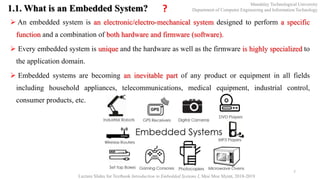
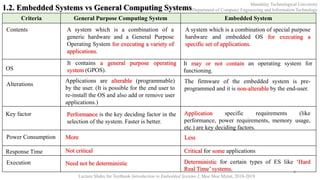
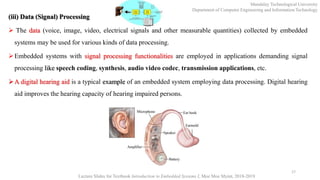
This document provides an introduction to embedded systems for a course at Mandalay Technological University. It includes chapters on what embedded systems are, their typical applications and domains, characteristics, designing systems with microcontrollers, hardware and software co-design, real-time operating systems, and product development processes. The document outlines learning objectives for understanding fundamentals of embedded systems and being able to recognize, comprehend, implement, practice, develop familiarity with tools, and perform lab work related to embedded systems. It also provides an overview of key topics in each chapter and keywords to note related to embedded systems.