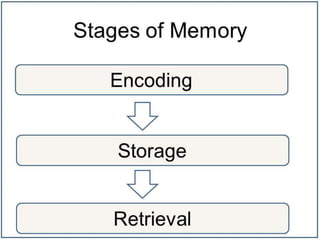
Memory involves three main stages: encoding, storage, and retrieval. Information is encoded using visual, acoustic, or semantic representations when it enters the memory system. It is then stored either in short-term memory (for up to 30 seconds) or long-term memory (which can last a lifetime). Retrieval involves accessing stored information through sequential ordering for short-term memory or associations for long-term memory. Many memory experiments are criticized for having low ecological validity since the laboratory setting and tasks like recalling word lists are artificial compared to real-world memory use.