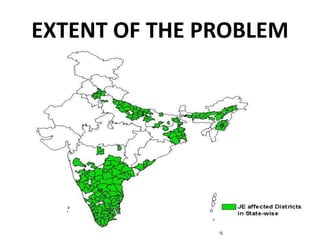
1. Japanese encephalitis is a viral disease transmitted through mosquito bites that causes brain swelling and inflammation.
2. The virus has a zoonotic transmission cycle between mosquitoes, pigs, and water birds, though humans are accidental hosts.
3. Symptoms range from fever and headache to meningitis or encephalitis. There is no specific treatment, so care is supportive.