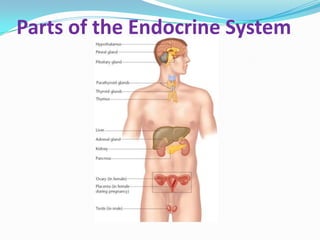
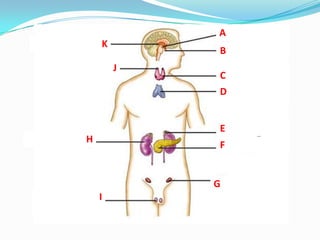
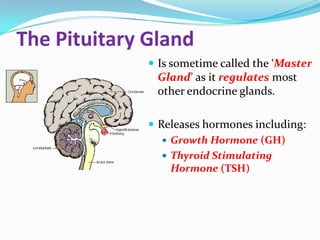
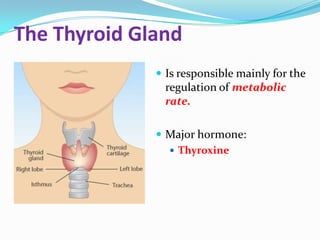
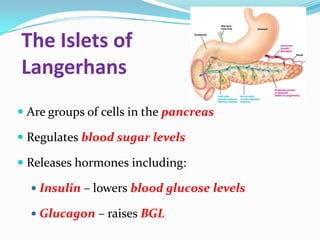
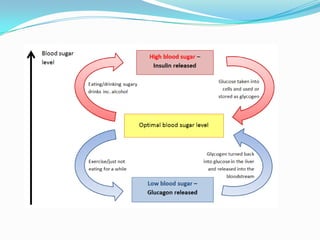
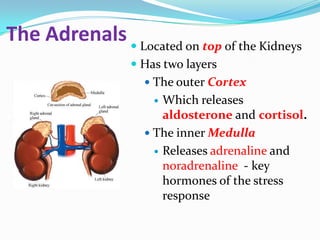
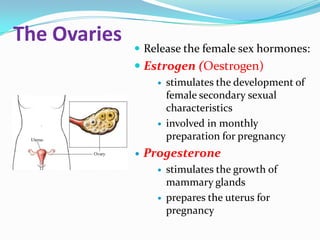
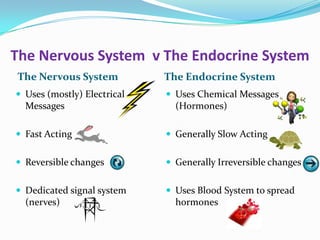
The endocrine system consists of glands that produce hormones, chemical messengers released into the bloodstream. Hormones cause slow, long-term, and often irreversible changes related to growth and reproduction. Key glands include the pituitary, thyroid, pancreas, adrenals, ovaries, and testes, each releasing important hormones like growth hormone, thyroxine, insulin, estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone. The endocrine system differs from the nervous system in using chemical signals instead of electrical ones, causing generally slower but often irreversible changes throughout the body.