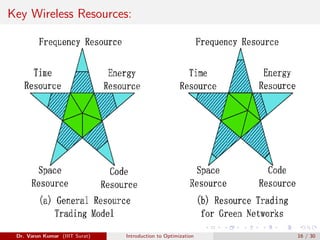
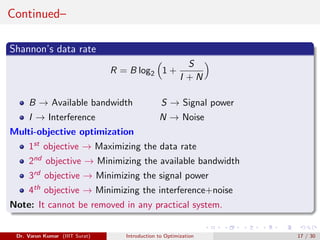
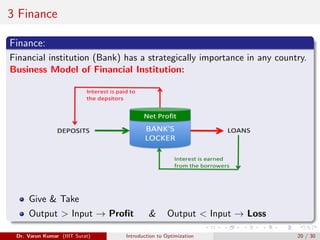
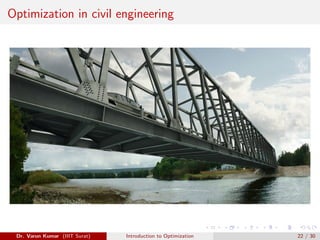
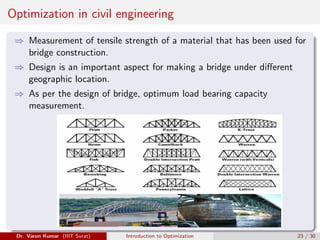
This document provides an introduction to optimization. It discusses constrained and unconstrained optimization problems and provides examples of optimization applications in various fields including supermarket chains, telecommunications, banking and finance, manufacturing, healthcare, machine learning, and industry 4.0. The goal of optimization is to obtain the most desirable outcome at minimum cost by applying mathematical techniques to real-world problems.