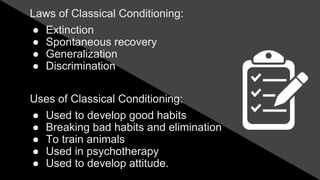
The document discusses learning as a permanent change in behavior resulting from experience or practice, highlighting key definitions and theories such as trial and error, classical conditioning, operant conditioning, cognitive learning, and social learning. Notable figures like Edward Thorndike and B.F. Skinner are mentioned for their contributions to understanding learning through experiments and conditioning. The text also offers effective strategies for enhancing learning, including goal-setting, diverse learning methods, and teaching others.