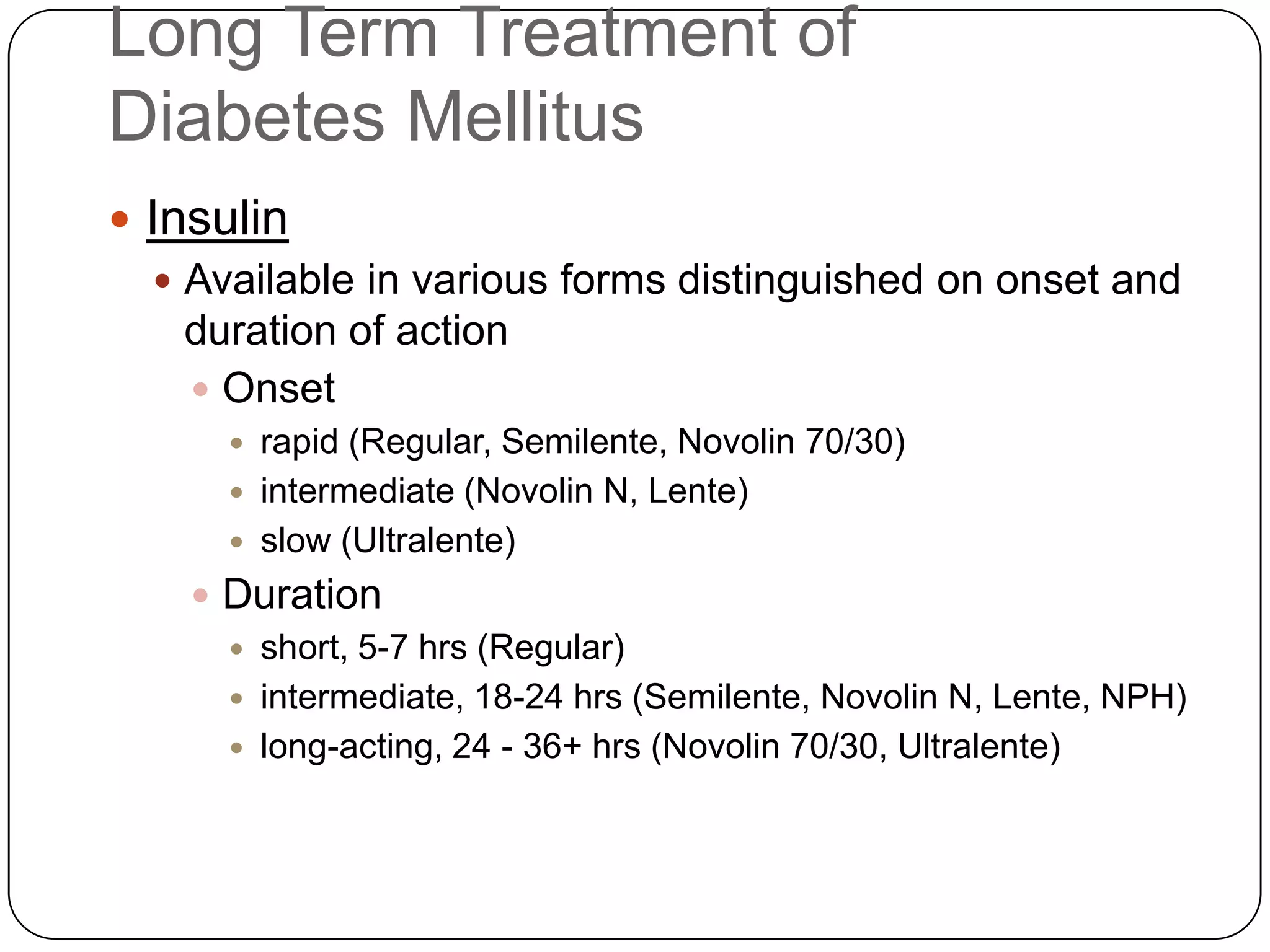

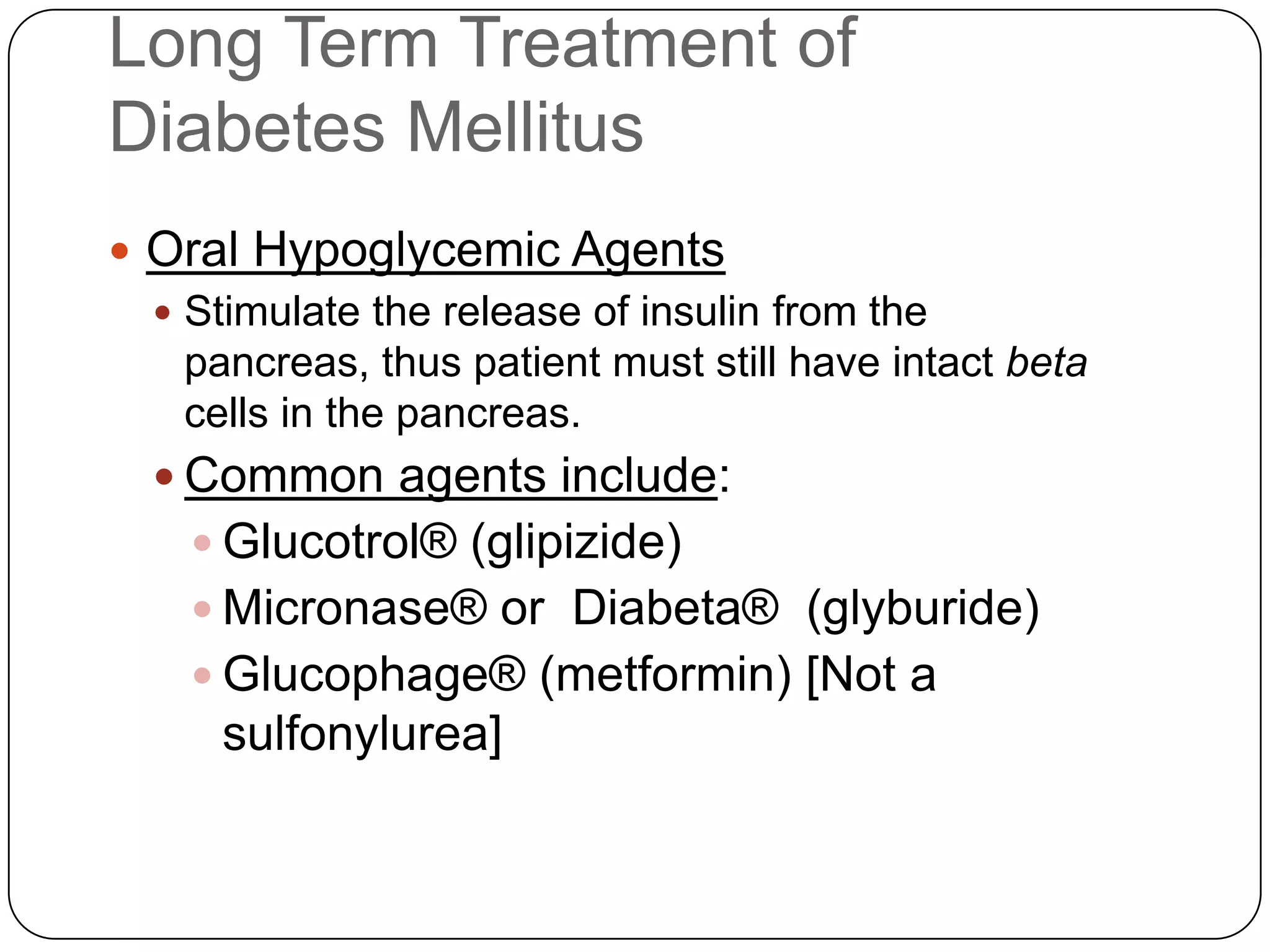
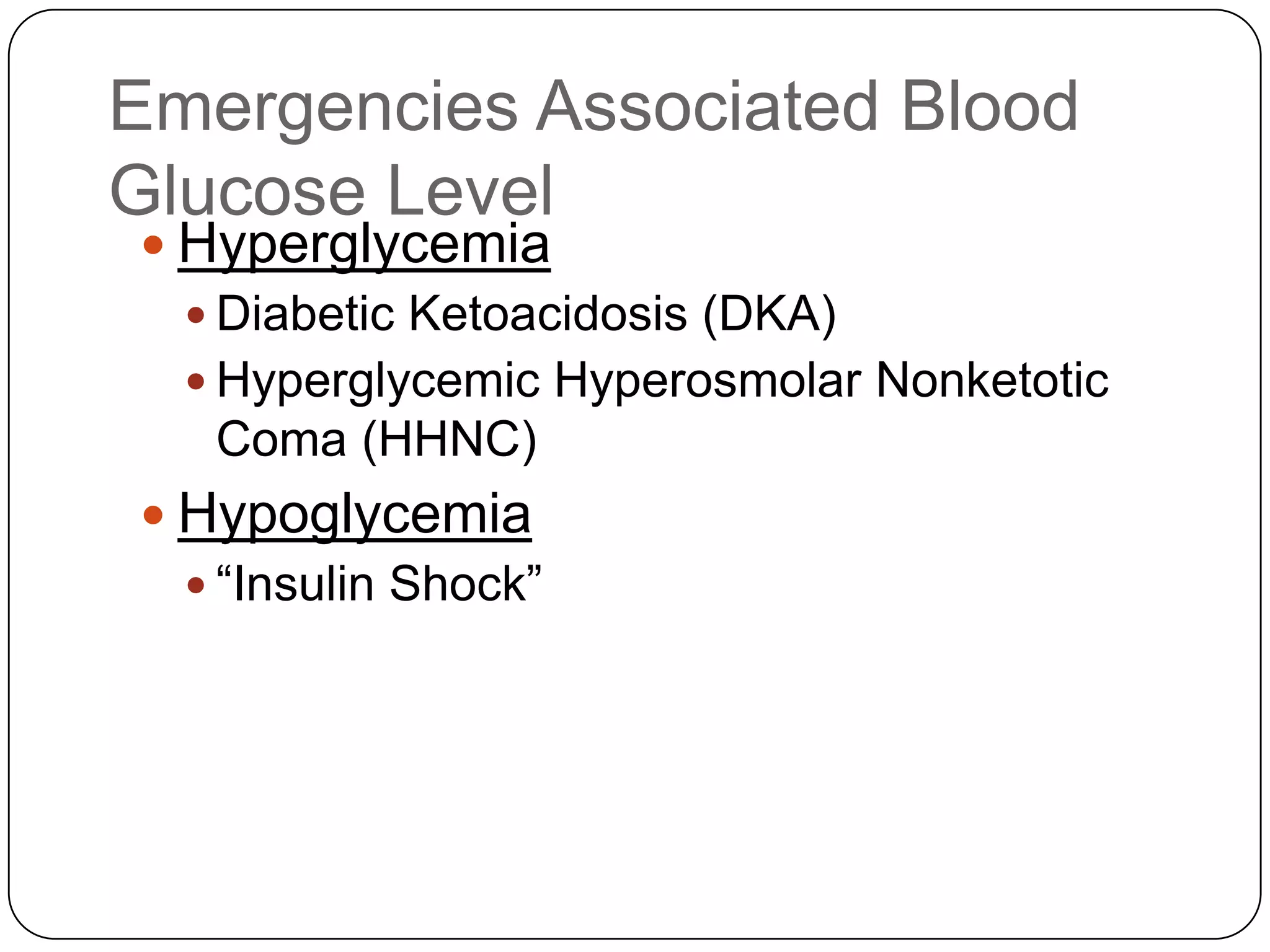





