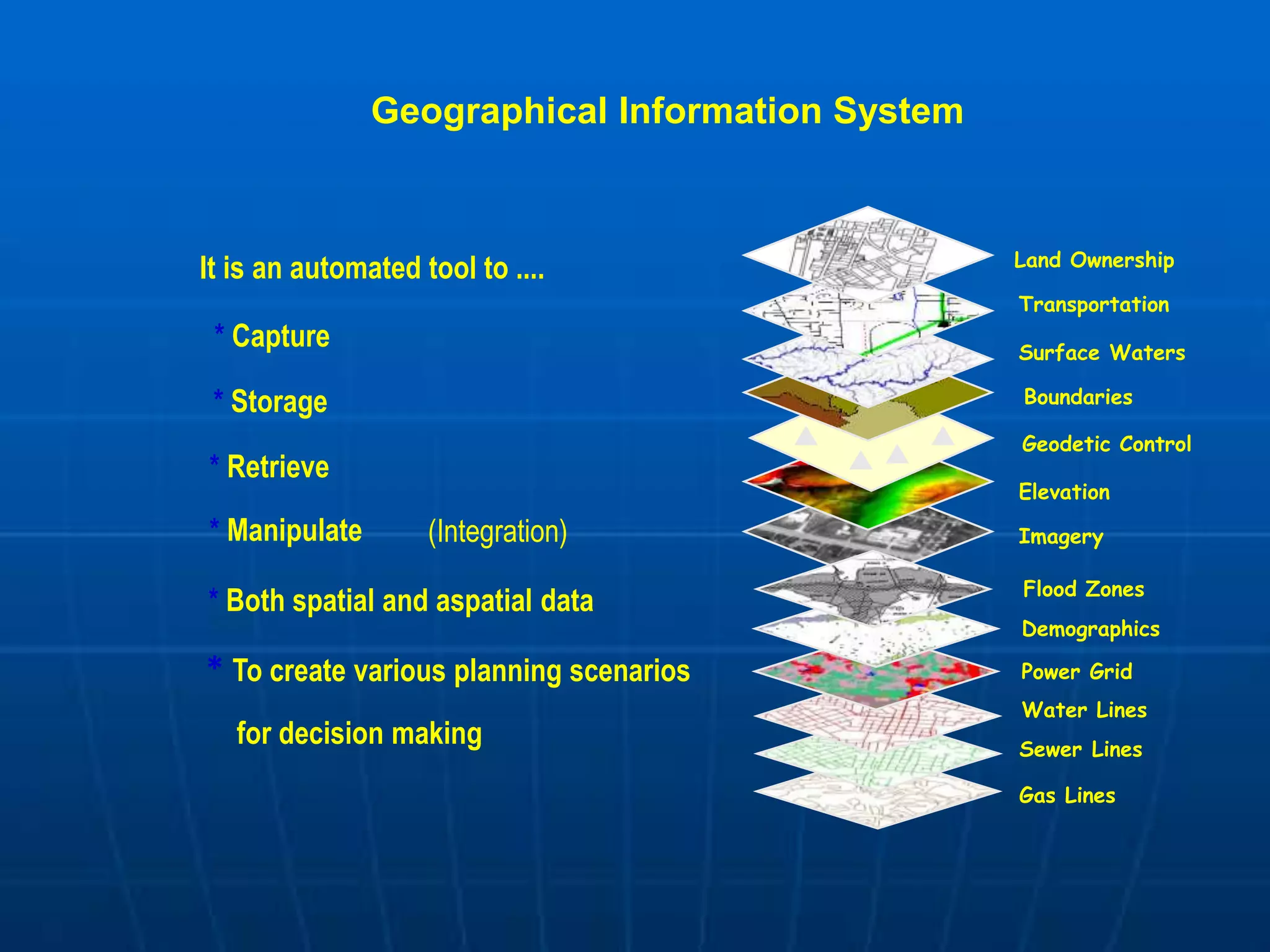
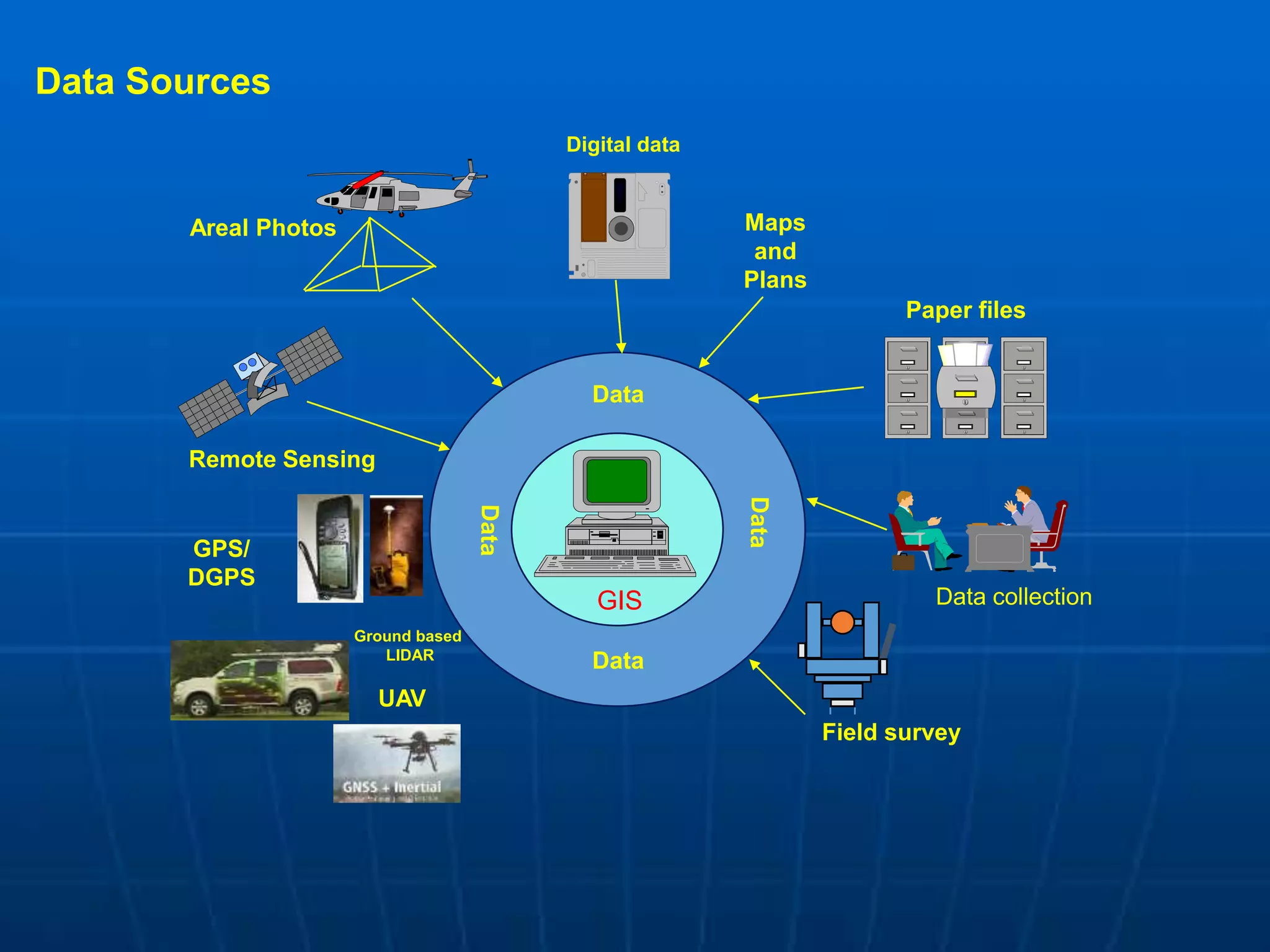
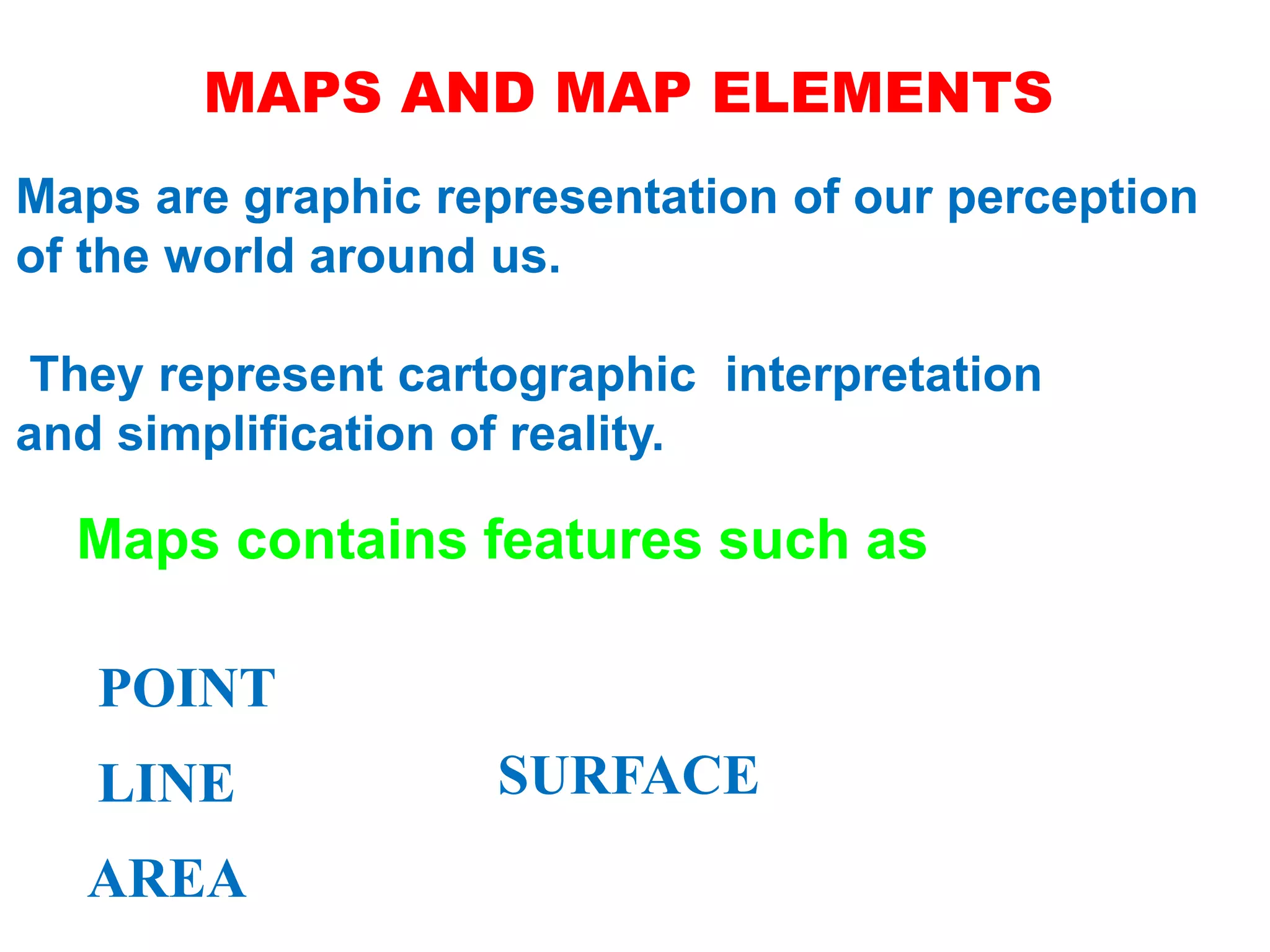
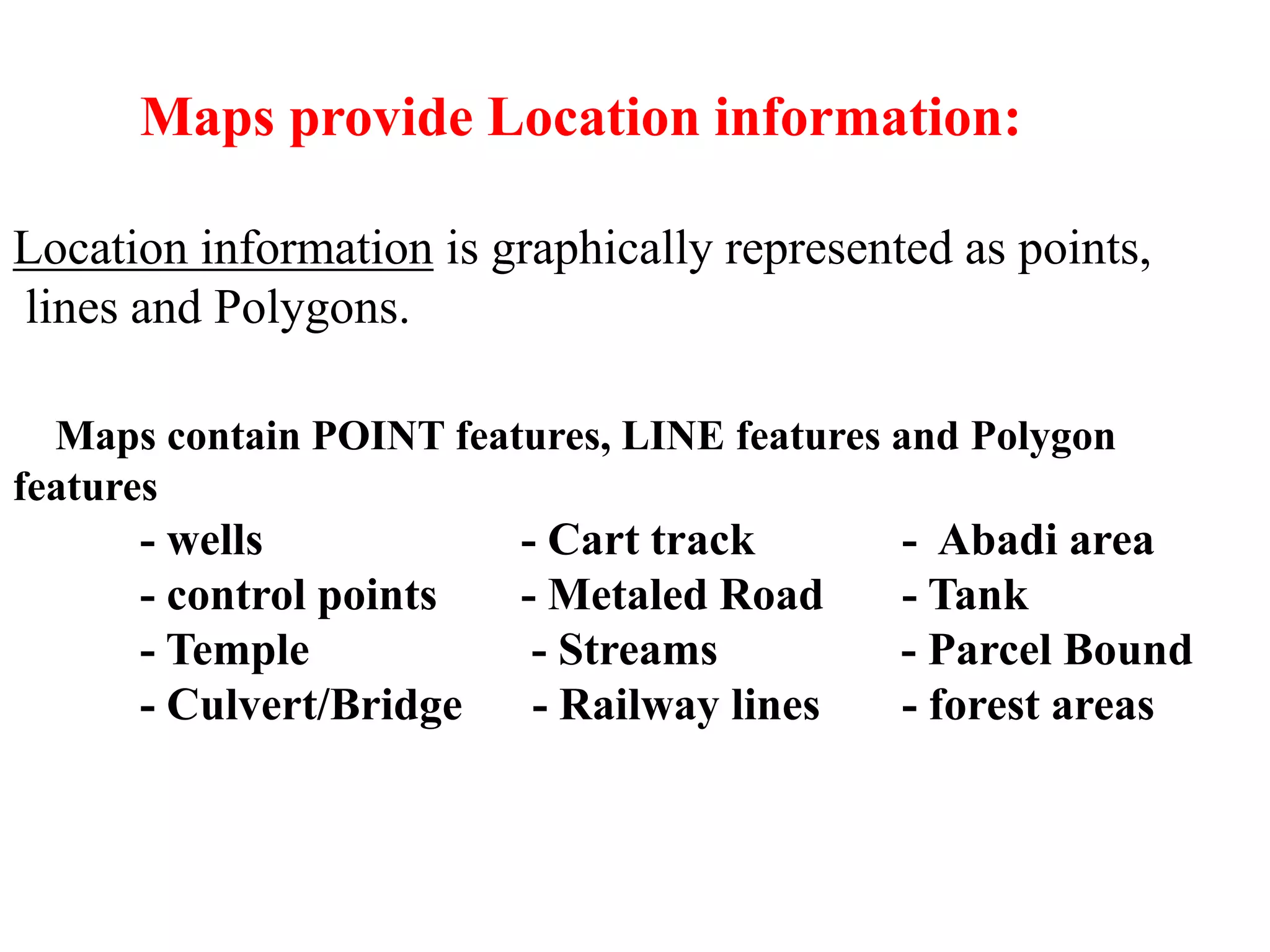
