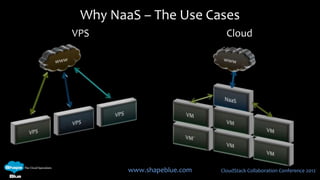
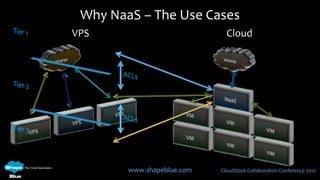
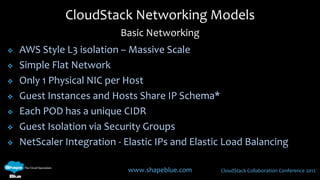
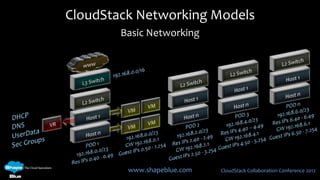
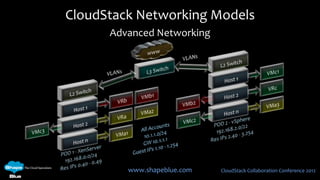
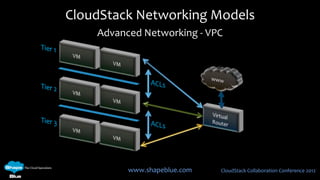
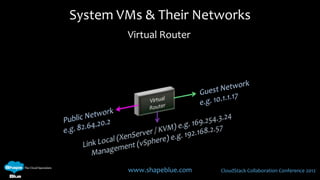
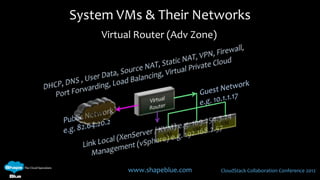
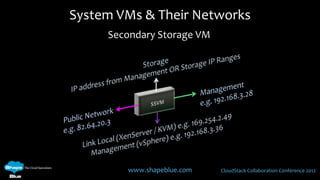
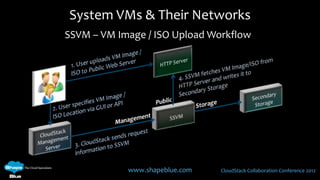
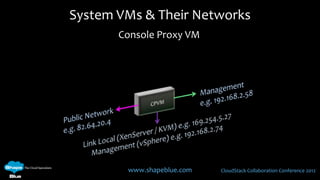
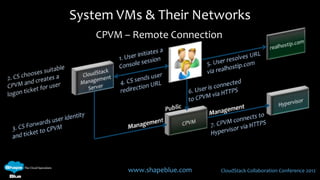
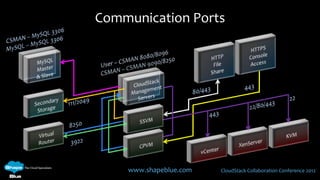
This document discusses CloudStack networking models. It describes the basic networking model which uses AWS-style L3 isolation and security groups. It also describes the advanced networking model which uses VLANs to isolate guest networks and provides virtual routers for accounts. An advanced networking option called VPC allows for private multi-tiered virtual networks with inter-VLAN routing and site-to-site VPN. The document also discusses system VMs like the virtual router and their networks, as well as real-world networking challenges and the potential of software defined networking.