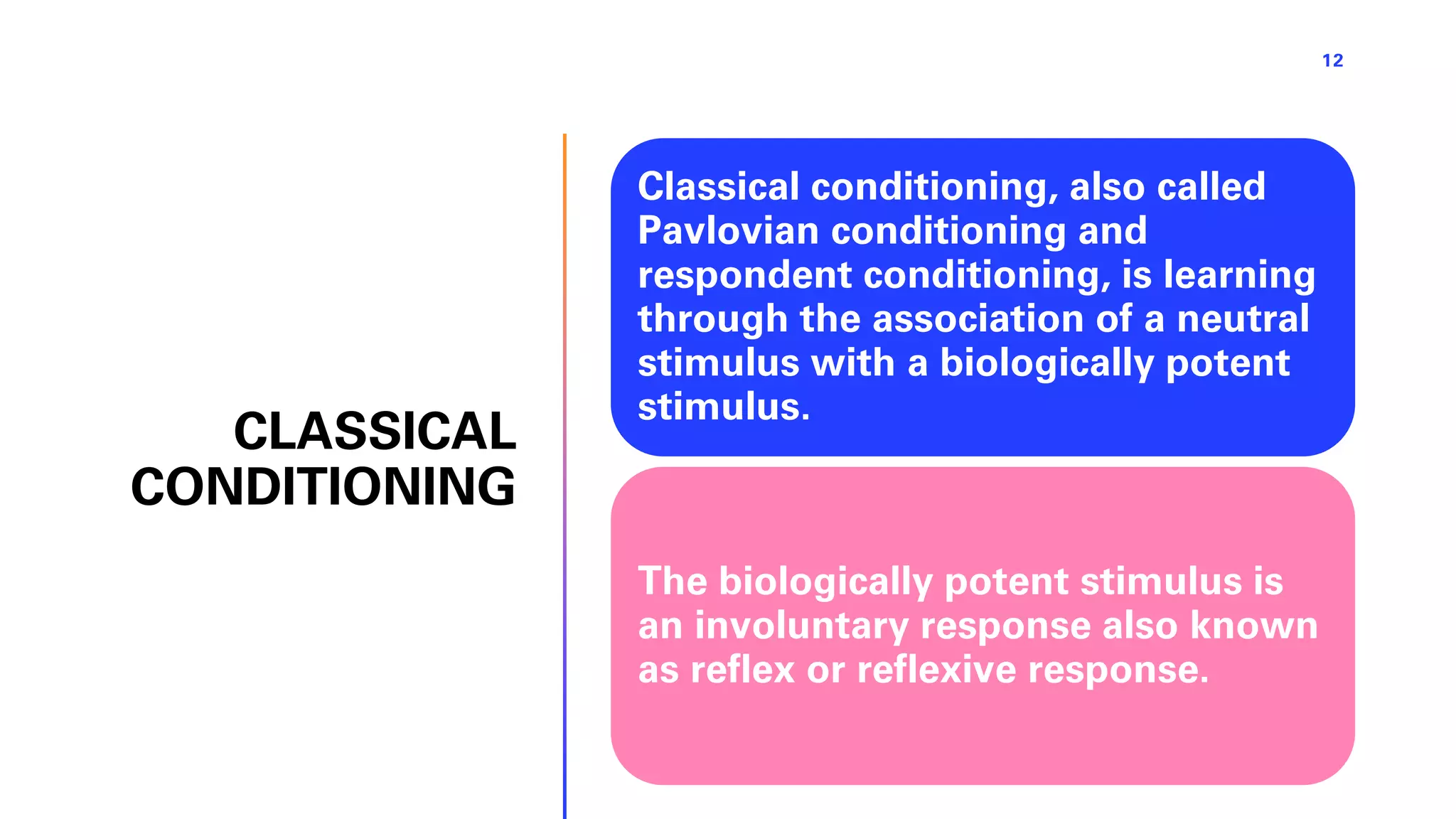
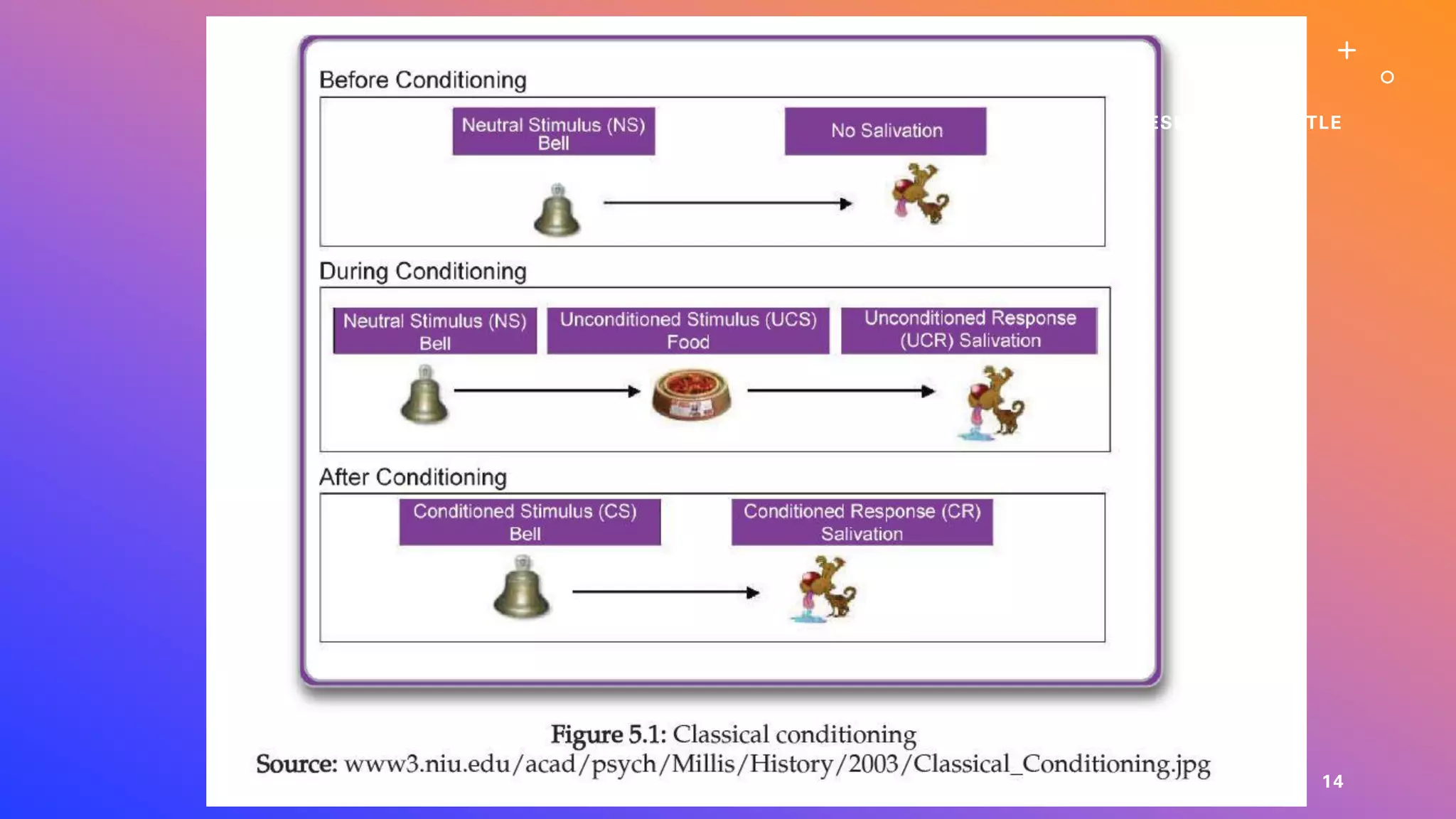
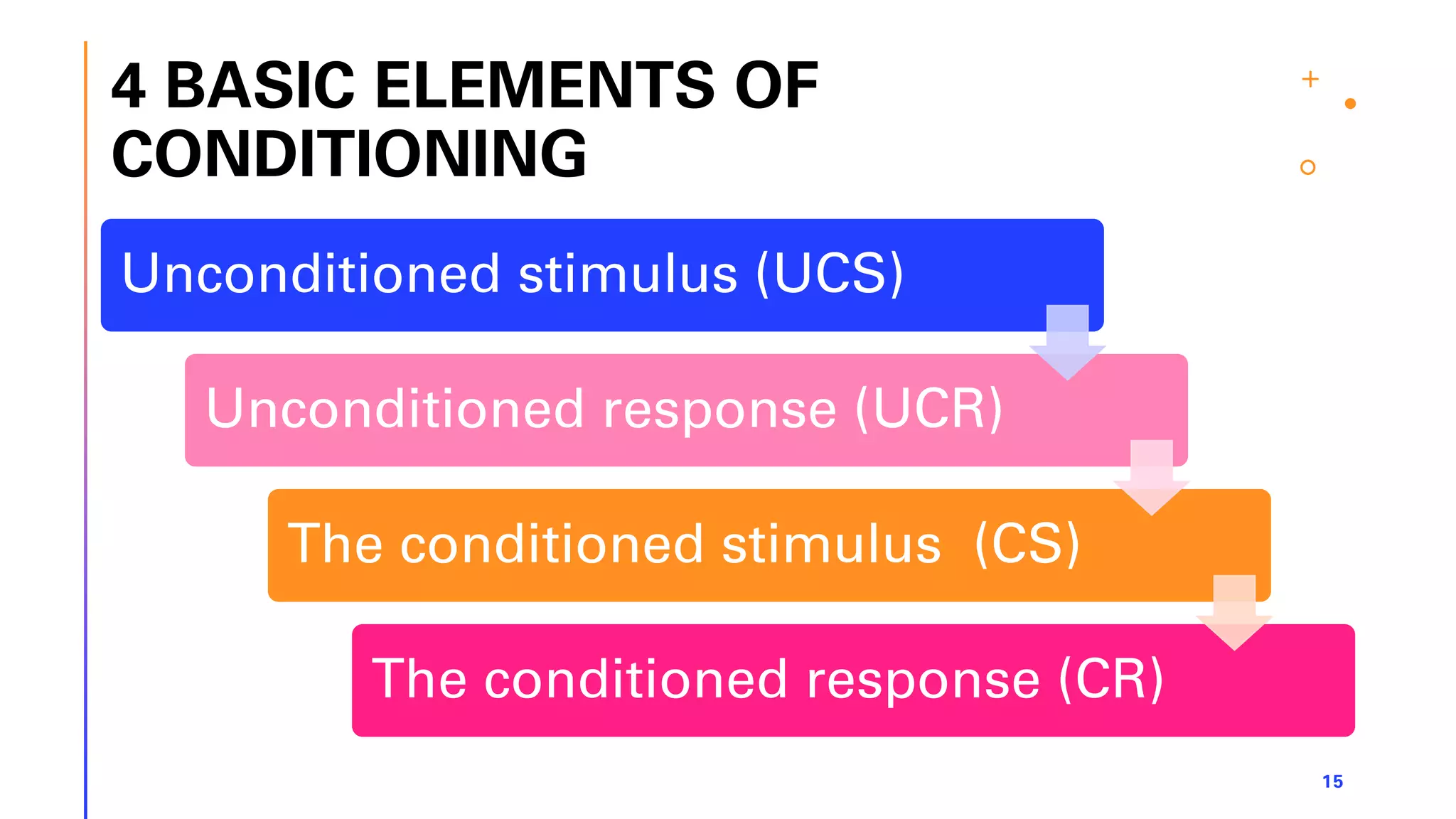
