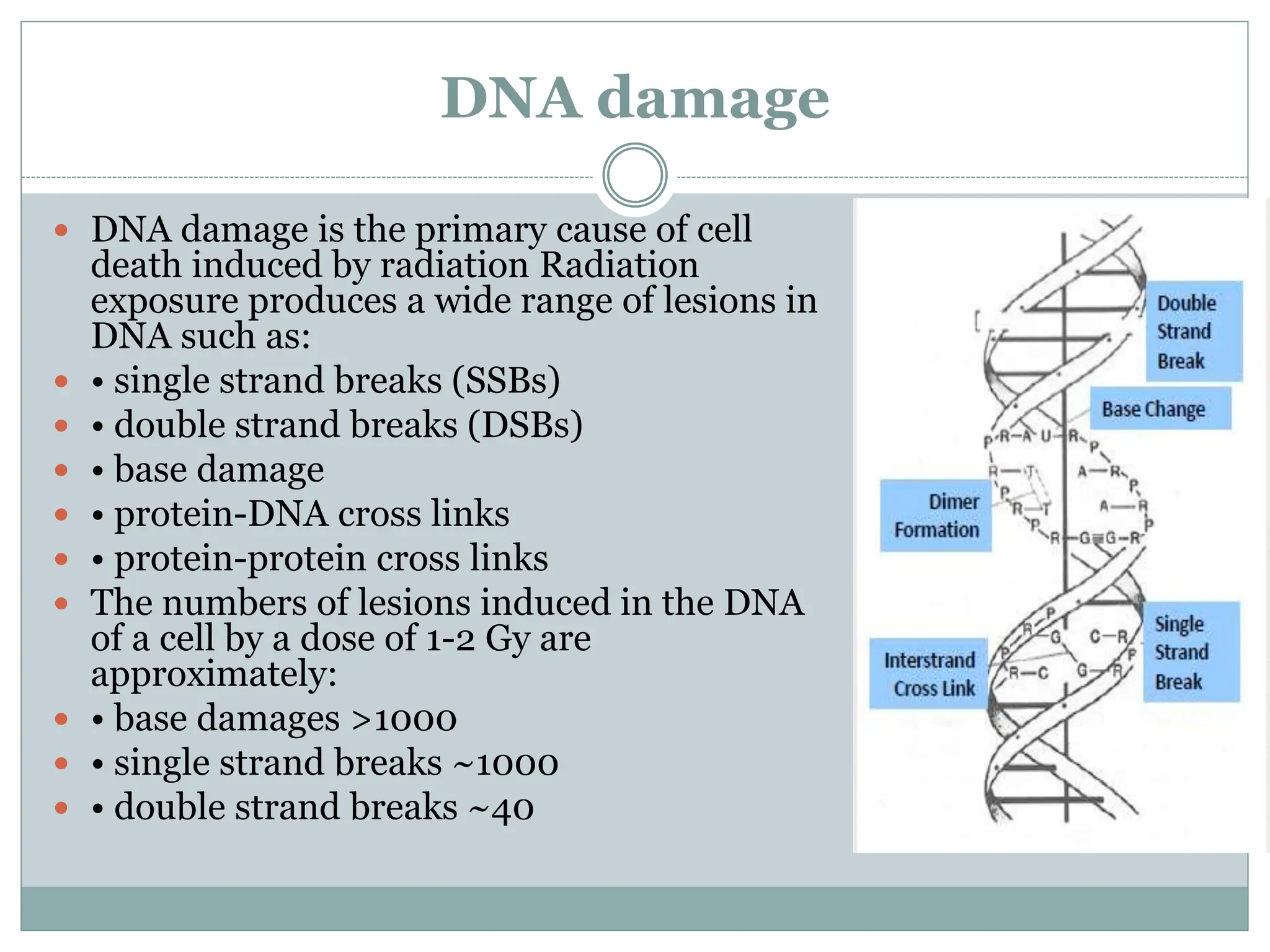
Radiation can damage water and DNA through indirect action. When water is exposed to ionizing radiation, it undergoes radiolysis producing reactive radicals like hydrogen and hydroxyl radicals. As living cells are mostly water, these radicals can damage cellular components like DNA. Radiation exposure can cause various types of DNA damage like single and double strand breaks, base damage and crosslinks. Unrepaired double strand breaks can lead to chromosomal aberrations. Cells have DNA repair mechanisms like non-homologous end joining and homologous recombination to repair radiation damage. Unrepaired DNA damage may result in mutations, cell death or hereditary effects depending on the severity.