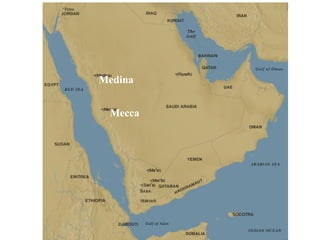
The document summarizes the origins and spread of Islam. It describes how Muhammad received revelations from Gabriel in Mecca and spread the monotheistic teachings of Islam. He was forced to flee to Medina where his following grew and he eventually conquered Mecca, destroying the pagan idols. The five pillars of Islam are outlined as well as key beliefs. The caliphs helped spread Islam through conquest from the Arabian Peninsula to North Africa and the Middle East. The document also discusses the Sunni-Shi'a split and cultural/scientific contributions of early Islamic civilizations.