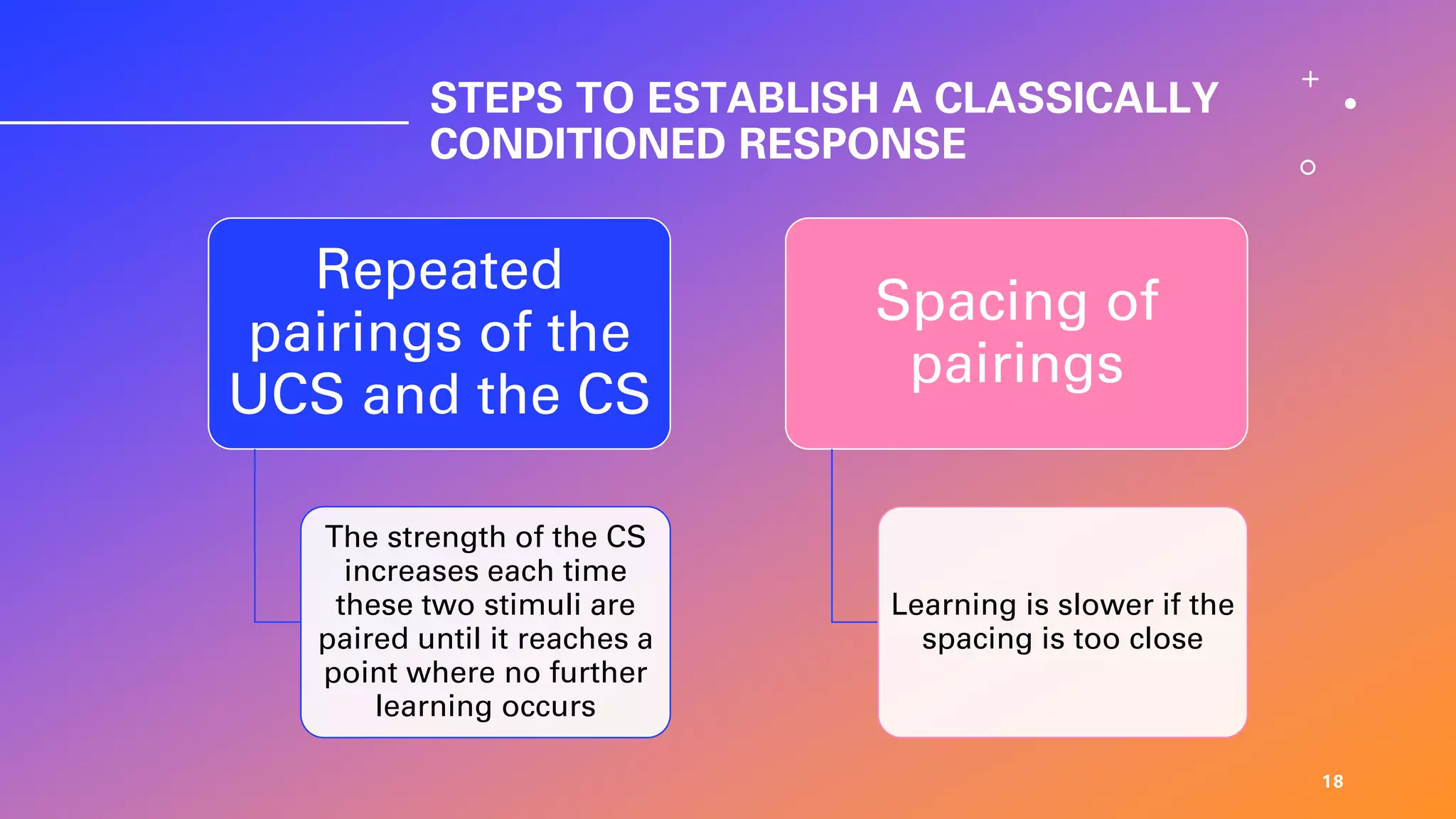
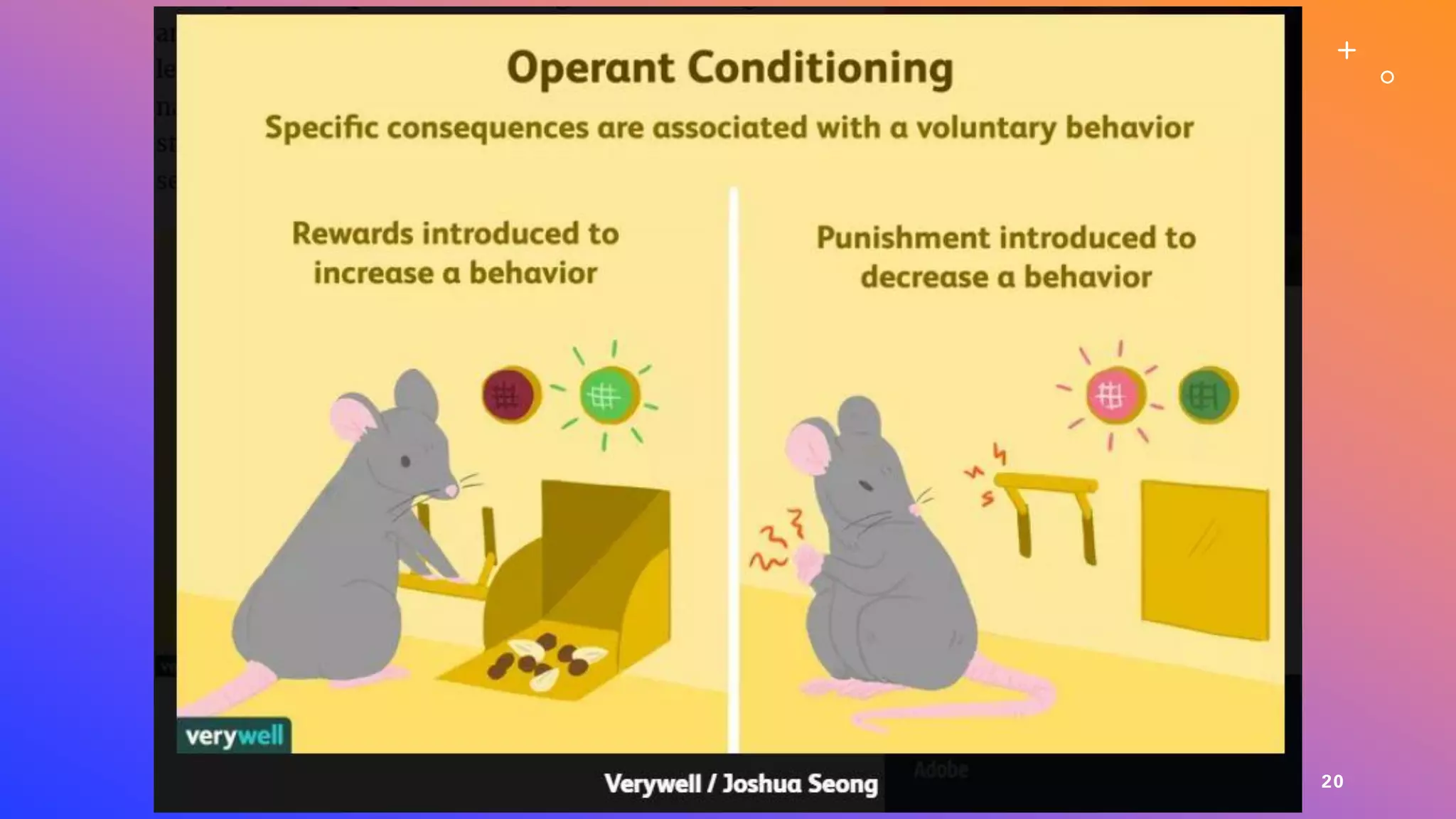
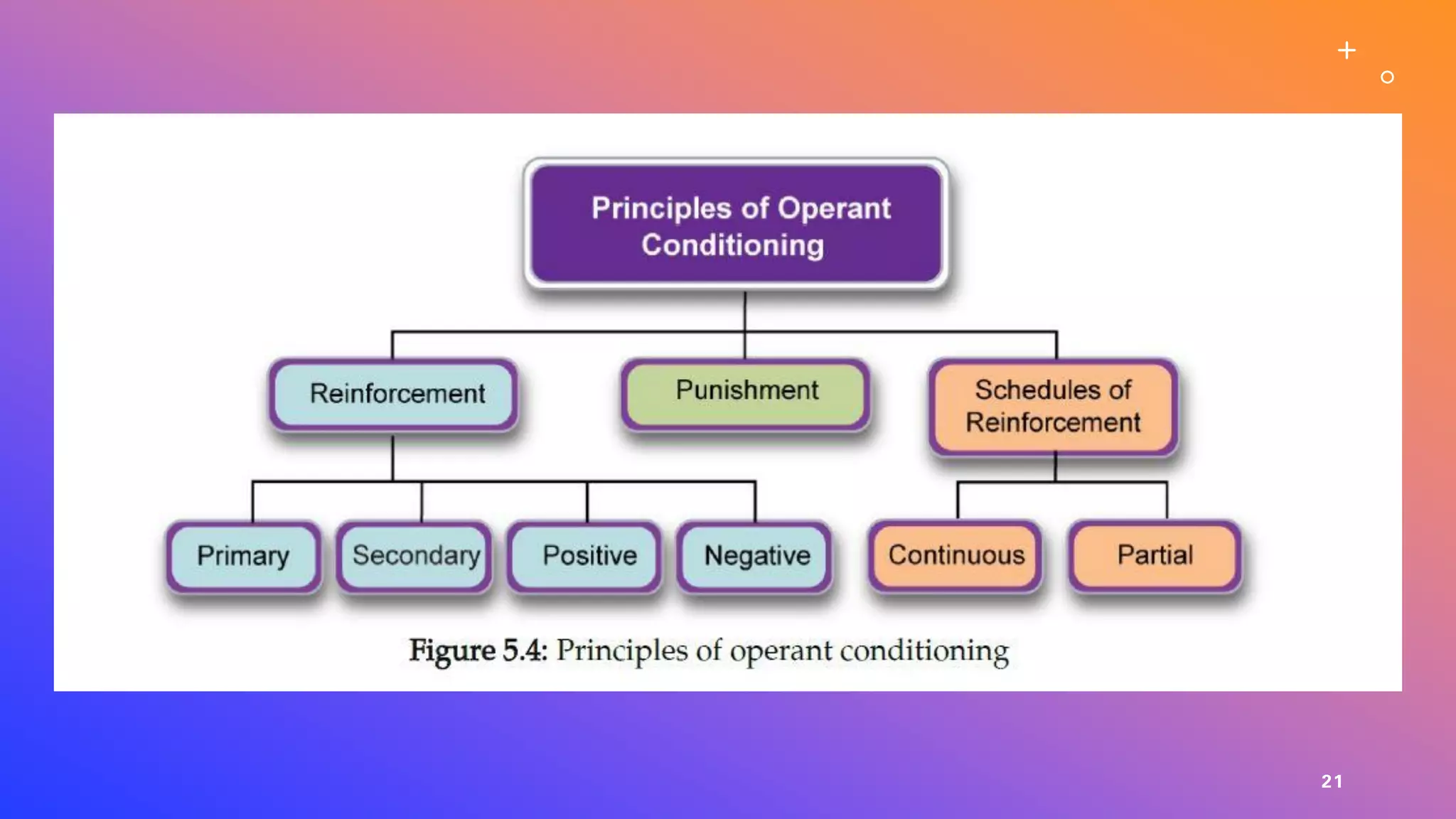
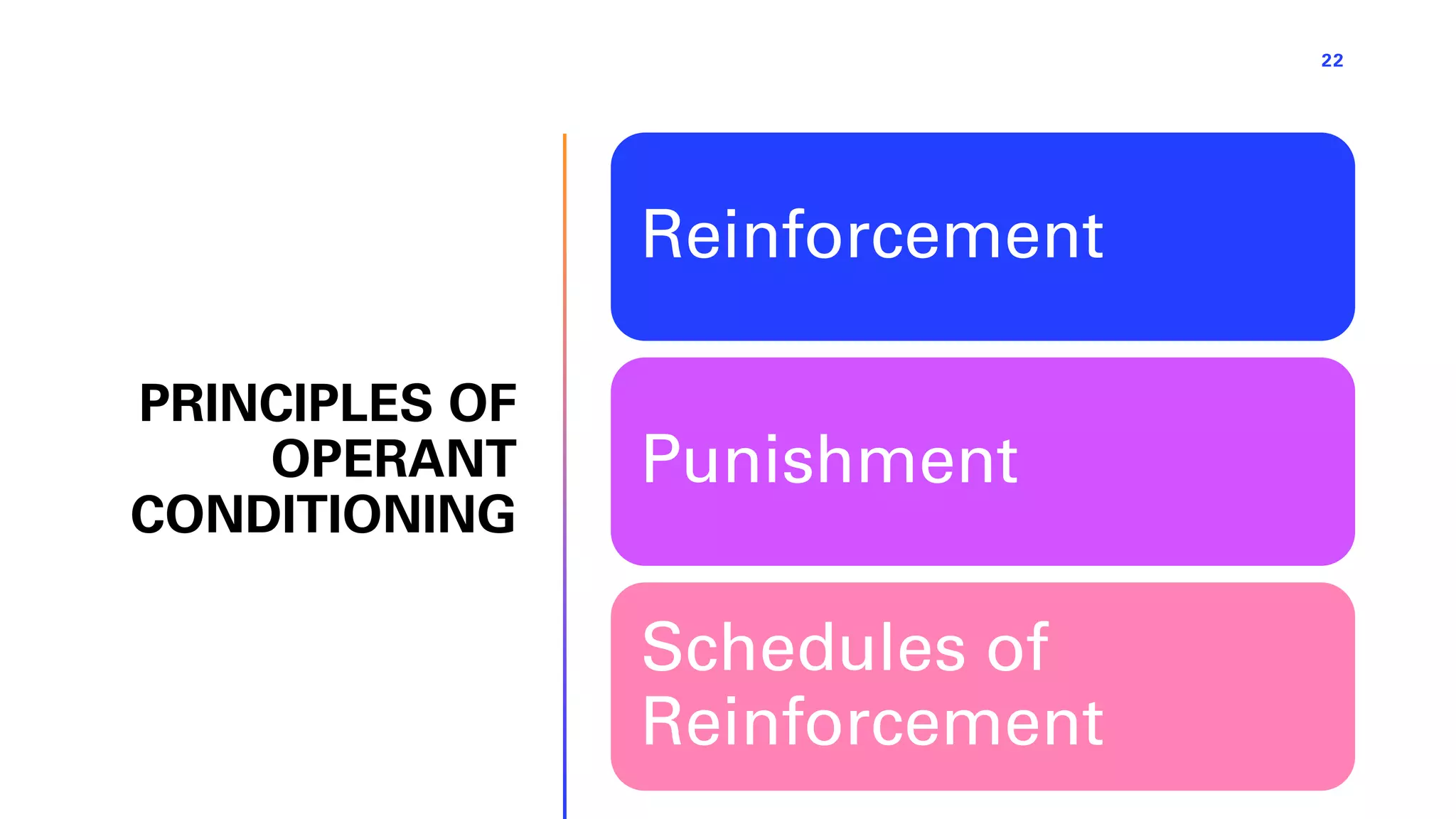
