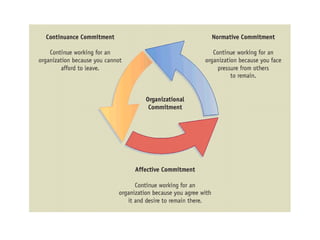
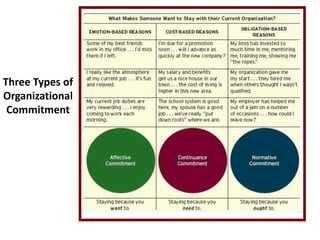
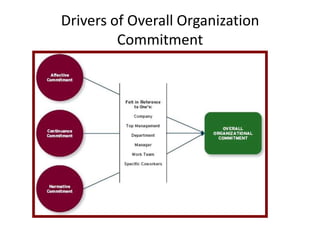
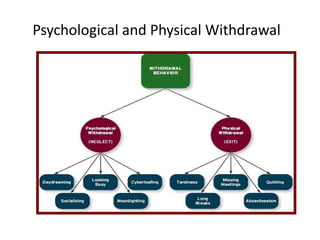
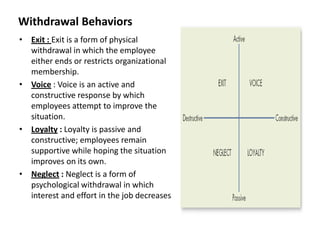
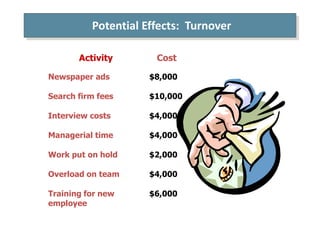
Organizational commitment refers to an employee's identification with and involvement in an organization. There are three main types of organizational commitment: affective, continuance, and normative. A survey of IT employees found moderate levels of organizational commitment, with higher variability in affective commitment. Job satisfaction was also moderate, with the lowest satisfaction regarding working hours, supervision, appreciation, and salary. Higher job satisfaction correlated with increased affective and normative commitment.