This document discusses how computers represent and process data. It covers:
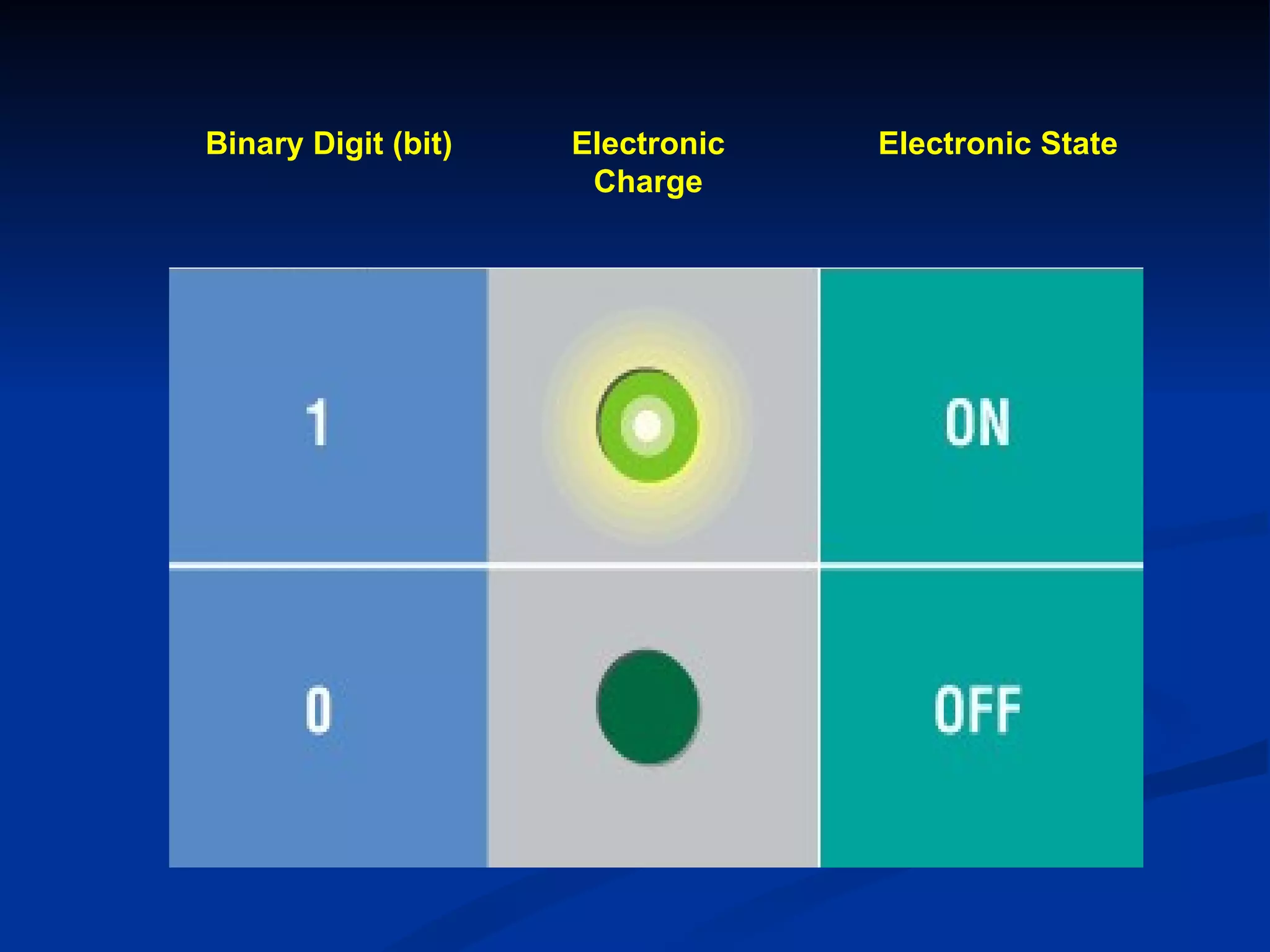
1) Computers use binary digits (bits) to represent data, with each bit being either 1 or 0 to represent an on or off state.