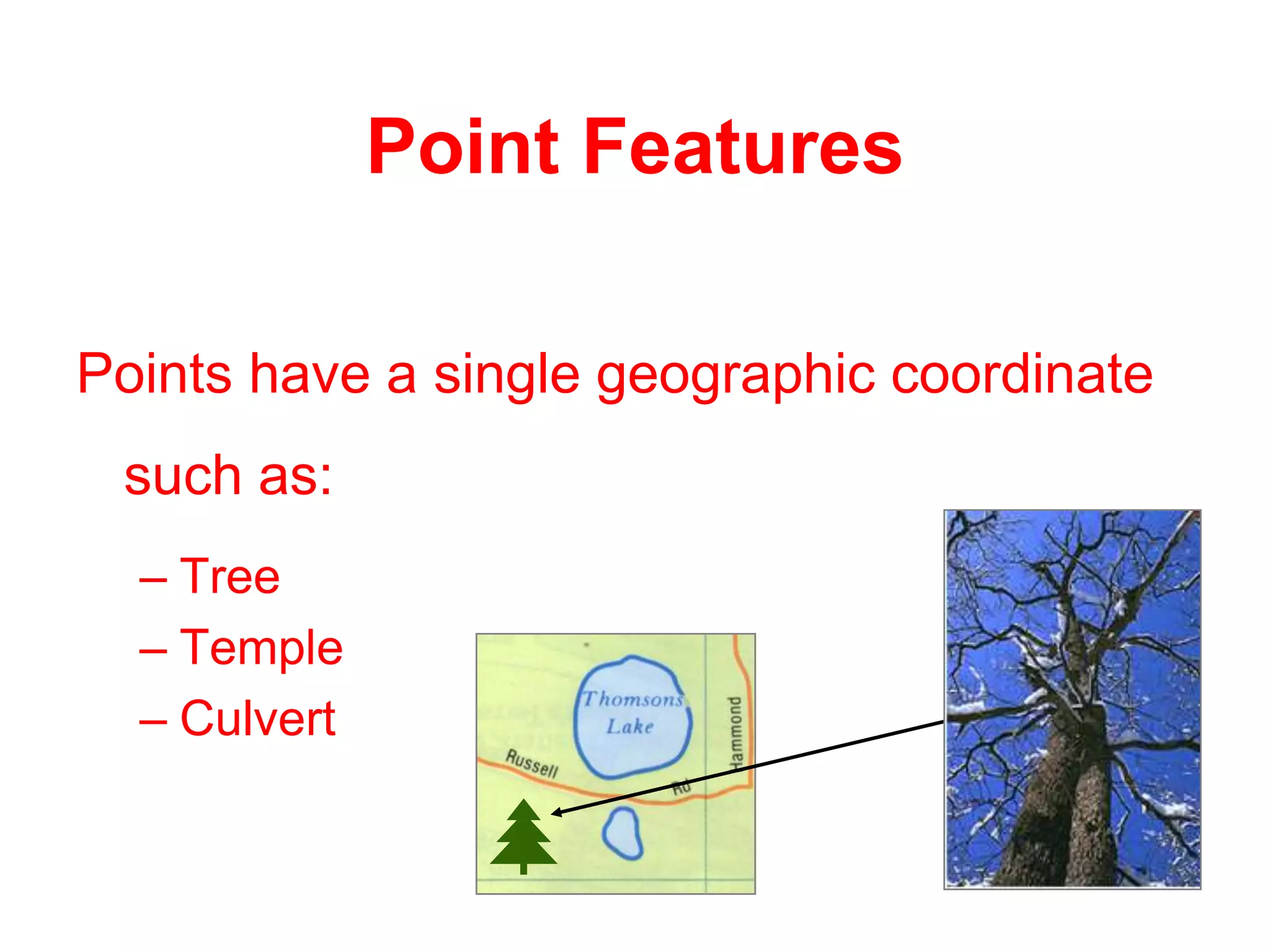
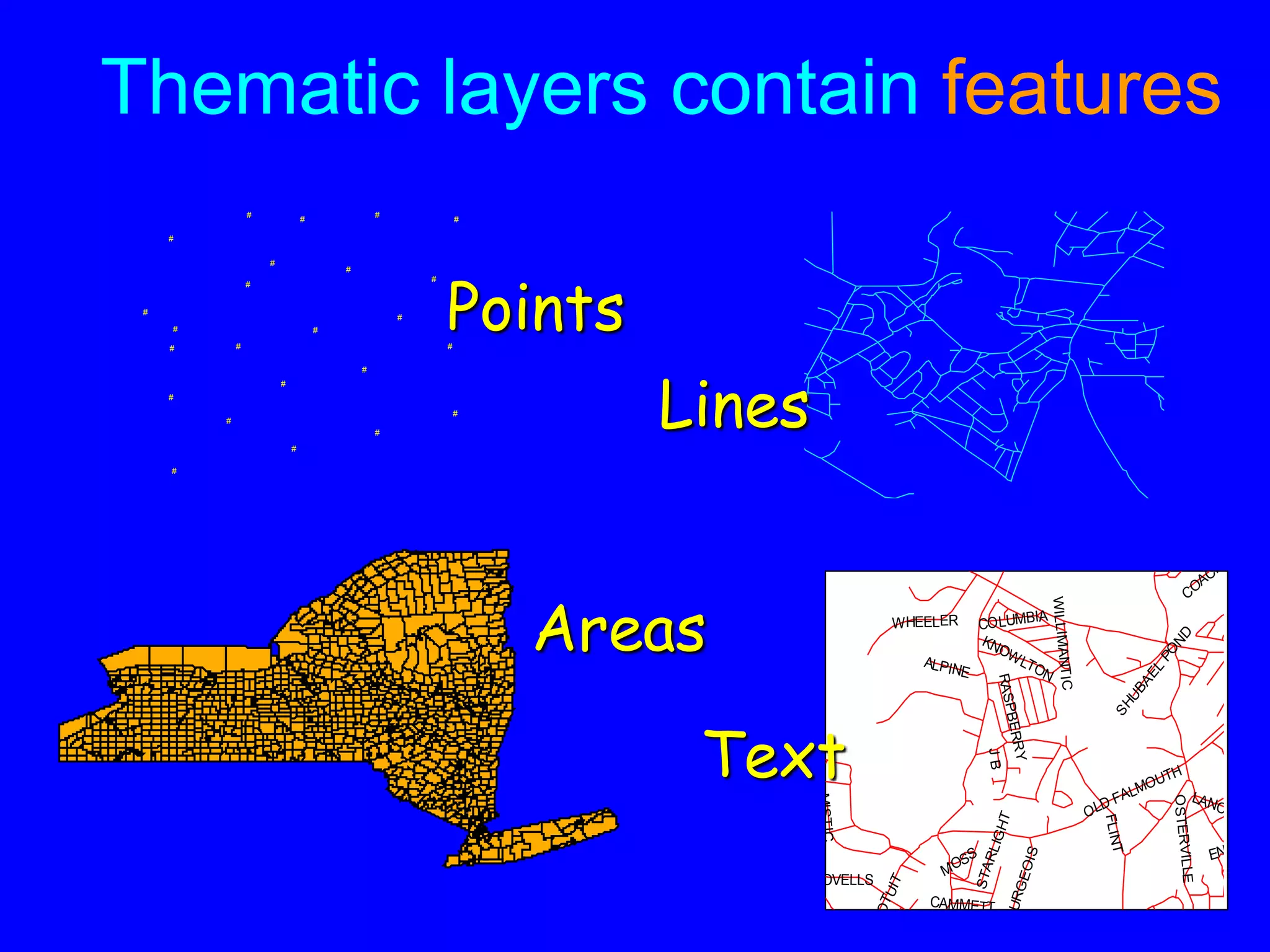
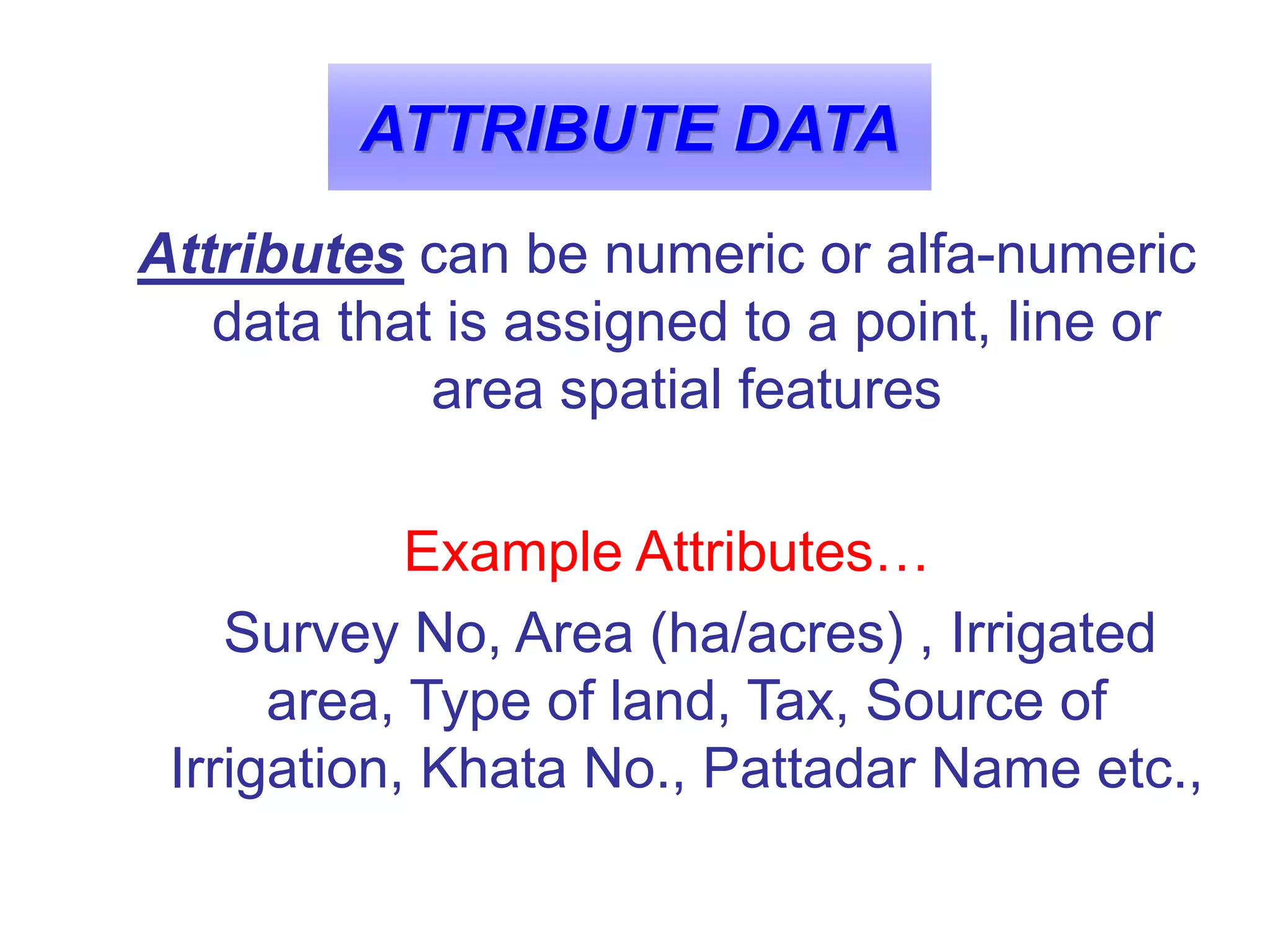
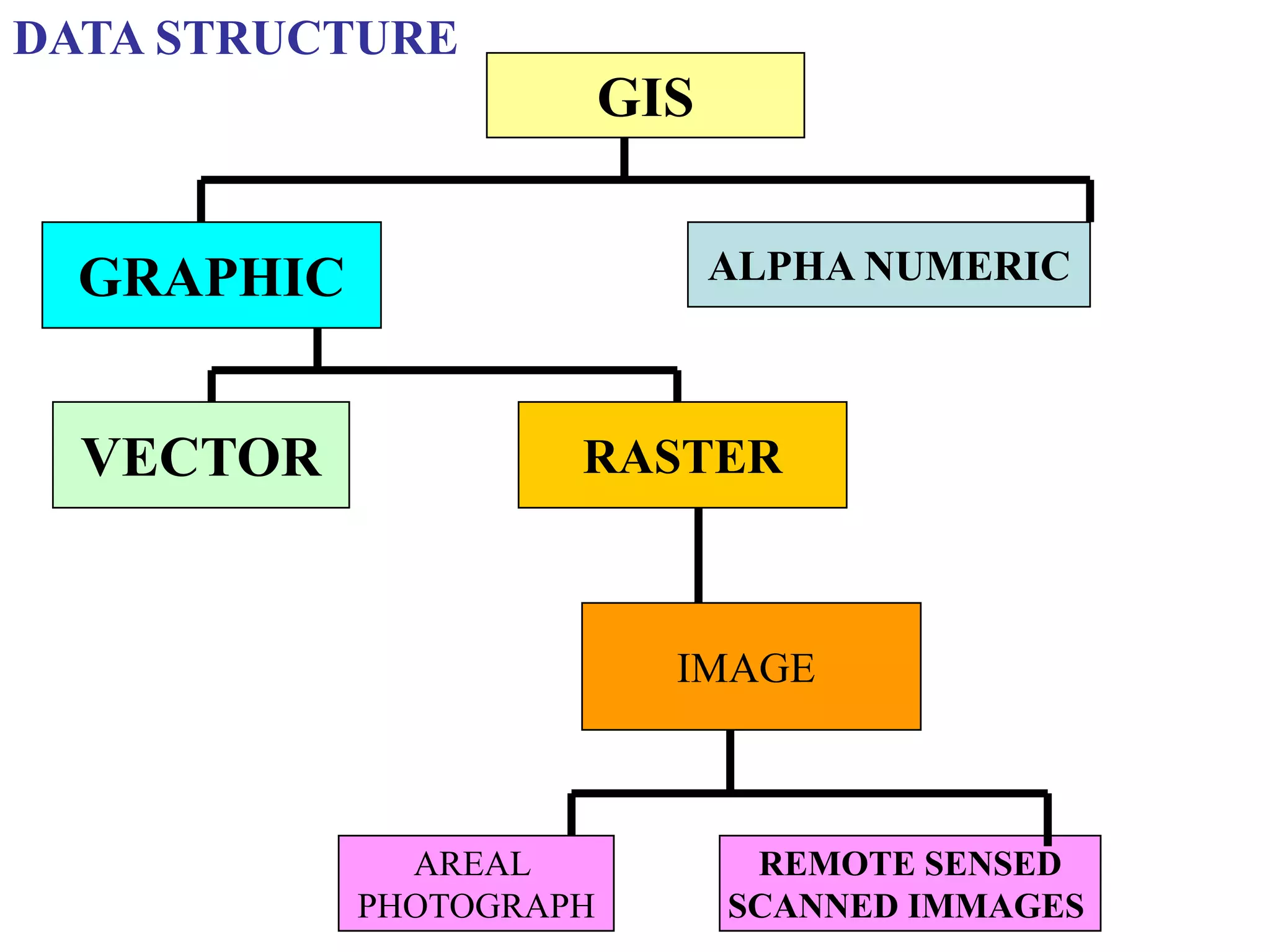
