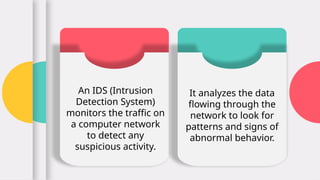
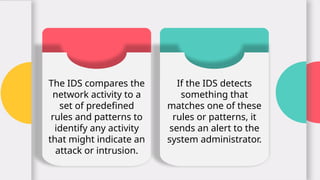
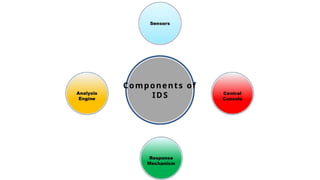
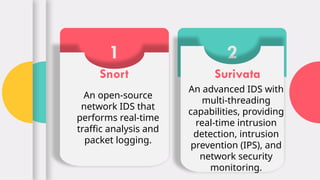
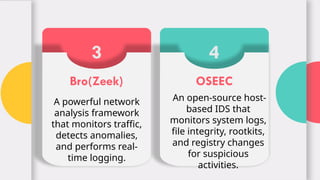
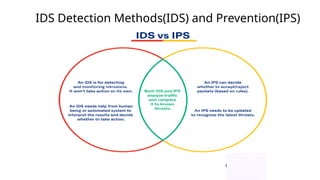
The document explains the concept and functionality of Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS), highlighting their role in monitoring network traffic for suspicious activity and alerting system administrators. It details the components of IDS, types such as network-based and host-based, as well as a comparison with firewalls. Additionally, it addresses the advantages and limitations of IDS, including early threat detection and challenges like false positives and resource consumption.