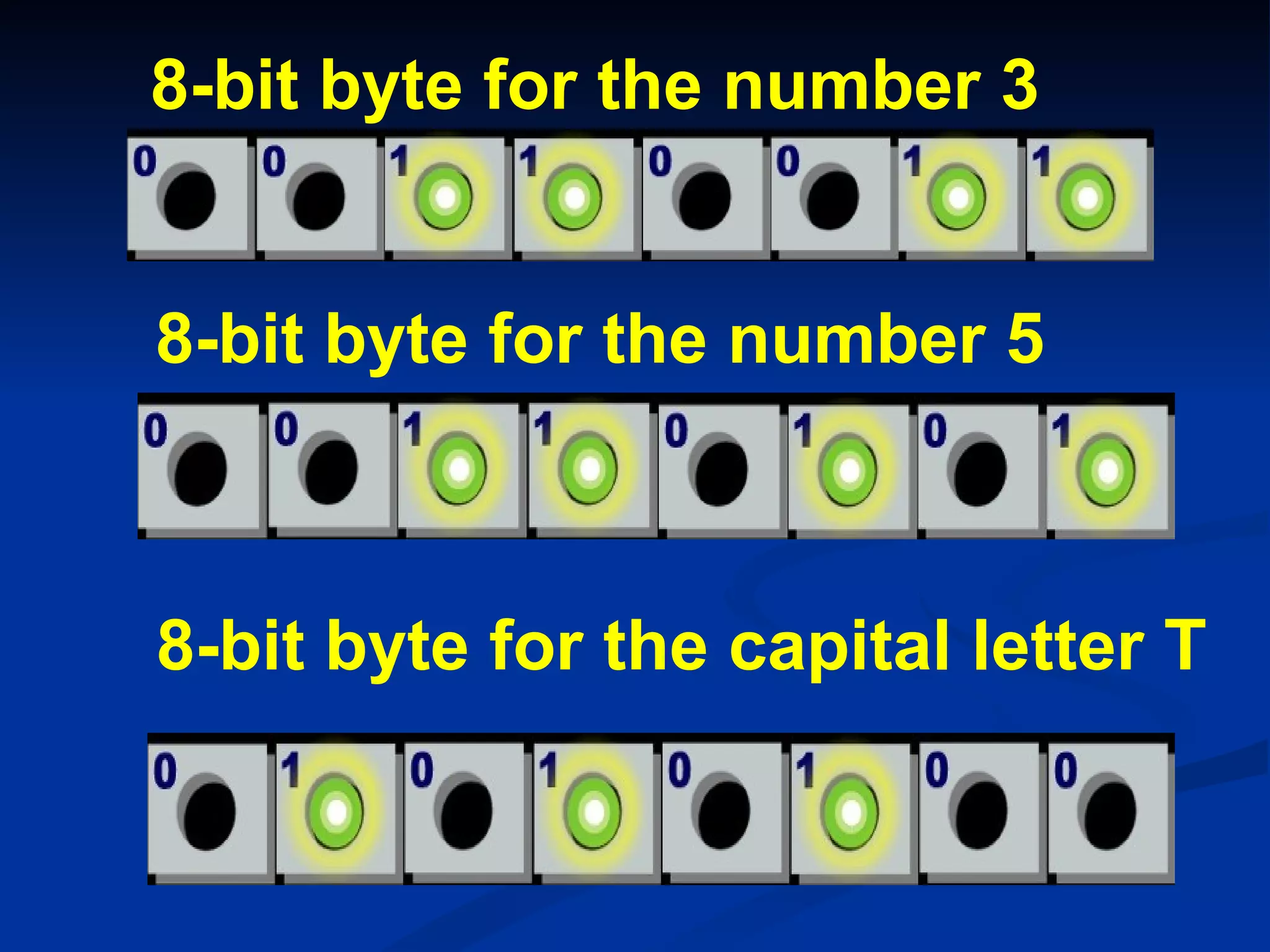
2) Eight bits are grouped together to form a byte, which can represent individual characters.
