Embed presentation
Download to read offline




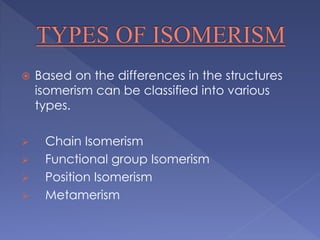
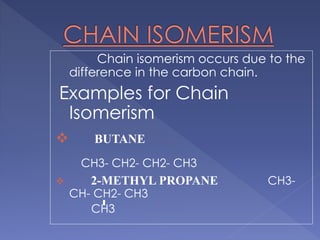

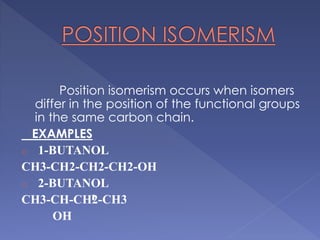

Organic compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas are called isomers. Isomerism can be classified into four main types: chain isomerism which is a difference in carbon chain, functional group isomerism due to differences in functional groups, position isomerism when functional groups are in different positions of the same carbon chain, and metamerism which is a difference in the number of carbon atoms on either side of a functional group. Examples are provided to illustrate each type of isomerism.








