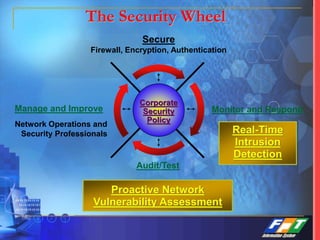
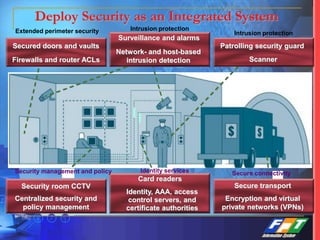
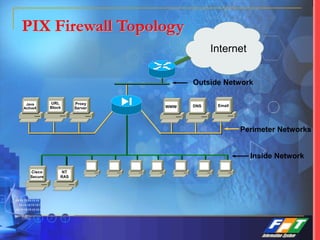
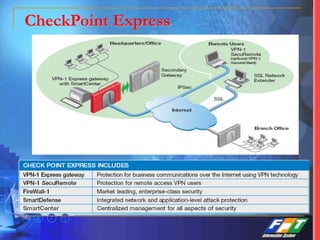
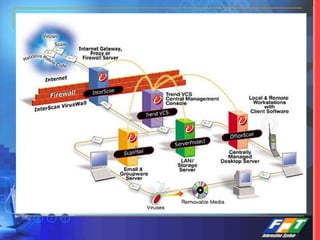
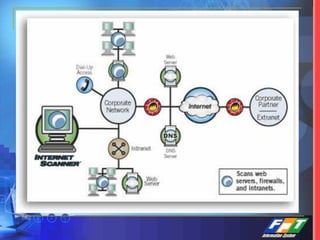
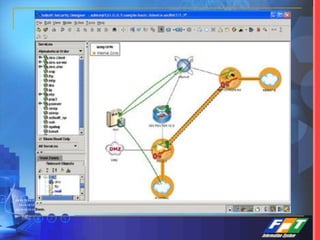
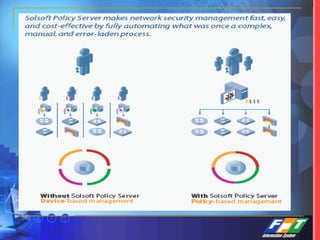
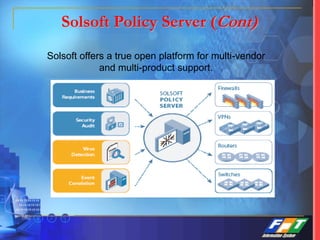
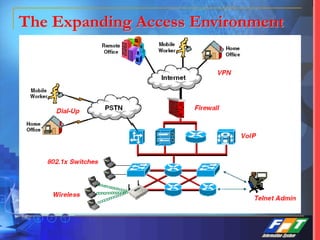
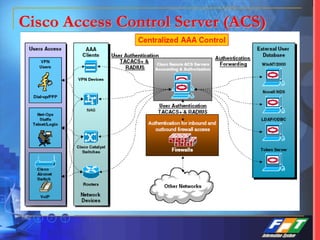
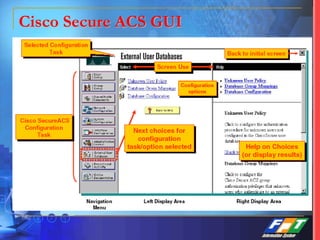
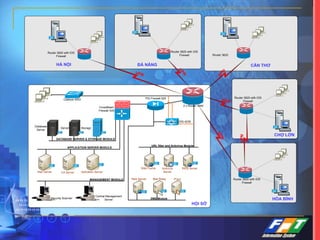
This document discusses network security solutions for Eximbank. It begins with an overview of network security and the need for an integrated defense-in-depth approach using firewalls, intrusion detection systems, antivirus software, vulnerability scanners, and centralized management. It then outlines types of attacks and provides a security blueprint. Specific solutions discussed include the Cisco PIX firewall, CheckPoint firewall, intrusion detection systems, antivirus systems, vulnerability scanners, and identity and policy management solutions. The document concludes with an overview of the proposed security design for Eximbank incorporating these various solutions.





![Service Name Port Number 30 day history Explanation
epmap 135 DCE endpoint resolution
nterm 1026 remote_login network_terminal
icq 1027 icq instant messanger
ms-sql-m 1434 Microsoft-SQL-Monitor
netbios-ns 137 NETBIOS Name Service
microsoft-ds 445 Win2k+ Server Message Block
dabber 9898 [trojan] Dabber Worm backdoor
sasser-ftp 5554 [trojan] Sasser Worm FTP Server
mydoom 3127 W32/MyDoom, W32.Novarg.A backdoor
netbios-ssn 139 NETBIOS Session Service
Microsoft Security Bulletins for June 2004
Source: The SANS Institute
Last update June 08, 2004 21:43 pm GMT](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eximbanksecuritypresentation-151217062022/85/Eximbank-security-presentation-9-320.jpg)