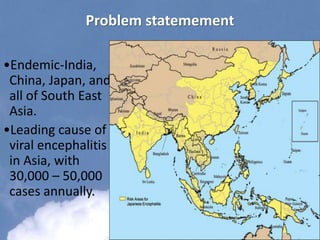
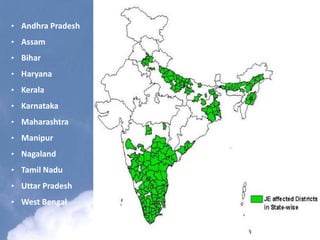
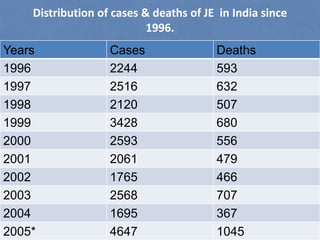
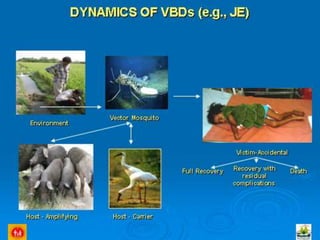
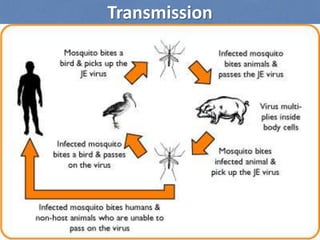
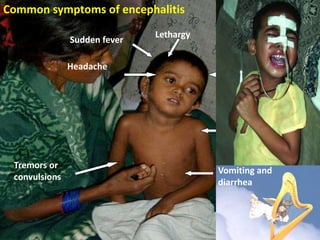
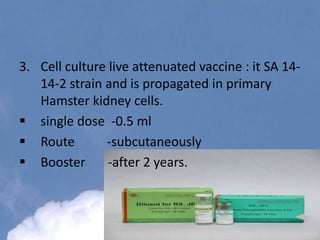
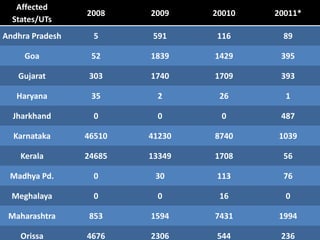
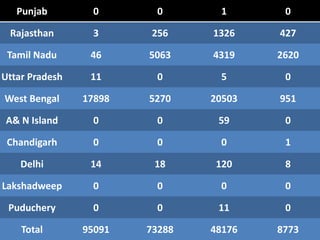
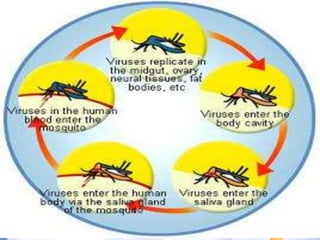
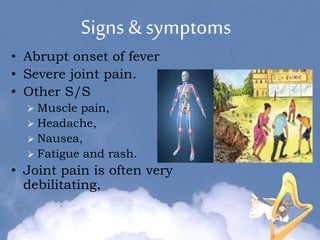
Japanese encephalitis is a viral disease transmitted through mosquito bites, primarily affecting children under 15 years of age. It is endemic in many parts of Asia, with an estimated 50,000 cases and 10,000 deaths annually. The virus is maintained in a zoonotic cycle between mosquitoes and pigs, birds, and horses, with humans as accidental hosts. There is no antiviral treatment available, so management focuses on supportive care and controlling mosquito vectors through integrated vector management strategies including larvicide use, insecticide spraying, and insecticide-treated bed nets. Vaccination programs aim to control the disease in endemic regions.