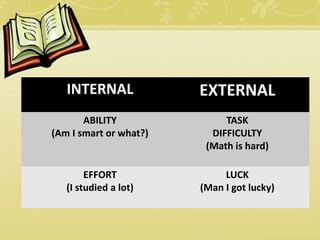
Attribution theory deals with how people make causal explanations for events and behaviors. It examines what information people gather and how they use it to form causal judgments. A key process is that people first perceive a behavior, believe it was intentional, and then determine whether internal characteristics or external forces caused it. People have biases like fundamental attribution error and self-serving bias that can lead to incorrect attributions. Kelley's co-variation model examines consensus, distinctiveness, and consistency to determine whether to attribute a behavior internally or externally. Teachers can help students develop self-efficacy, the belief in one's abilities, through performance experiences, social persuasion, and helping students visualize success.