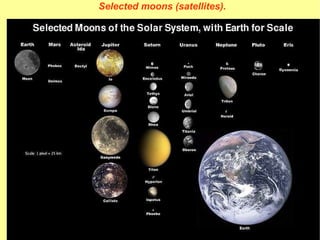
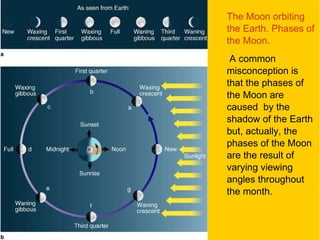
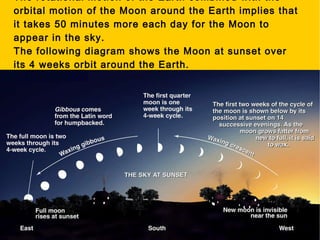
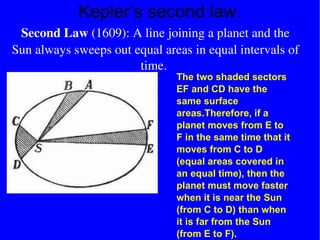
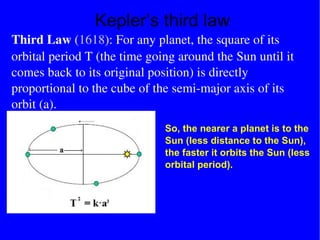
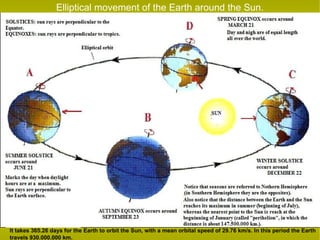
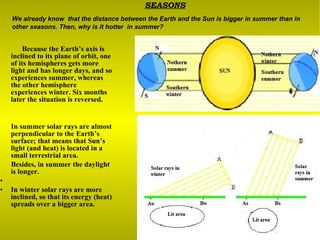
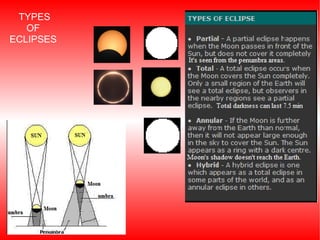
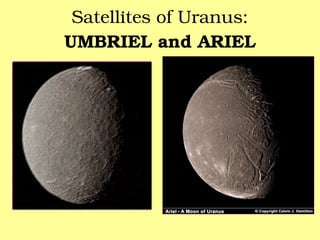
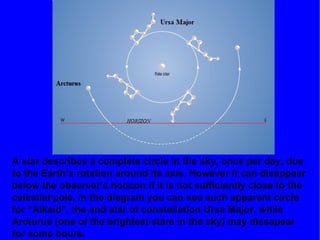
The document provides information about astronomy and the solar system. It discusses the definition of astronomy and describes the solar system including the eight planets, their satellites, asteroids, comets, and other objects within the sun's gravitational influence. It then focuses on specific planets like Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, Venus, and Mercury. Details are given about their composition, orbits, moons, and other characteristics.