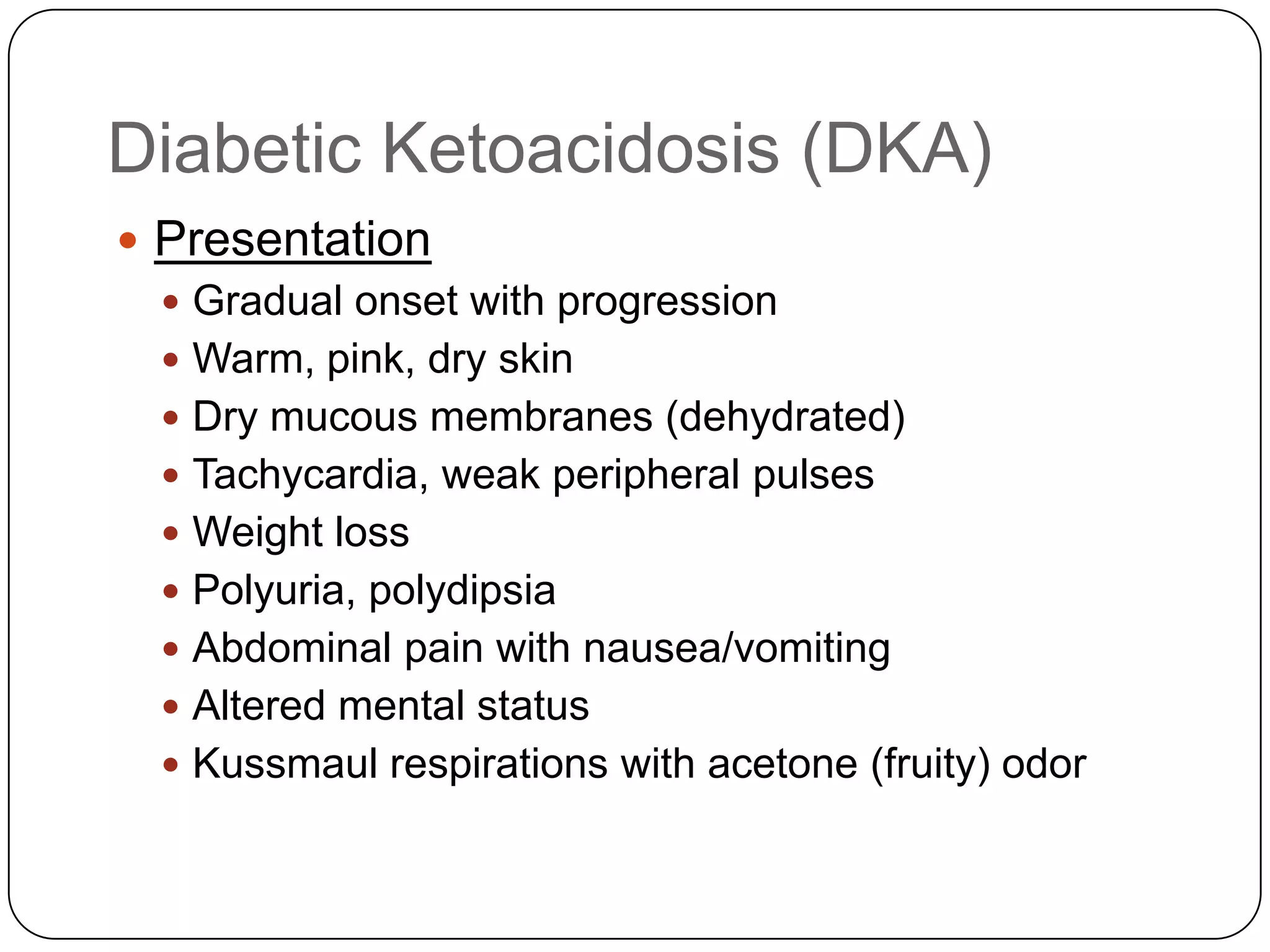


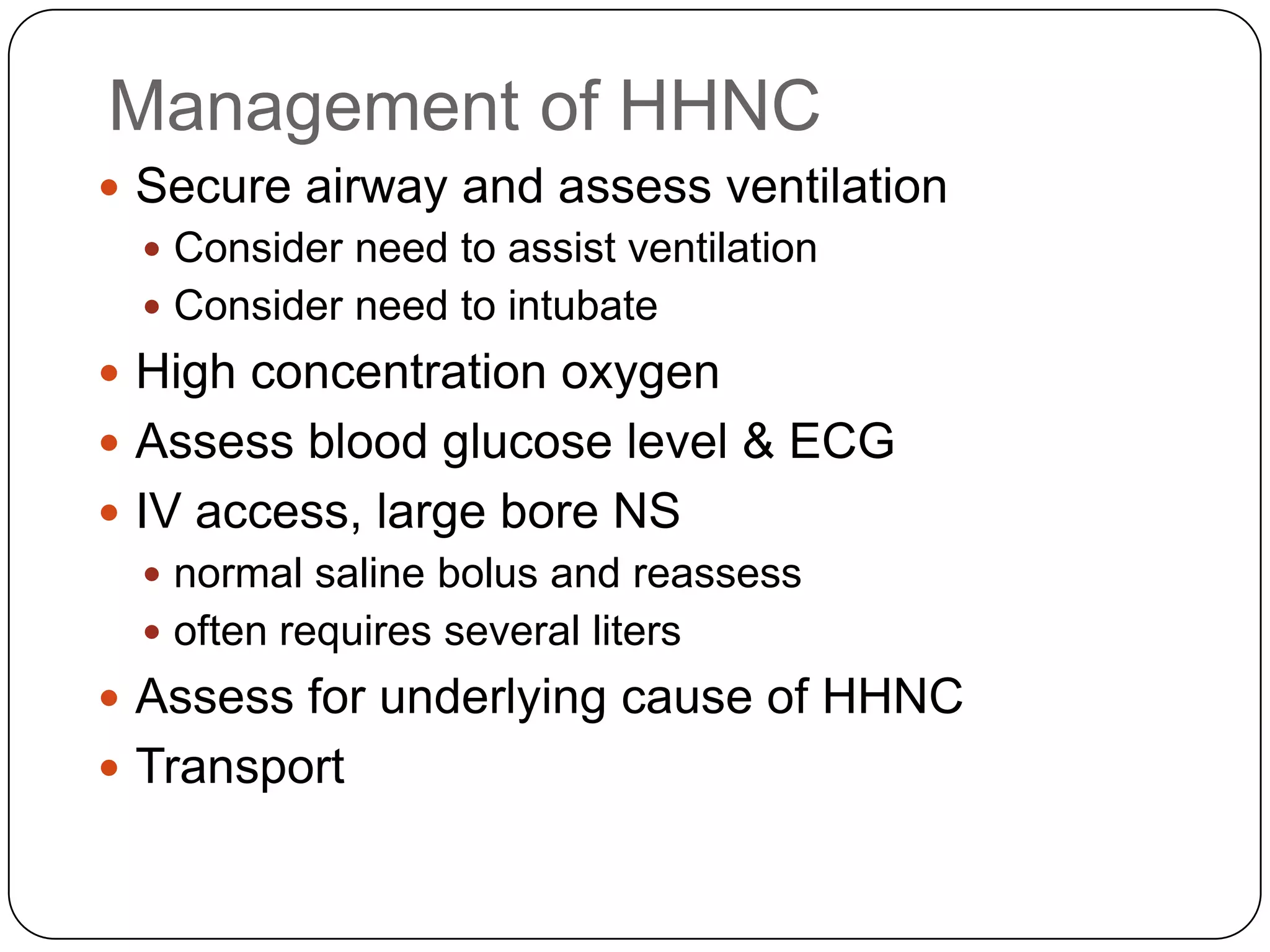
