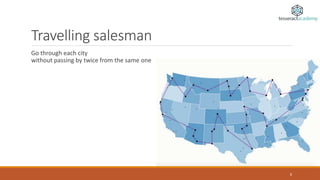
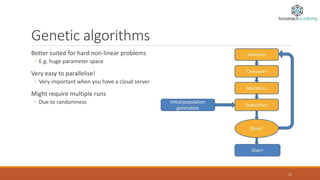
The document discusses the distinctions between optimization and prediction in data science, emphasizing their roles in evaluating causality and solving complex problems. It provides examples of predictive analytics and various optimization methods, including common algorithms and their applications. Additionally, it offers decision-making tips and resources for further learning in data science and analytics.