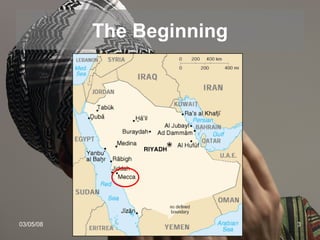
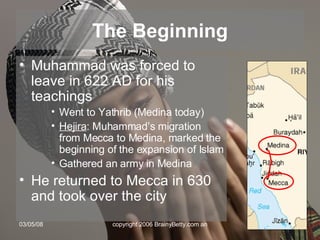
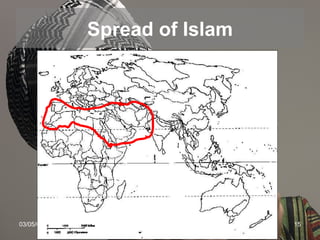
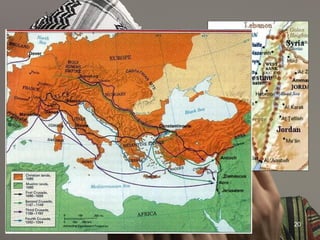
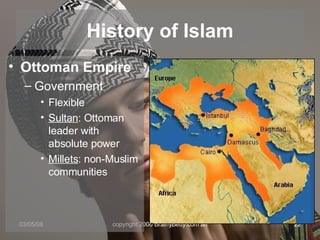
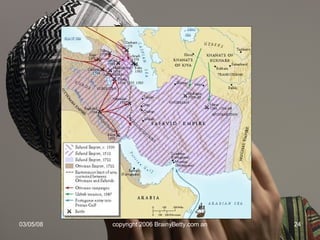
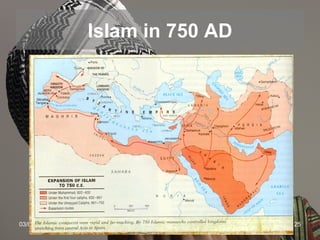
The document provides an overview of the history and teachings of Islam. It discusses the origins of Islam with the prophet Muhammad and the revelations he received from Gabriel. The core teachings of Islam are outlined as the Five Pillars and the divisions between Sunni and Shia sects are introduced stemming from disagreements over leadership succession after Muhammad. The spread of Islam through early dynasties like the Umayyads and Abbassids is summarized alongside foreign invaders like the Seljuks, Mongols, and the Crusades. Major Islamic empires like the Ottomans and Safavids are also briefly mentioned.