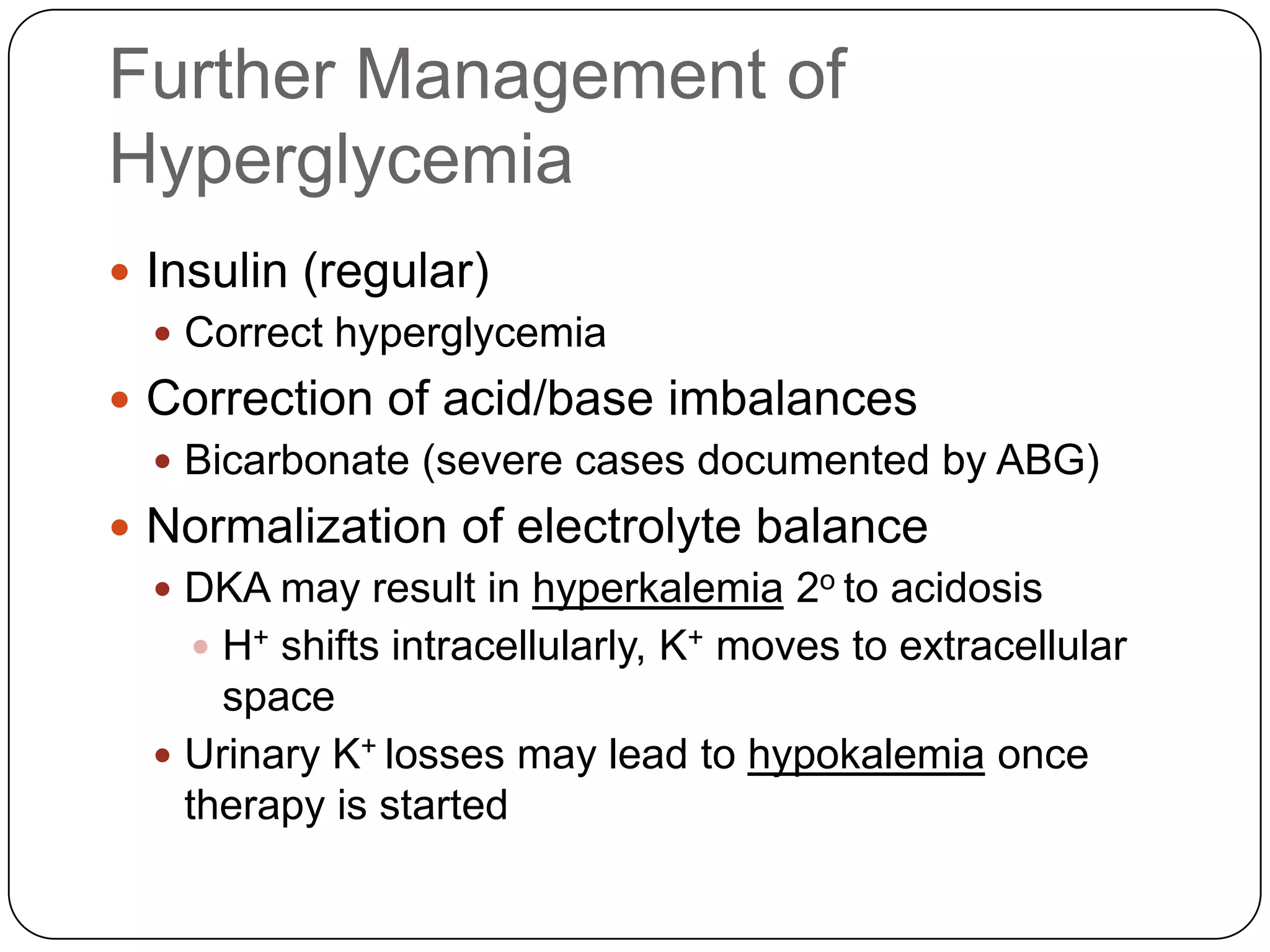
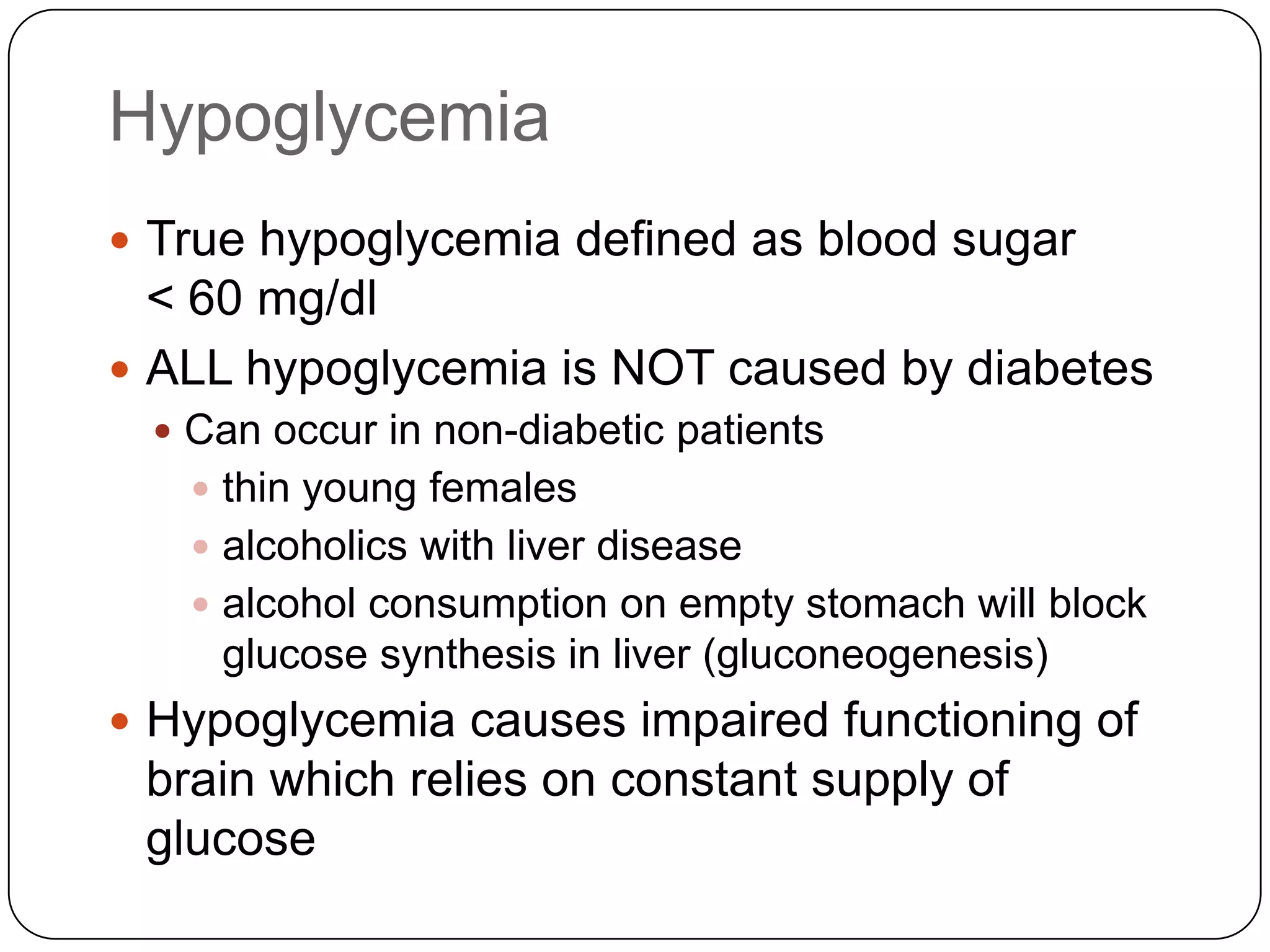