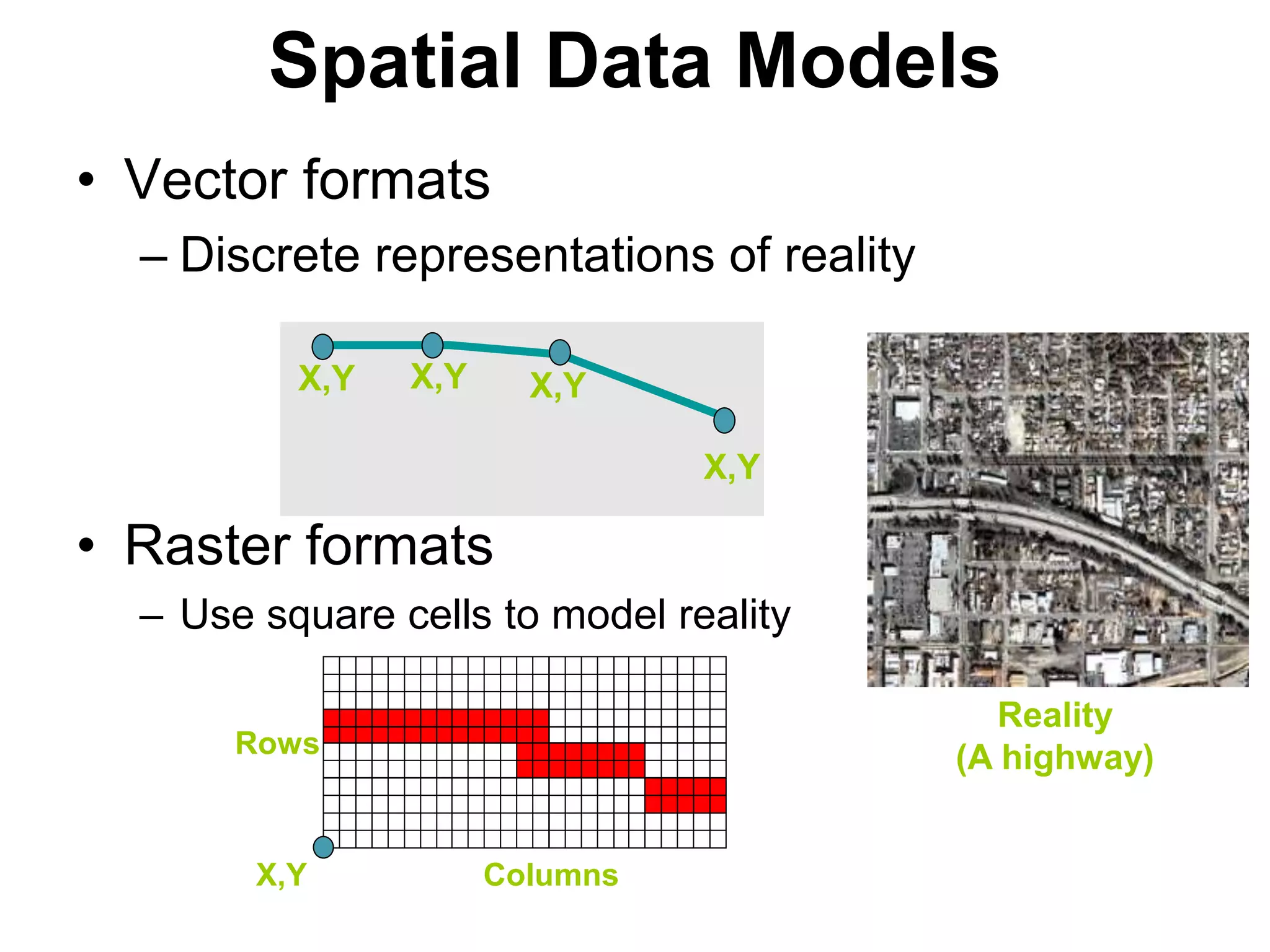
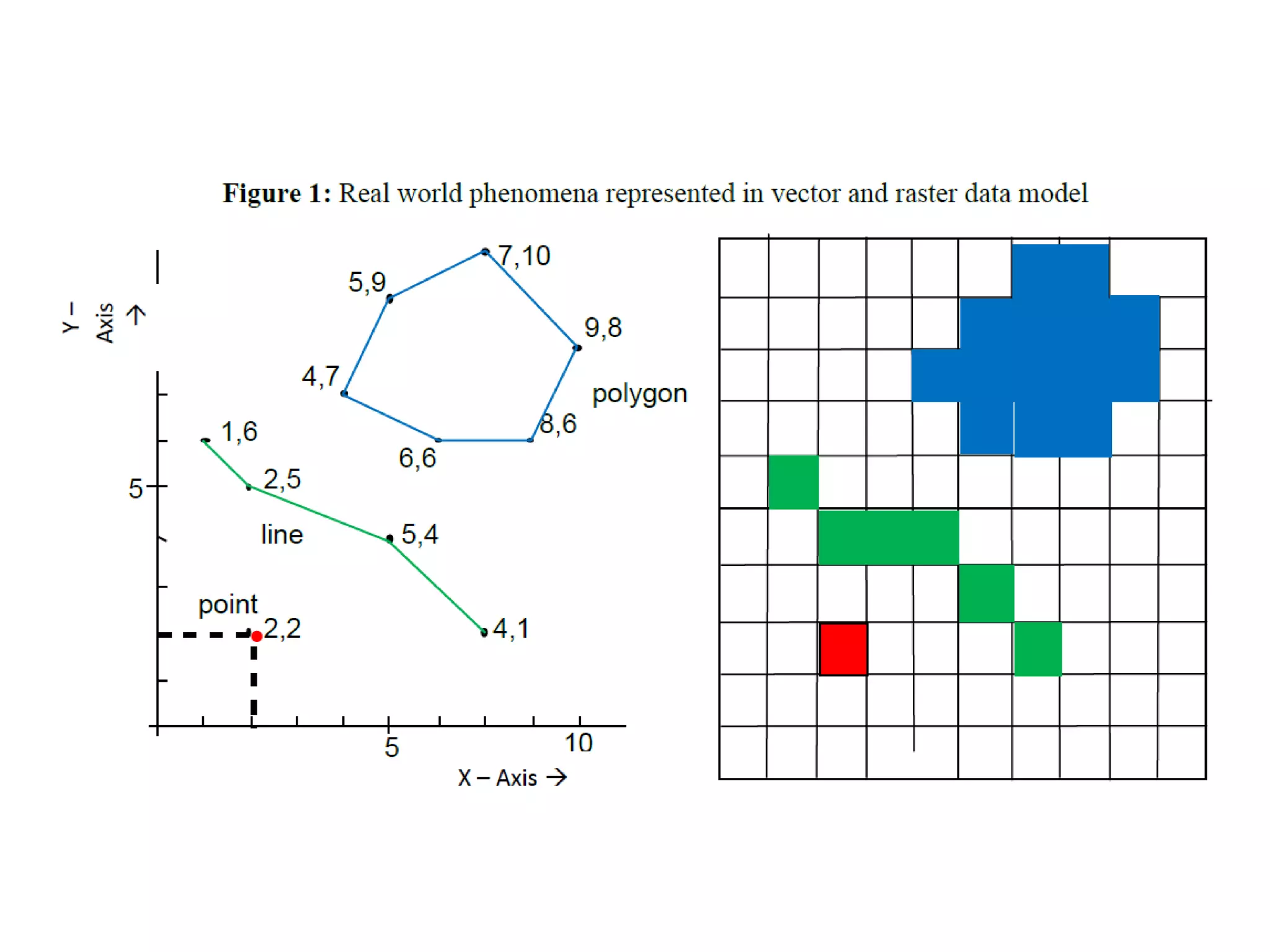
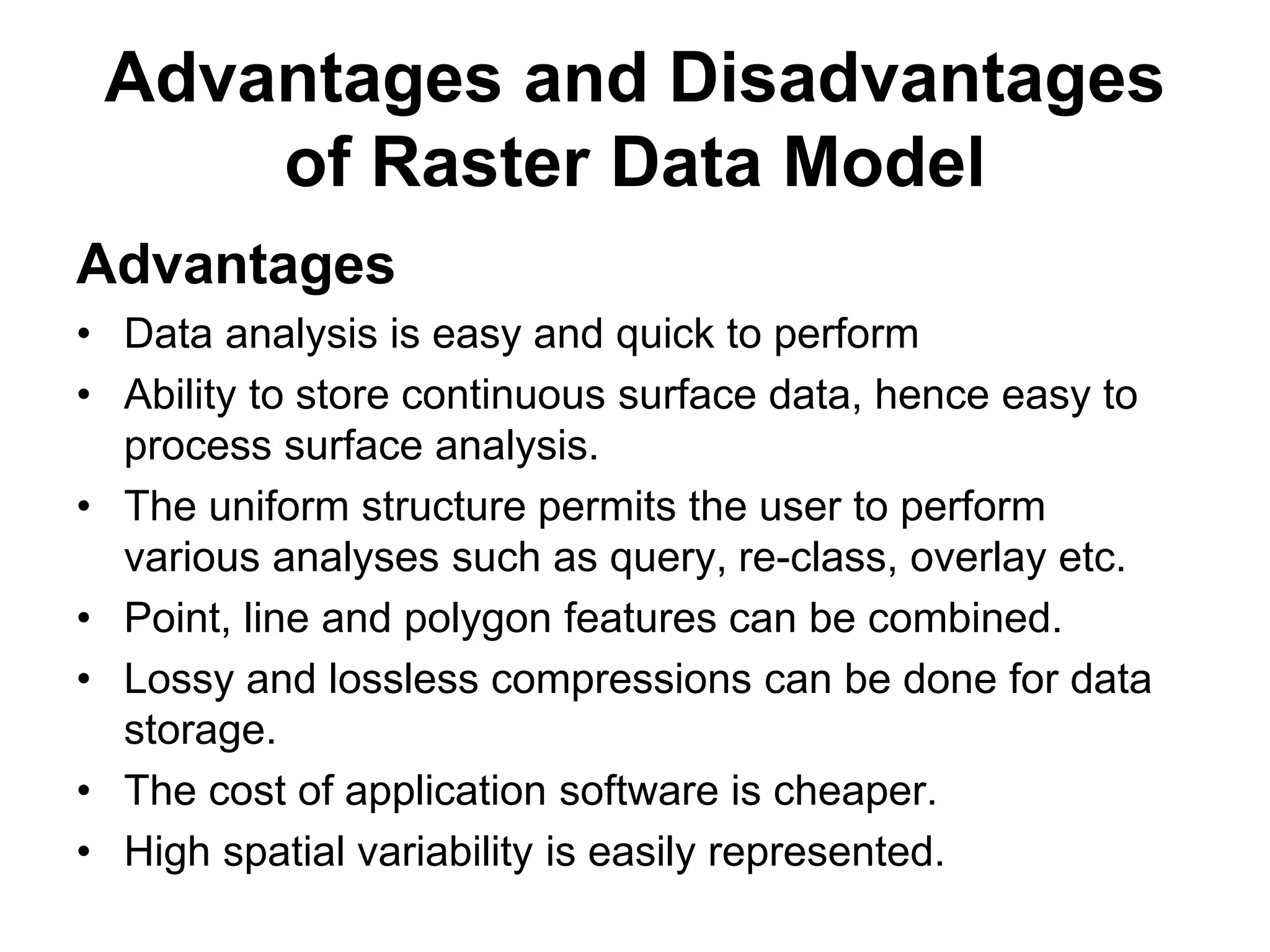
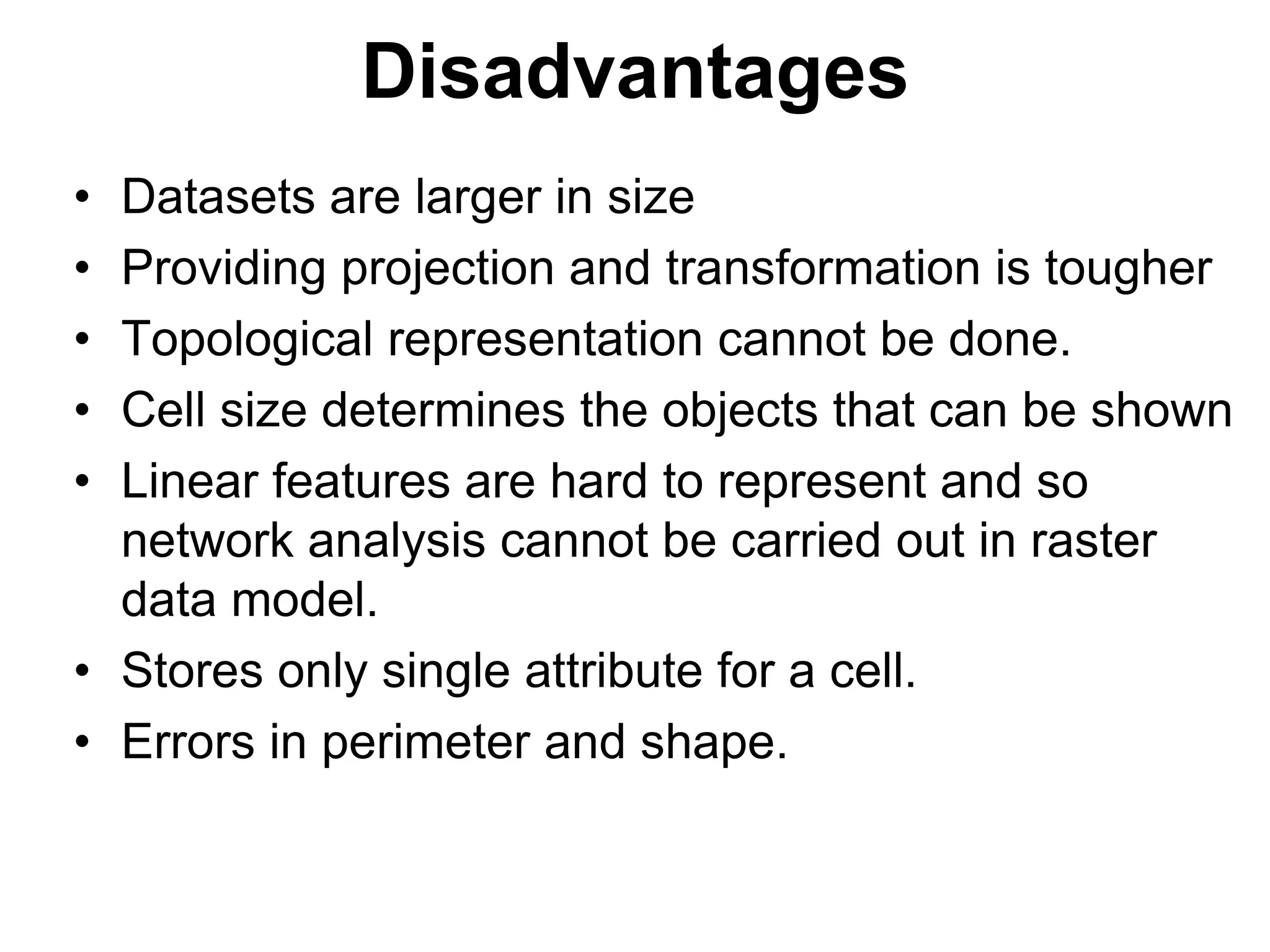
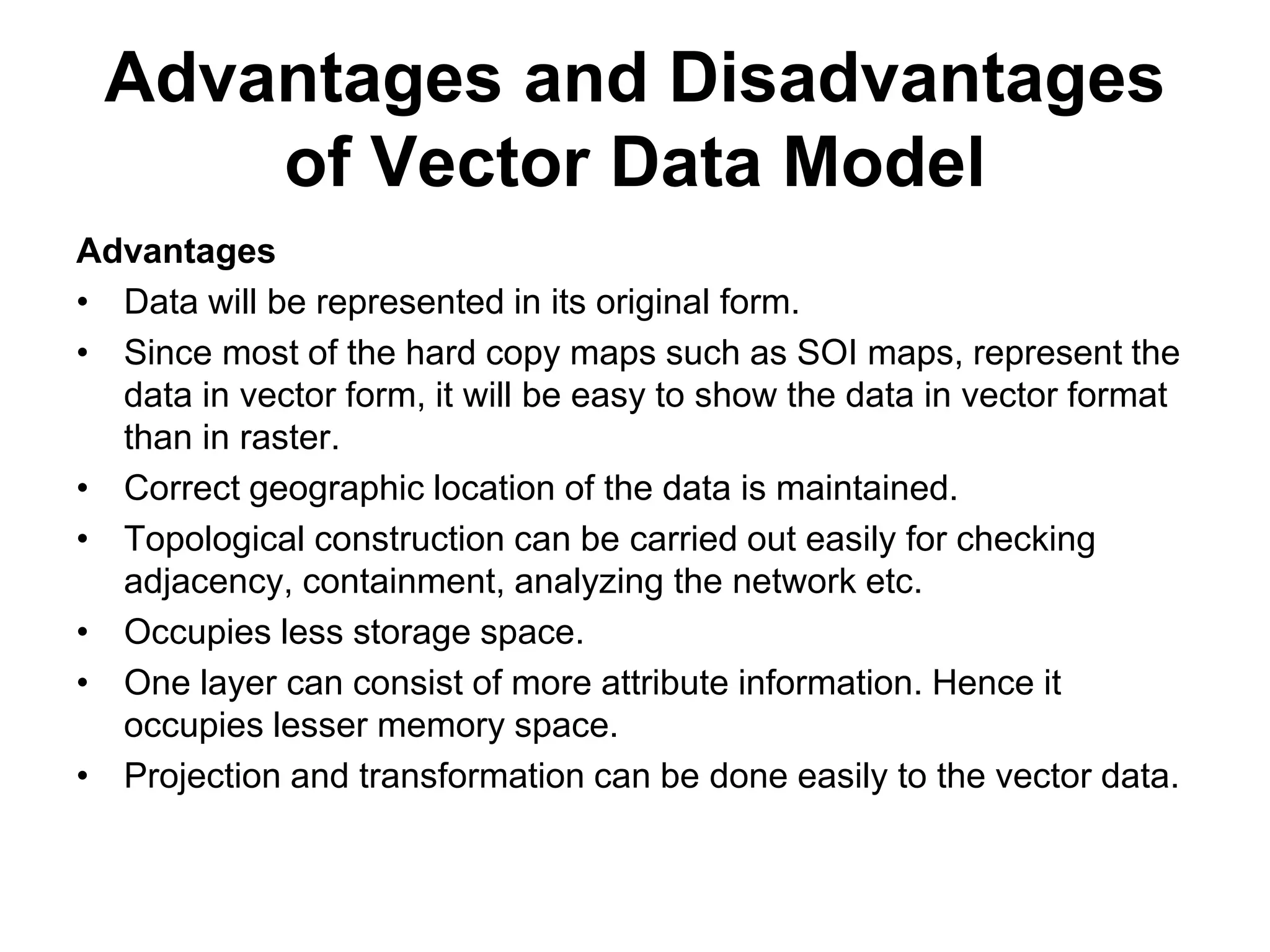
