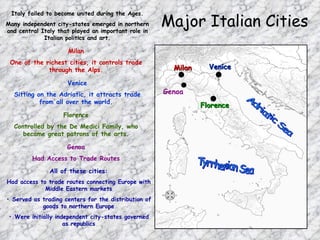
The Renaissance began in Italy in the 14th century as a period of renewal and recovery from the plague and Dark Ages. Major Italian city-states like Florence, Venice, and Milan served as centers of trade and patronage of the arts as people moved away from the church and focused more on secular and humanist ideas. Artists like Michelangelo and Leonardo da Vinci produced renowned works that captured realistic human emotion. The printing press helped spread Renaissance ideas throughout Europe, influencing literature, philosophy, and culture.