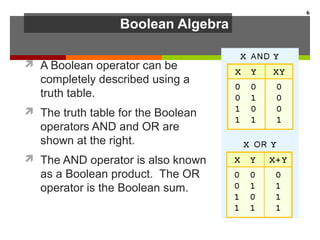
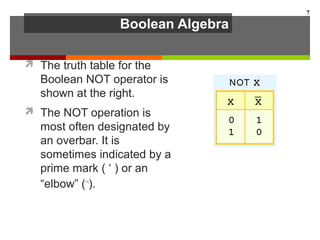
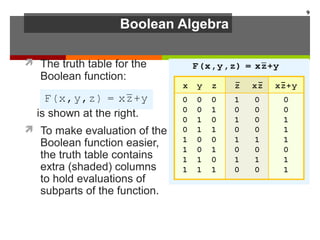
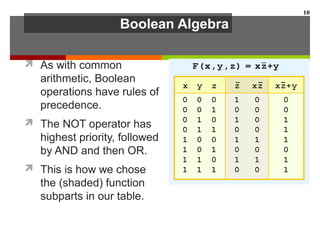
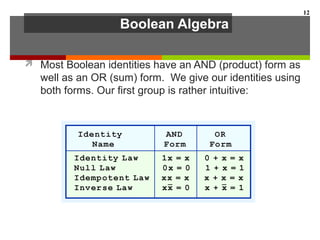
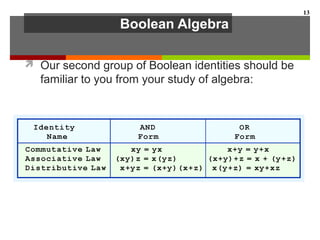
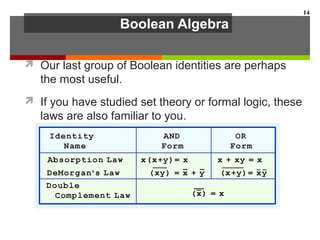
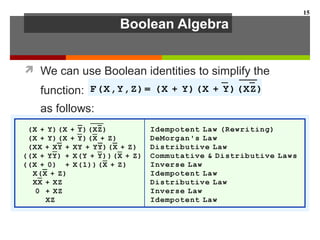
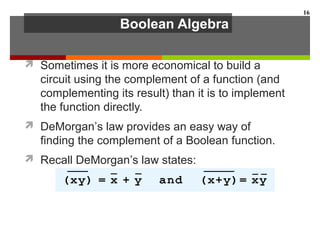
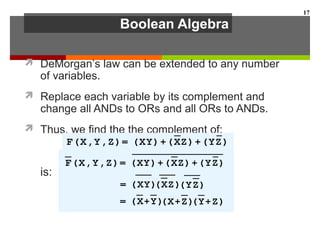
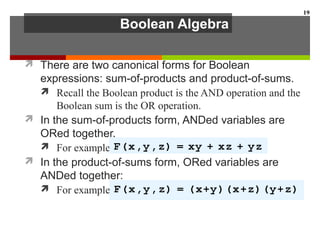
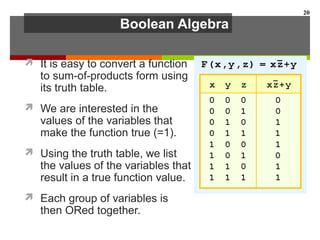
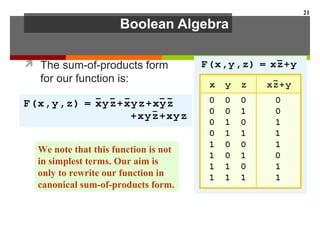
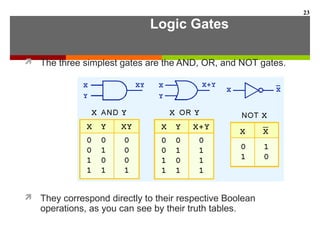
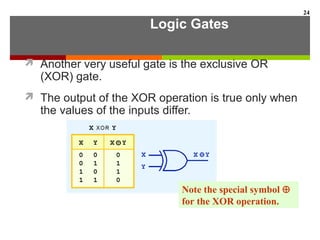
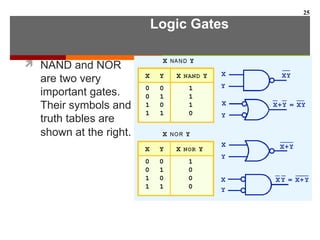
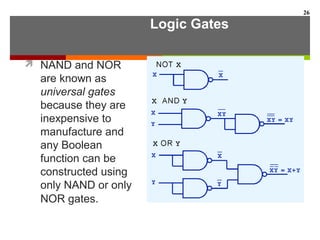
