The document presents a method for detecting distributed denial of service (DDoS) and false data injection attacks in cyber-physical systems, specifically targeting smart grids. It describes the use of chi-square detectors and fuzzy logic-based classifiers to improve attack detection accuracy and outlines an intrusion detection algorithm tested in a simulated environment. The findings aim to enhance the security of interconnected physical systems vulnerable to cyber threats.






![Continue….
Then through statistical measurement of sensitivity
and specificity, we derived the confusion matrix [5],
True Positive = Correctly identified
False Positive = Incorrectly identified
True Negative = Correctly rejected
False negative = Incorrectly rejected
In general, positive = identified
Negative = rejected. Therefore,
Confusion Matrix
11
DDoS False Data
Injection
DDoS 96% 4%
False Data
Injection
4% 96%](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/attackdetectionandpreventioninthecyber-160217195154/75/Attack-detection-and-prevention-in-the-cyber-11-2048.jpg)
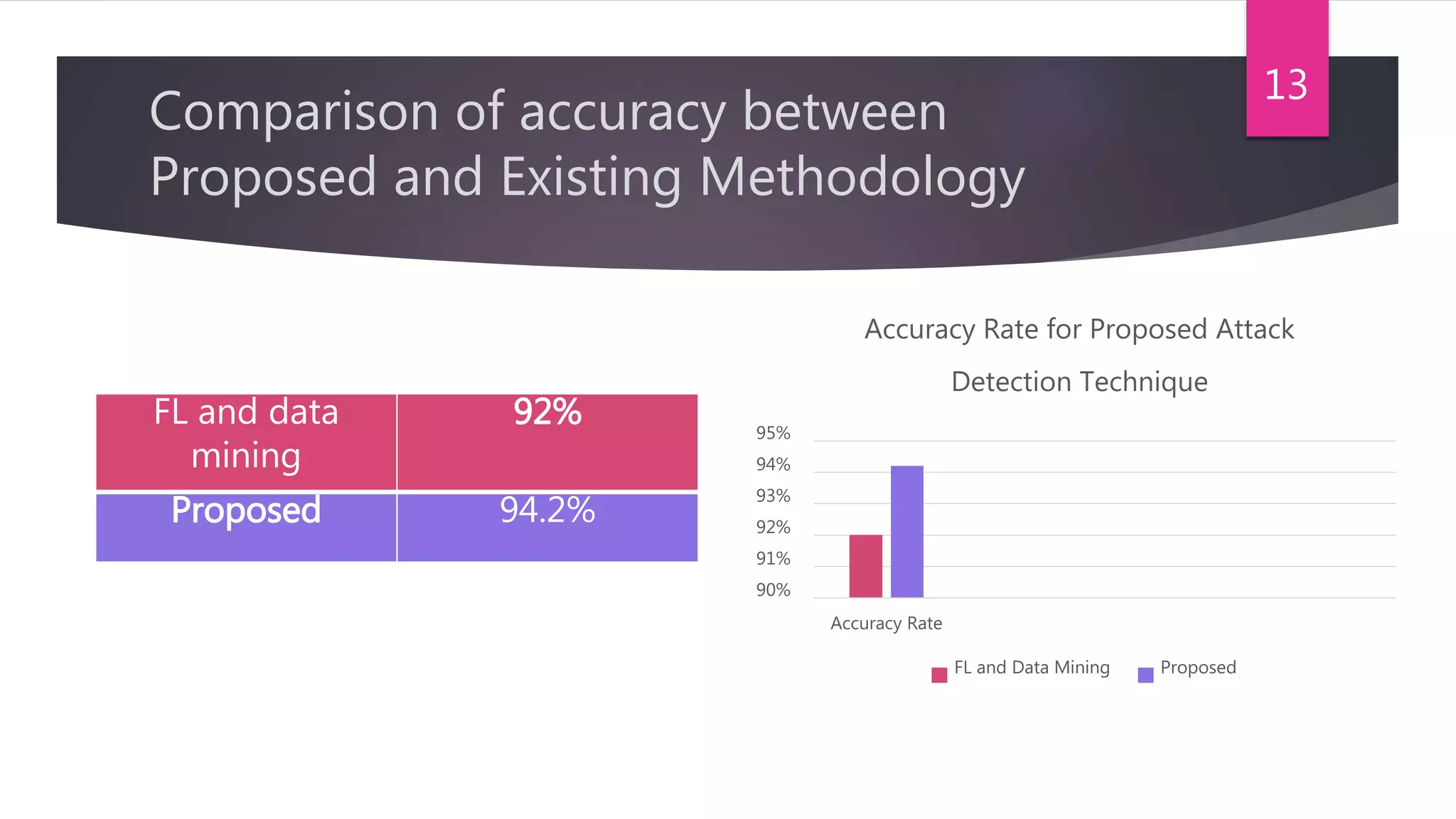
![Continue….
Data miner along with Kuok’s algorithm is used for optimizing association rule
algorithm.[6]
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/attackdetectionandpreventioninthecyber-160217195154/75/Attack-detection-and-prevention-in-the-cyber-12-2048.jpg)
![References
[1]F. Aloul, A. R. Al-Ali, R. Al-Dalky, M. Al-Mardini, and W. El-Hajj, “Smart grid security: Threats,
vulnerabilities and solutions,” International Journal Of Smart Grid And Clean Energy, pp. 1–6, 2012.
[2]K. Manandhar, X. Cao, F. Hu, and Y. Liu, “Detection of faults and attacks including false data injection
attack in smart grid using kalman filter,” IEEE Transactions On Control Of Network Systems, vol. 1, no. 4,
pp. 370–379, 2014.
[3]K. Sgouras, A. Birda, and D. Labridis, “Cyber attack impact on critical smart grid infrastructures,” in
Innovative Smart Grid Technologies Conference (ISGT), 2014 IEEE PES, pp. 1–5, Feb 2014.
14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/attackdetectionandpreventioninthecyber-160217195154/75/Attack-detection-and-prevention-in-the-cyber-14-2048.jpg)
![Continue
[4]R. B. Bobba, K. M. Rogers, Q. Wang, H. Khurana, K. Nahrstedt, and T. J. Overbye, “Detecting
false data injection attacks on dc state estimation,” Preprints Of the First Workshop On Secure
Control Systems, CPSWEEK, vol. 2010, 2010.
[5]Wikipedia, "Sensitivity and specificity", 2015. [Online]. Available:
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sensitivity_and_specificity. [Accessed: 31- DEC- 2015]
[6]C. M. Kuok, A. Fu, and M. H. Wong, “Mining fuzzy association rules in databases,” ACM
SIGMOD Record, vol. 27, no. 1, pp. 41–46, 1998.
15](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/attackdetectionandpreventioninthecyber-160217195154/75/Attack-detection-and-prevention-in-the-cyber-15-2048.jpg)