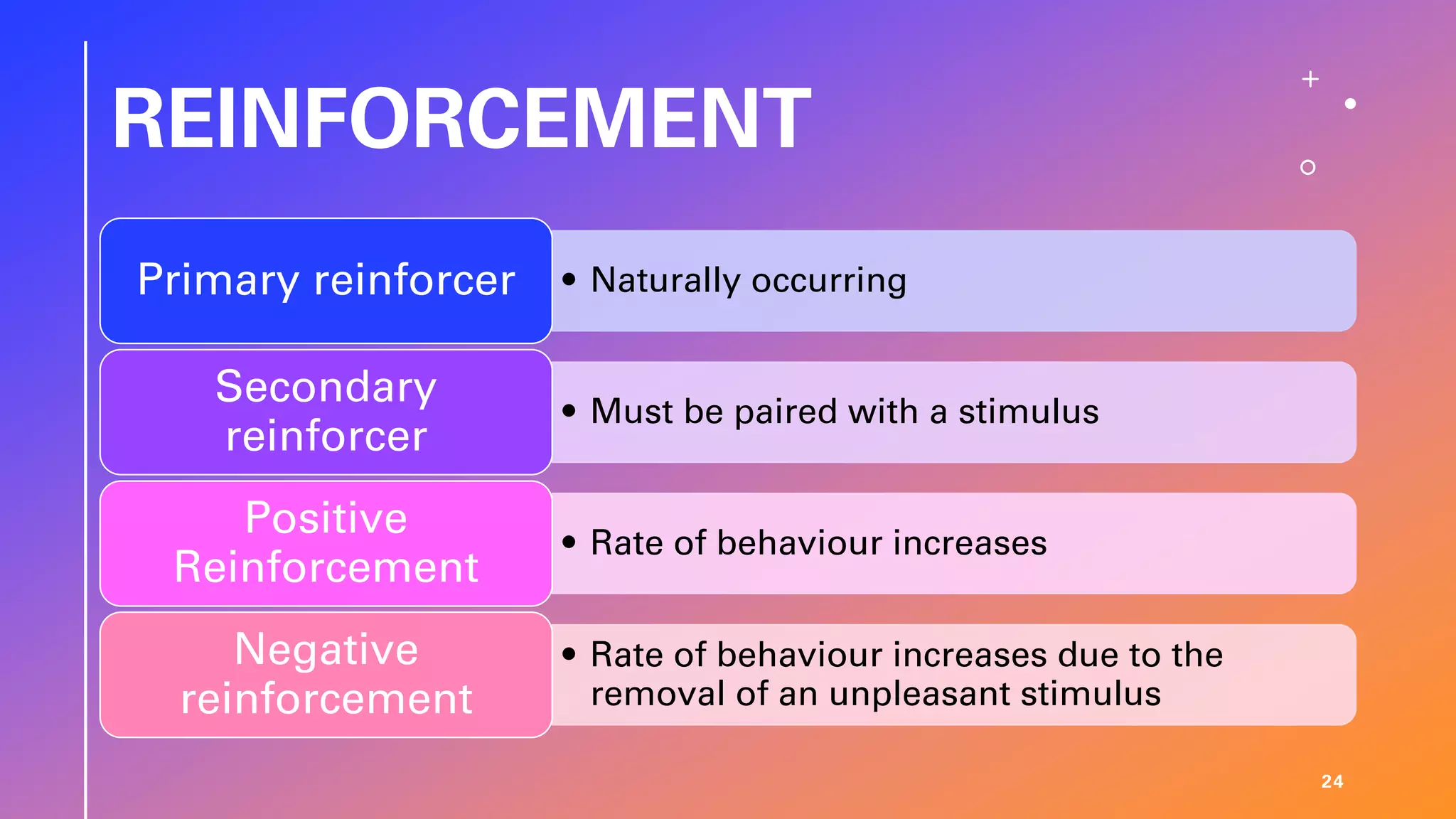
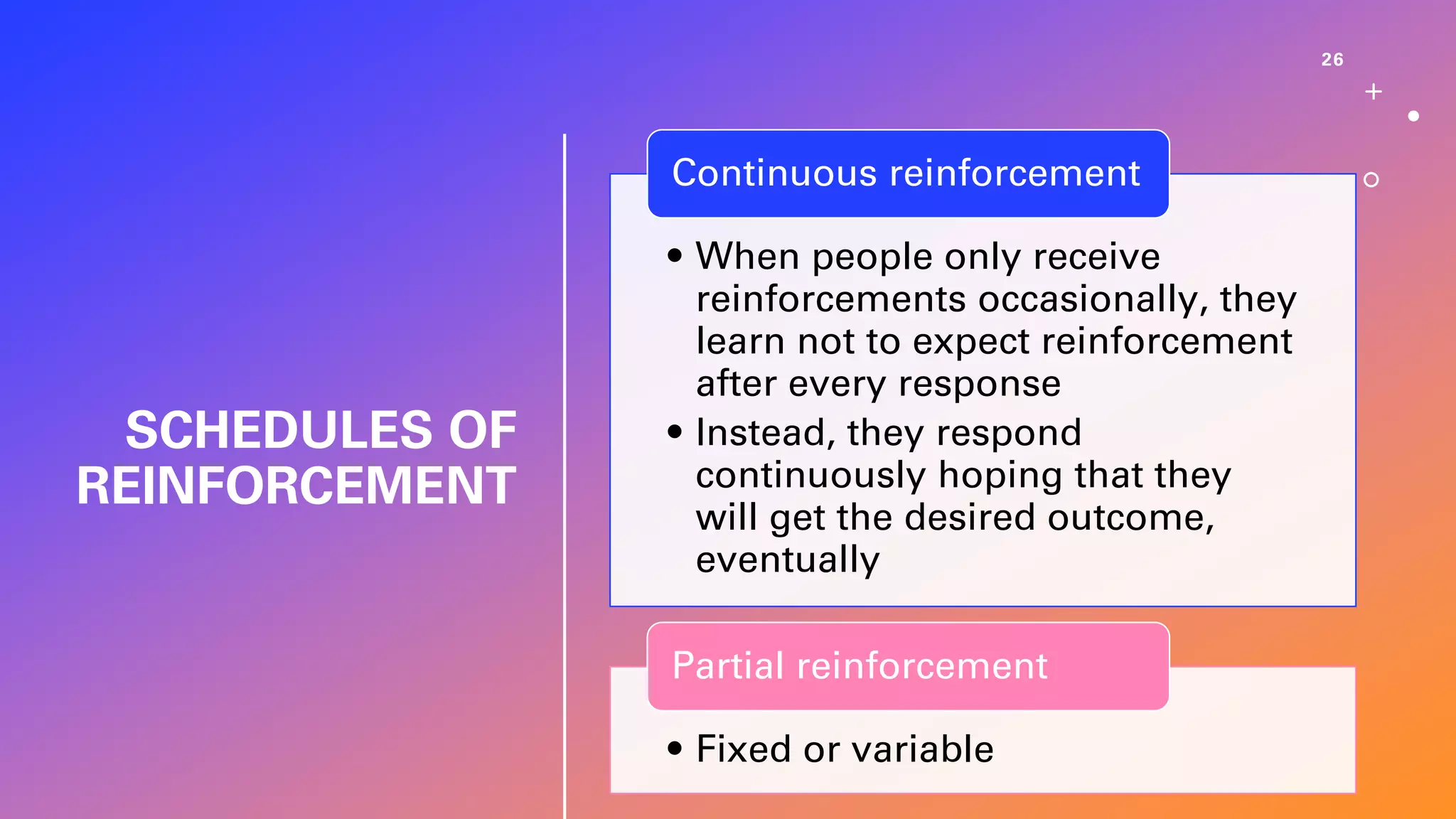
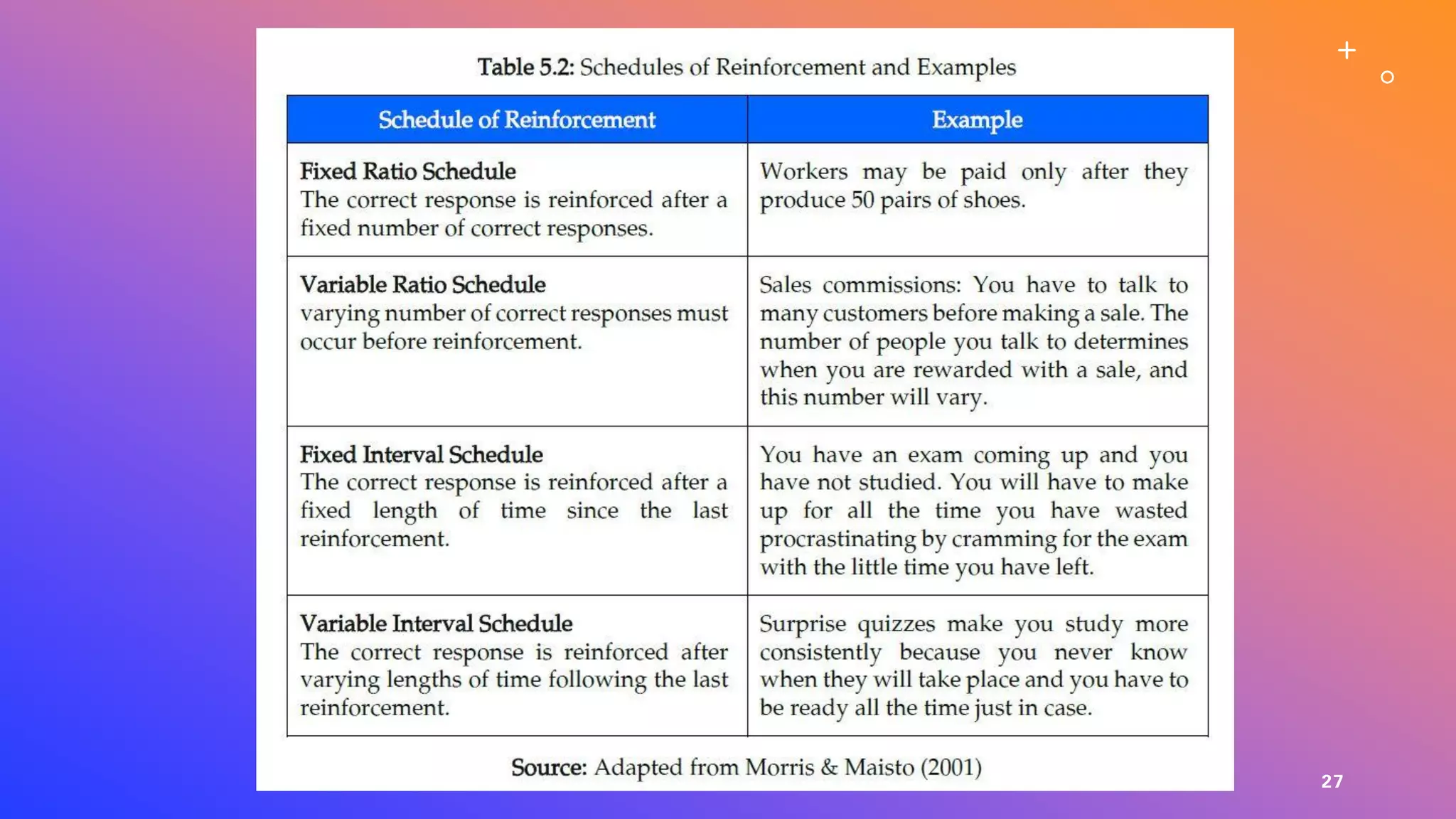
This document defines learning and describes several theories of how learning occurs. It begins by defining learning as a relatively permanent change in behavior resulting from experience. It then compares and contrasts classical and operant conditioning, explaining that classical conditioning involves associating a neutral stimulus with a reflexive response, while operant conditioning uses rewards and punishments to shape behavior. Finally, it describes cognitive learning theory, which focuses on mental processes, and observational learning theory, which explains how people learn by watching others. The document provides examples and explanations of how these different learning theories apply to everyday life.