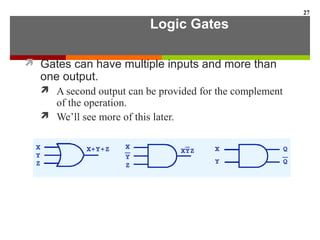
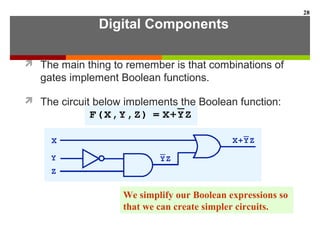
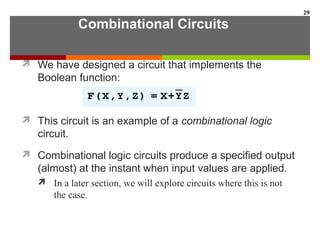
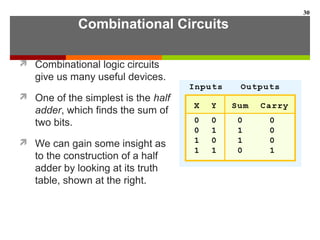
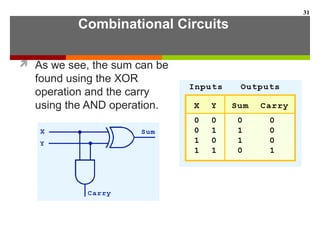
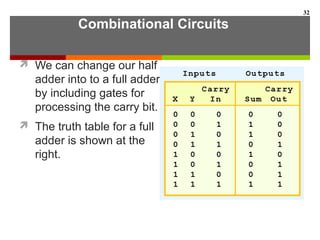
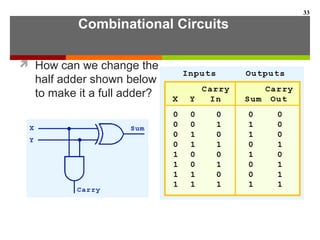
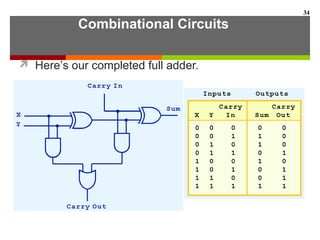
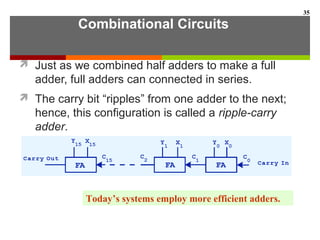
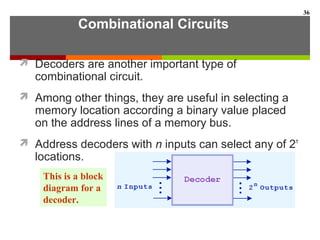
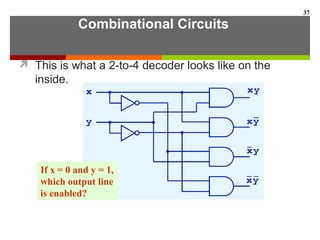
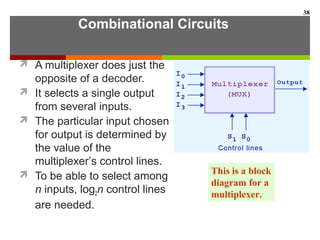
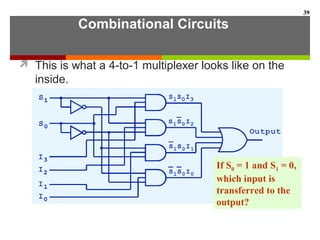
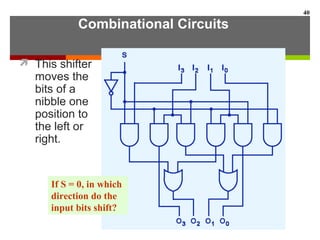
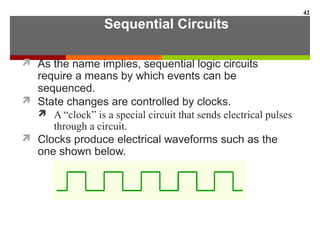
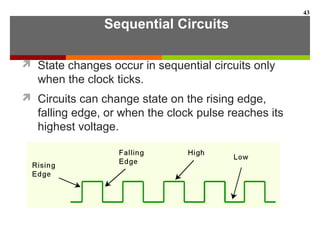
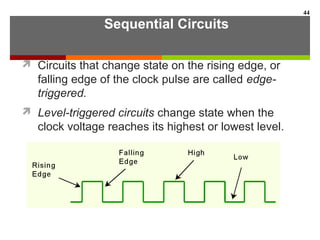
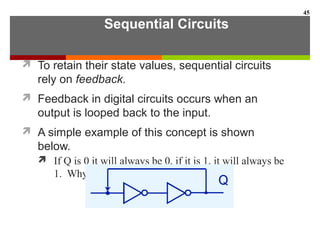