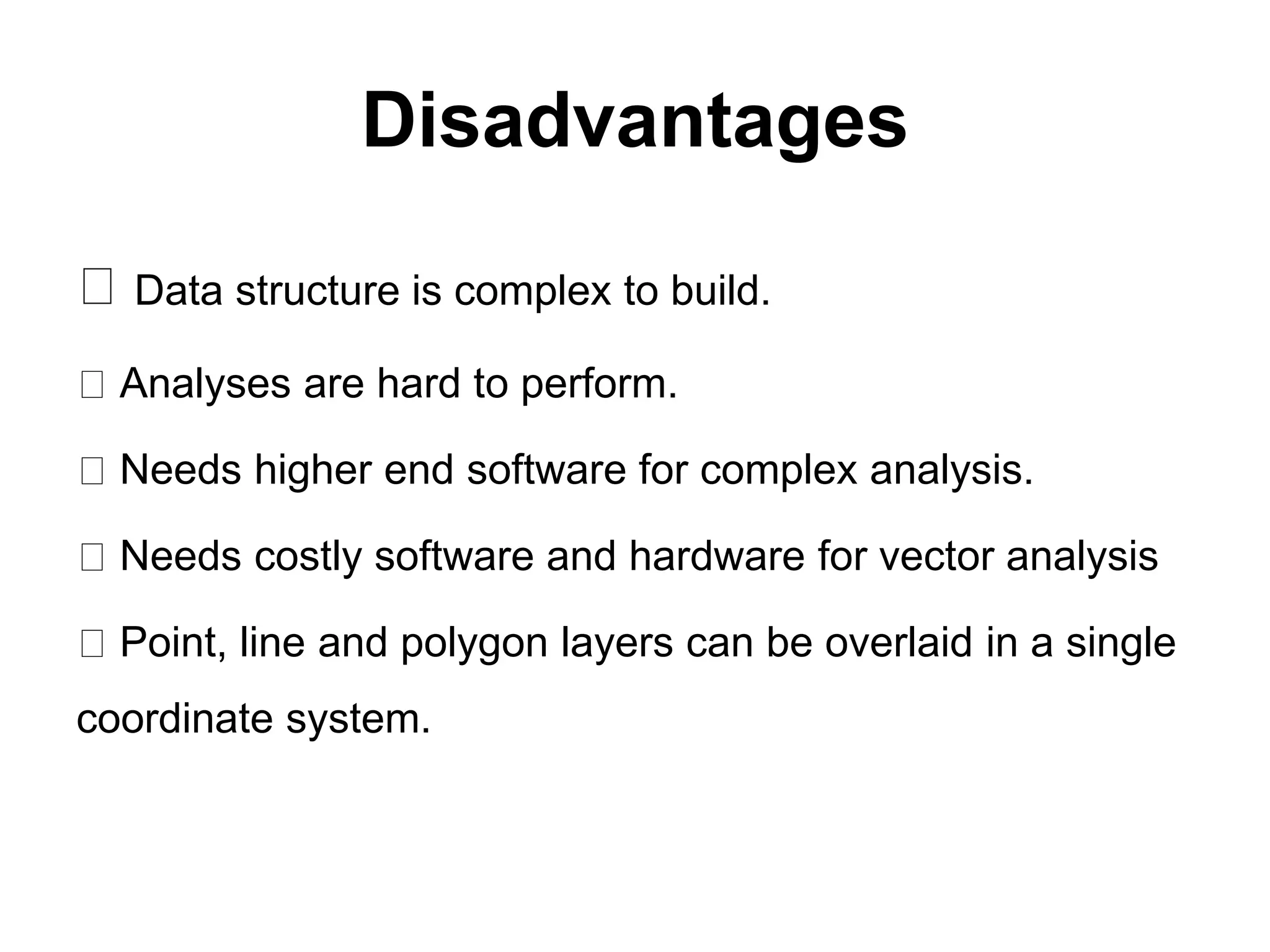
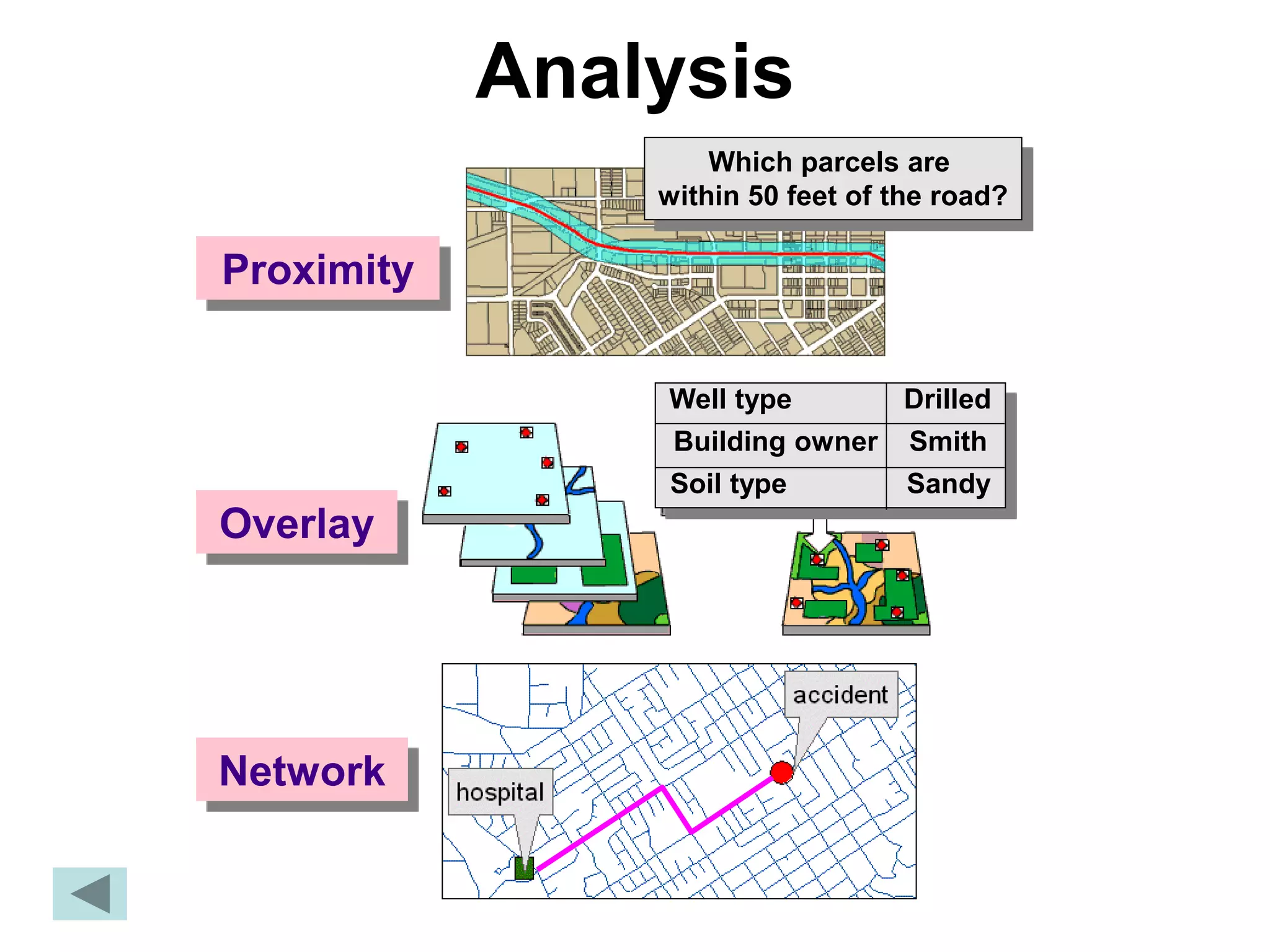
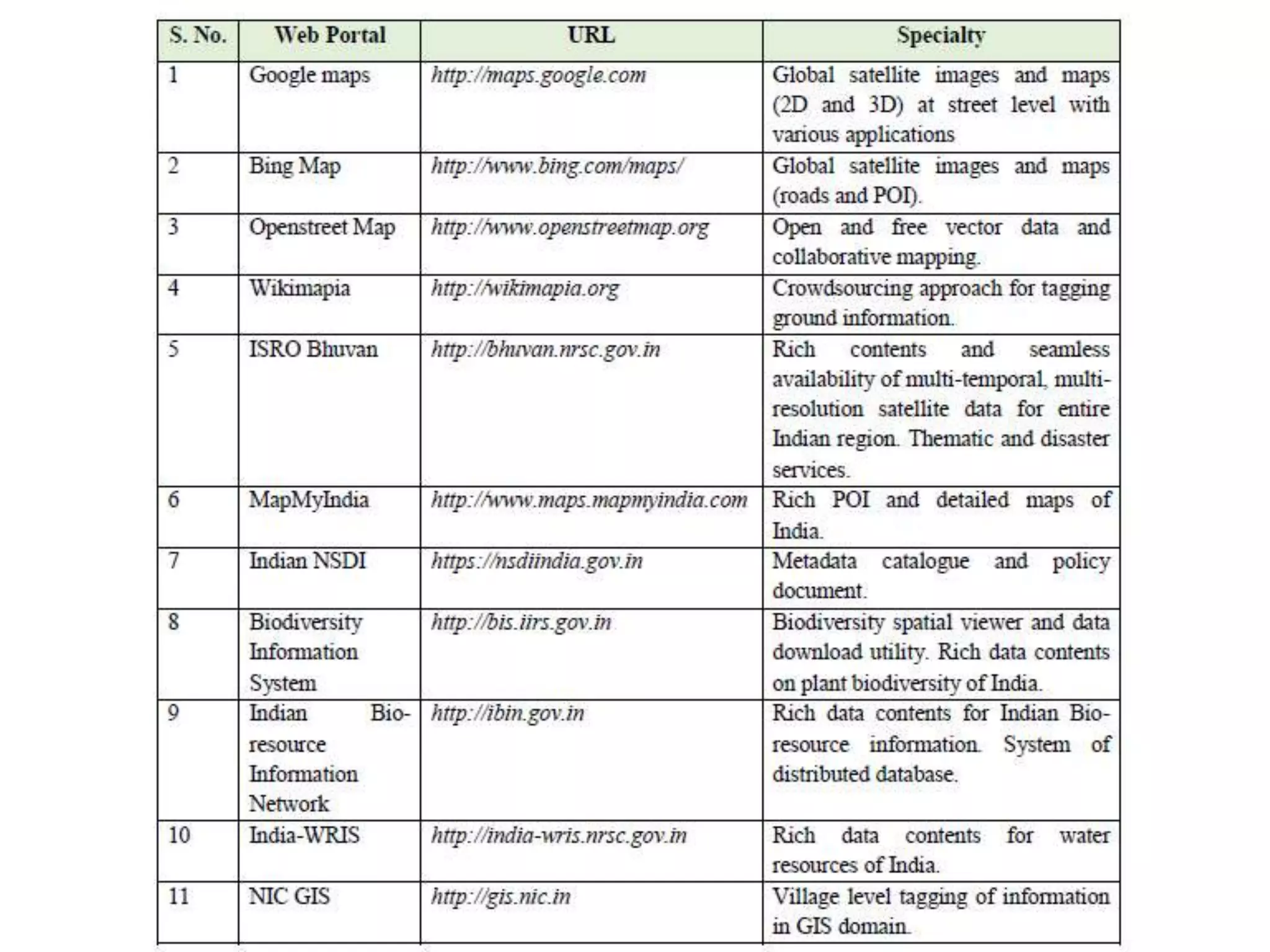
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are systems for capturing, storing, analyzing and managing spatial and geographic data and information. A GIS allows users to create interactive queries (user-created searches), analyze spatial information, edit data in maps, and present the results of all these operations. Key components of a GIS include geographic data, hardware, software, and personnel with GIS skills. GIS has many applications, including land information systems, land use and thematic mapping, environmental impact assessments, facility management, health care analysis, forestry and wildlife tracking, waste land development, groundwater resource management, urban and town planning, and more.