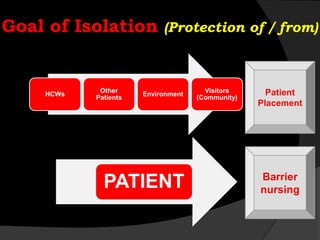
This document discusses various isolation precautions used to prevent the spread of infectious diseases in healthcare settings. It describes the goal of isolation as protecting healthcare workers, other patients, visitors, and the environment from pathogens. The key components of isolation include patient placement in private rooms, use of personal protective equipment like gloves and masks, and cleaning and disinfection of equipment and surfaces. Standard precautions should be used for all patient care. Additional precautions may be needed based on the route of transmission, such as airborne precautions for tuberculosis or droplet precautions for influenza. Contact precautions use gloves and gowns to prevent spread through direct contact. Reversed isolation protects immunocompromised patients from environmental pathogens. Proper hand hygiene