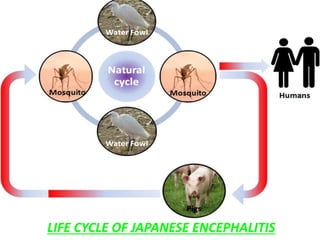
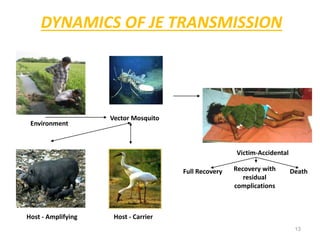
Japanese encephalitis (JE) is a viral disease transmitted by Culex mosquitoes that infects humans and animals. It is a major public health problem in Asia, where an estimated 50,000 cases and 10,000 deaths occur annually. The virus is maintained in a cycle between mosquitoes and amplifying hosts like pigs and wading birds. Mosquitoes become infected by feeding on infected hosts and transmit the virus to humans and horses. The virus enters through the mosquito bite and travels to the brain, where it can cause neurological damage and symptoms ranging from fever and headache to convulsions and coma. Prevention strategies focus on mosquito control through spraying and reducing breeding habitats, as well as vaccines for humans.