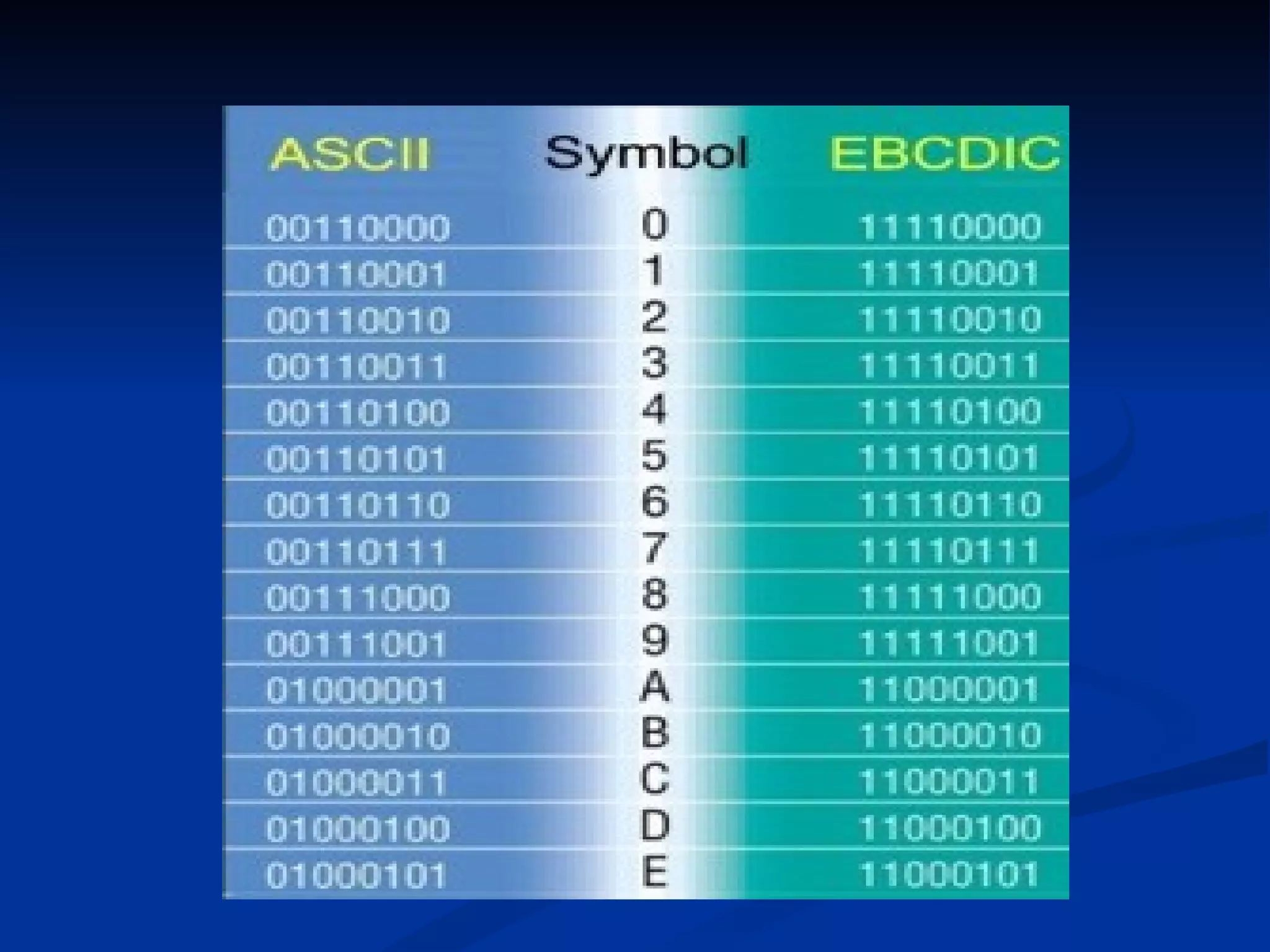
3) There are different coding systems like ASCII to represent characters and numbers with binary codes.
4) Data entered from keyboards is converted to binary codes and stored in memory for processing before being converted back to characters on output devices.