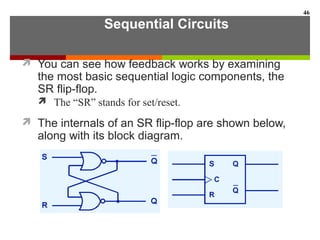
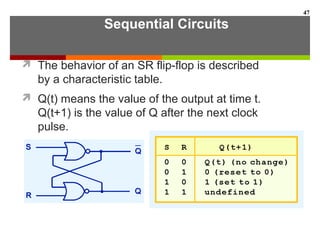
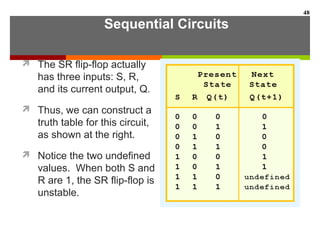
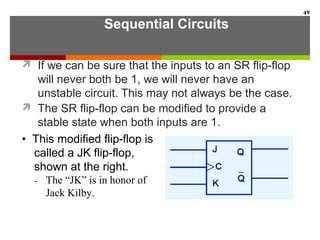
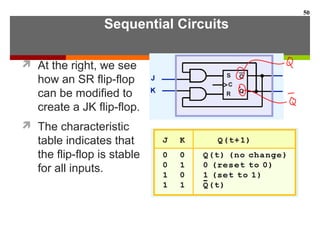
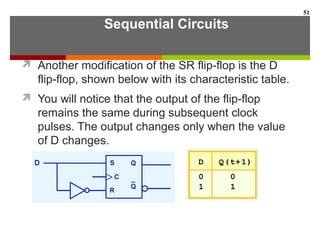
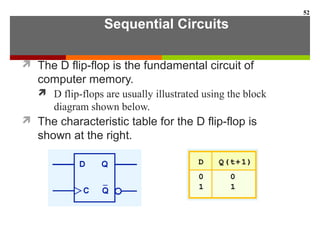
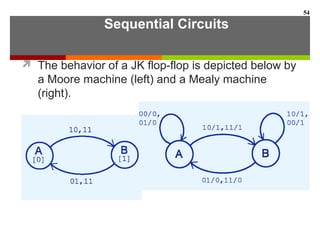
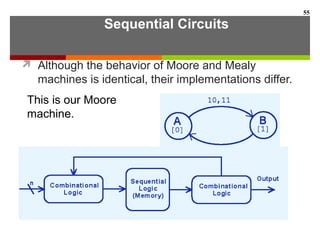
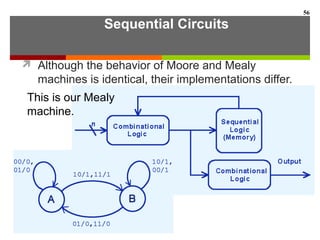
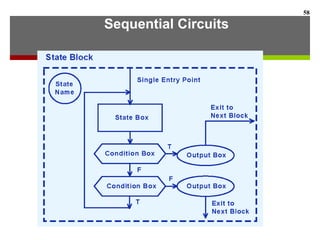
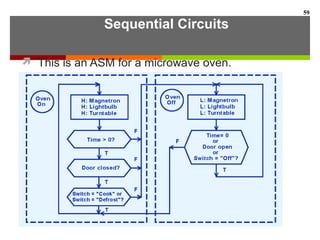
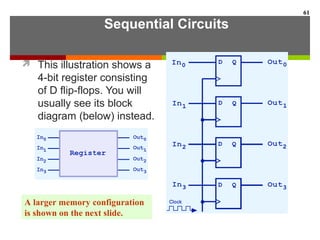
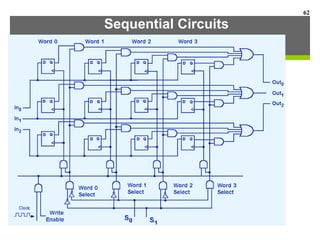
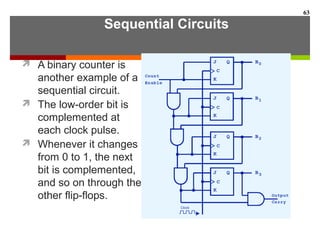
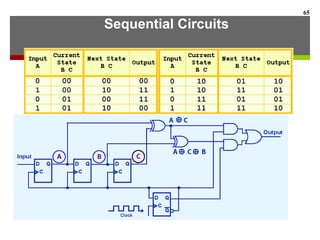
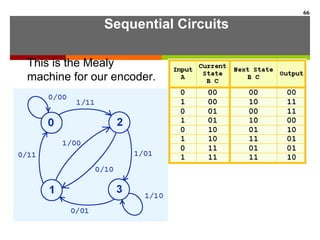
