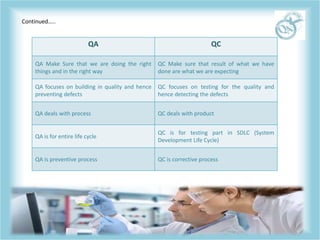
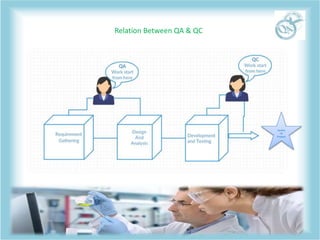
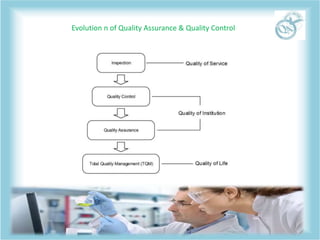
QA and QC are related but distinct concepts in quality management. QA refers to the overall system that aims to prevent defects through processes, while QC tests products to identify defects. QA is a preventative system involving all employees to ensure quality standards are met throughout development. In contrast, QC is reactive and conducted by a specialized team to detect defects in finished products before release. Both work together to continually meet customer requirements, with QA focusing on building quality in from the start and QC checking for quality along the way.