Embed presentation










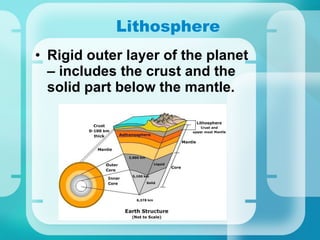




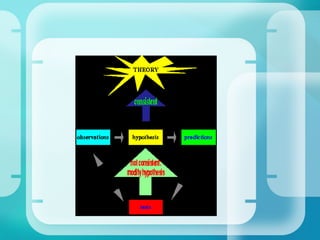



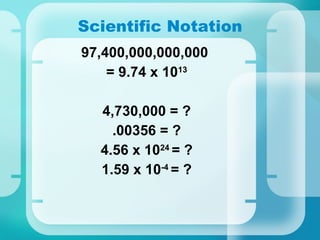




This document provides an introduction to key concepts in Earth science. It discusses how Earth science incorporates several disciplines including astronomy, meteorology, geology, and oceanography. It also outlines Earth's four main systems - the lithosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere, and biosphere. Additionally, it introduces the scientific method and important Earth science concepts such as scientific communication, measurement, scientific notation, theories and laws.




























