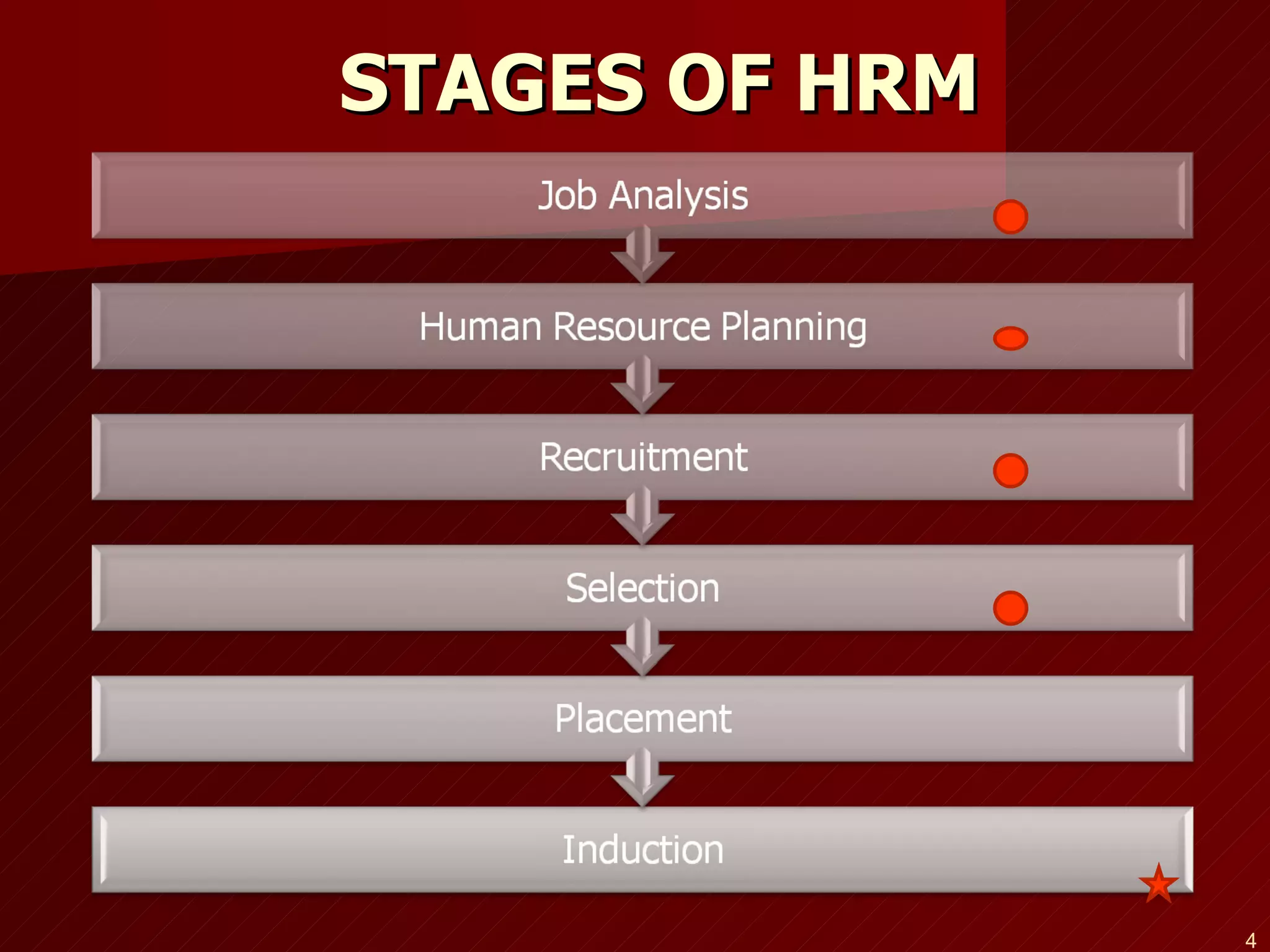
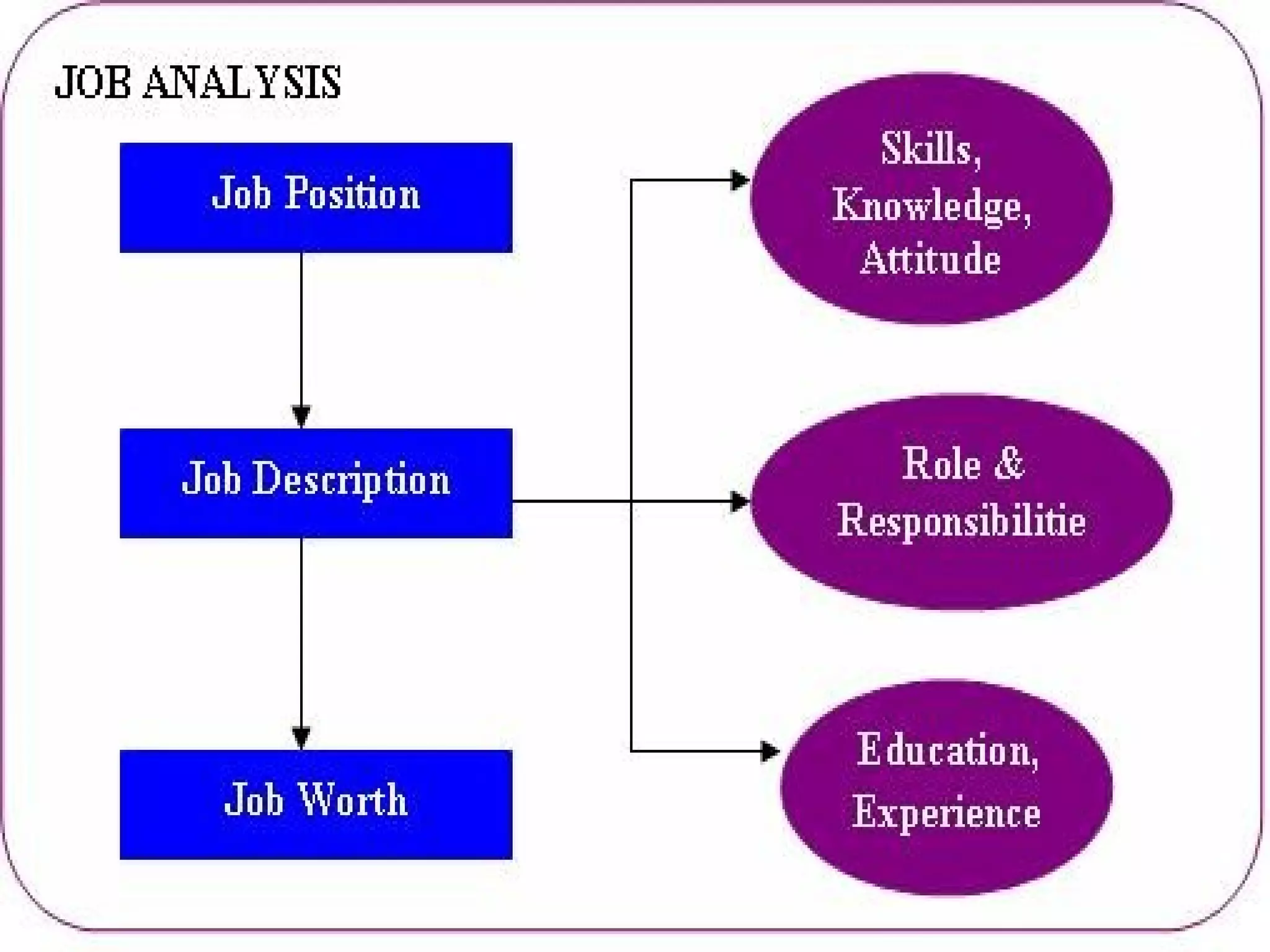
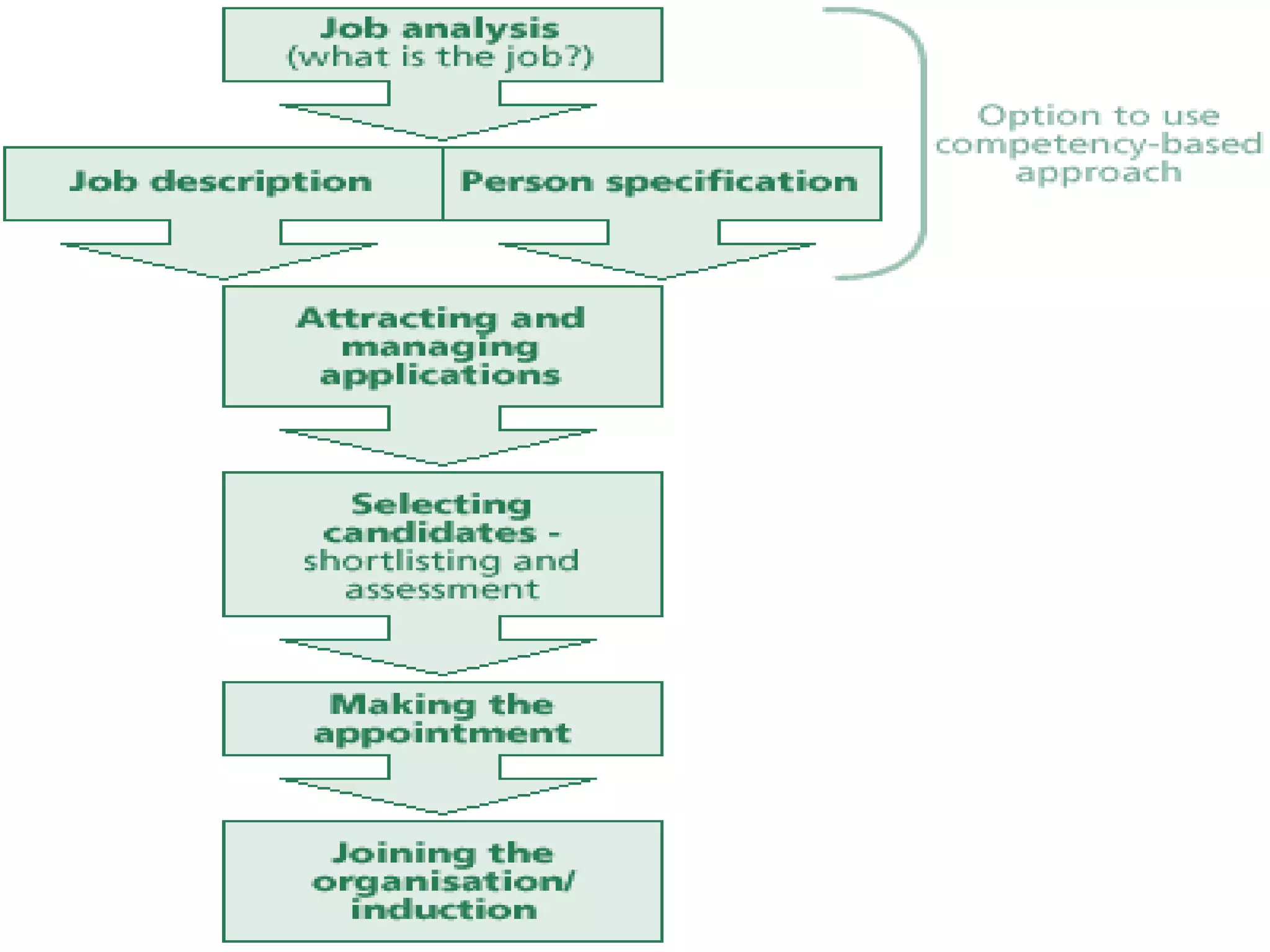
The document discusses job analysis, which is the process used to collect information about the duties, responsibilities, skills, outcomes, and work environment of a particular job. It outlines several key stages and methods of job analysis, including defining job tasks and requirements, developing job descriptions and specifications, setting performance standards, and determining important applications like selection, training, and compensation. Common methods of collecting job analysis information discussed are observation, interviews, questionnaires, previous studies, and work diaries.