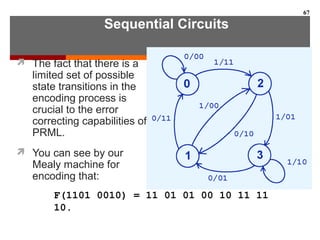
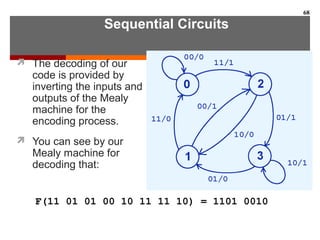
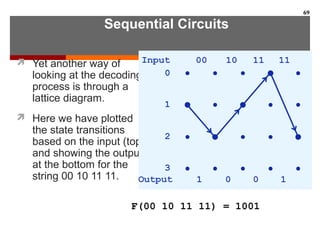
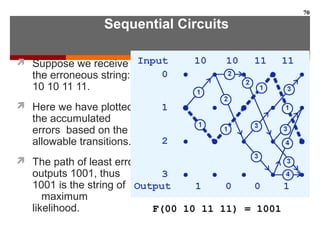
This document discusses Boolean algebra and digital logic circuits. It begins by introducing Boolean algebra, which uses variables that can have two values (true/false, on/off, 1/0) and operations like AND, OR, and NOT. Boolean functions are implemented using logic gates like AND, OR, NAND and NOR gates. Combinational logic circuits like adders, decoders, and multiplexers perform Boolean functions without state, while sequential circuits like flip-flops use feedback and clocks to remember state over time. Finite state machines can model sequential circuits.