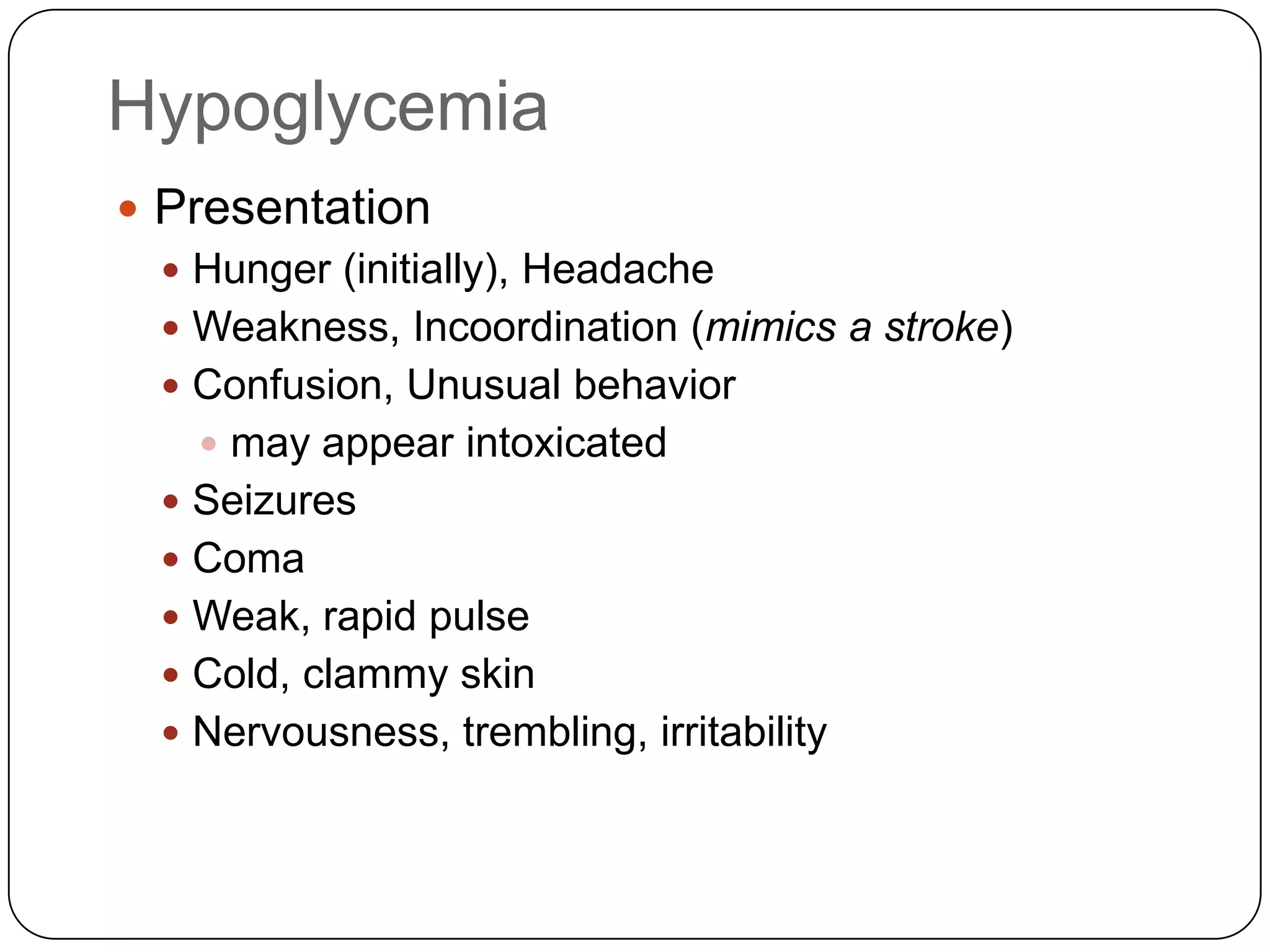



![Long Term Treatment of Diabetes MellitusOral Hypoglycemic AgentsStimulate the release of insulin from the pancreas, thus patient must still have intact beta cells in the pancreas.Common agents include:Glucotrol® (glipizide)Micronase® or Diabeta® (glyburide)Glucophage® (metformin) [Not a sulfonylurea]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/endocrinebasicandadvancedbydrashvinijakhar-110801074921-phpapp02/75/Endocrine-basic-and-advanced-by-dr-ashvini-jakhar-114-2048.jpg)



