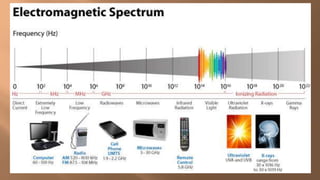
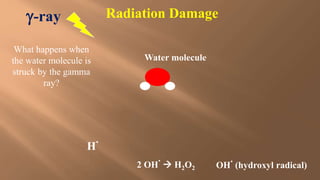
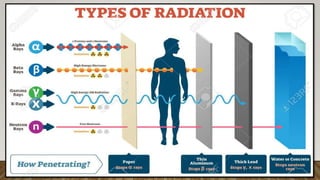
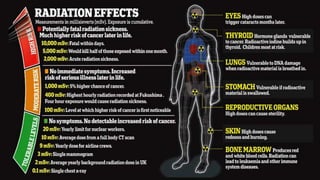
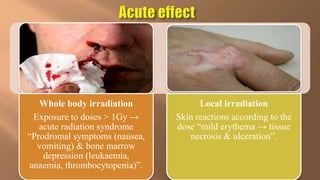
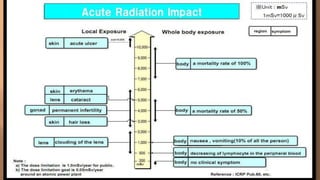
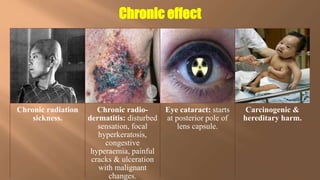
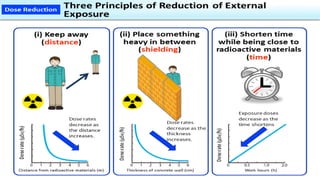
This document discusses ionizing and non-ionizing radiation. It defines ionizing radiation as radiation capable of producing ions through direct or indirect interaction with matter, while non-ionizing radiation does not have a wavelength sufficient for ionization. The document discusses the different types of ionizing radiation including electromagnetic radiation like x-rays and gamma rays, and corpuscular radiation like alpha particles, beta particles, neutrons, and protons. It also discusses the mechanisms of radiation damage, relative biological damage of different types of radiation, sources of background radiation exposure, and medical uses and effects of ionizing radiation.